Abstract
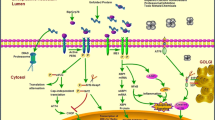
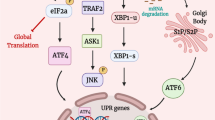
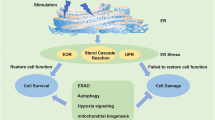
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is induced by protein misfolding and nutritional deprivation in many eukaryotic cells. Meantime, an imbalance between protein synthesis and folding capacity of ER also caused the unfolded protein response (UPR). The UPR included three different protein family signals: double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase like ER kinase, inositol-requiring kinase 1, and activating transcription factor 6, all of which are triggered during ER stress. Malfunction of UPR is induced by aging, genetic mutations, or environmental factors and results in various diseases, especially metabolic disease. The main adverse effects of chronic fluorosis are skeletal, dental, or enamel damages. The soft tissue lesions of fluorosis have been observed and discussed. The underlying mechanisms that mediated these effects remained poorly understand. This section is to review the role of ER stress in mechanism that overdosal fluoride exposure caused body lesion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R. Nrf2-keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865:721–33.
Brookes SJ, Barron MJ, Dixon MJ, Kirkham J. The unfolded protein response in amelogenesis and enamel pathologies. Front Physiol. 2017;8:653.
Couasnay G, Bon N, Devignes CS, Sourice S, Bianchi A, Véziers J, et al. PiT1/Slc20a1 is required for ER homeostasis, chondrocyte survival, and skeletal development. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:387–98.
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Bettigole SE, Glimcher LH. Tumorigenic and immunosuppressive effects of ERS in cancer. Cell. 2017;168:692–706.
Deng H, Kuang P, Cui H, Chen L, Luo Q, Fang J, et al. Sodium fluoride (NaF) induces the splenic apoptosis via ER (ER) stress pathway in vivo and in vitro. Aging. 2016;8:3552–67.
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, et al. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell. 2003;11:619–33.
Hino SI, Kondo S, Yoshinaga K, Saito A, Murakami T, Kanemoto S, et al. Regulation of ER molecular chaperone prevents bone loss in a murine model for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28:131–8.
Hu CY, Ren LQ, Li XN, Wu N, Li GS, Liu QY, et al. Effect of fluoride on insulin level of rats and insulin receptor expression in the MC3T3-E1 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012;150:297–305.
Ito M, Nakagawa H, Okada T, Miyazaki S, Matsuo S. ER-stress caused by accumulated in triacontanol granules activates autophagy through a different signal pathway from unfolded protein response in exocrine pancreas cells of rats exposed to fluoride. Arch Toxicol. 2009;83:151–9.
Jang WG, Kim EJ, Kim DK, Ryoo HM, Lee KB, Kim SH, et al. BMP2 protein regulates osteocalcin expression via Runx2-mediated Atf6 gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:905–15.
Li X, Meng L, Wang F, Hu X, Yu Y. Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis and autophagy via the ERS pathway in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;454:77–85.
Li XN, Lv P, Sun Z, Xu H. Role of unfolded protein response in affecting osteoblast differentiation induced by fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014;158:113–21.
Liu L, Zhang Y, Gu H, Zhang K, Ma L. Fluorosis induces ERS and apoptosis in osteoblasts in vivo. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015;164:64–71.
Lü P, Li X, Ruan L, Xu H, Liu Q. Effect of siRNA PERK on fluoride-induced osteoblastic differentiation in OS732 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014;159:434–9.
Mohammadi AA, Yousefi M, Yaseri M, Jalilzadeh M, Mahvi AH. Skeletal fluorosis in relation to drinking water in rural areas of West Azerbaijan. Iran Sci Rep. 2017;7:17300.
Niu Q, Chen J, Xia T, Li P, Zhou G, Xu C, et al. Excessive ERS and the resulting autophagic flux dysfunction contribute to fluoride-induced neurotoxicity. Environ Pollut. 2018;233:289–99.
Schmoll D, Engel CK, Glombik H. The Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction: a suitable target for small molecules. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2017;24:11–7.
Schwarz DS, Blower MD. The ER: Structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:79–94.
Sun F, Li X, Yang C, Lv P, Li G, Xu H. A role for PERK in the mechanism underlying fluoride-induced bone turnover. Toxicology. 2014;15:52–66.
Suzuki M, Bartlett JD. Sirtuin1 and autophagy protect cells from fluoride-induced cell stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:245–55.
Tabuchi Y, Yunoki T, Hoshi N, Suzuki N, Kondo T. Genes and gene networks involved in sodium fluoride-elicited cell death accompanying ERS in oral epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:8959–78.
Tohmonda T, Yoda M, Mizuochi H, Morioka H, Matsumoto M, Urano F, et al. The IRE1α-XBP1 pathway positively regulates parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide receptor expression and is involved in PTH-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:1691–5.
Wang J, Yang J, Cheng X, Xiao R, Zhao Y, Xu H, et al. Calcium alleviates fluoride-induced bone damage by inhibiting ERS and mitochondrial dysfunction. Agric Food Chem. 2019;67:10832–43.
Wang M, Kaufman R. Protein misfolding in the ER as a conduit to human disease. Nature. 2016;529:326–35.
Wei J, Sheng X, Feng D, McGrath B, Cavener DR. PERK is essential for neonatal skeletal development to regulate osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2008;217:693–707.
Wei W, Gao Y, Wang C, Zhao K, Sun D, et al. Excessive fluoride induces ERS and interferes enamel proteinases secretion. Environ Toxicol. 2013;28:332–41.
Xu H, Ling J, Li GS. Proteomic analysis of osteoblasts exposed to fluoride in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2008;123:91–7.
Xu H, Zhou YL, Zhang XY, Lu P, Li G. Activation of PERK signaling through fluoride-mediated ERS in OS732 cells. Toxicology. 2010;277:1–5.
Yang Y, Lin X, Huang H, Feng D, Ba Y, Cheng X, et al. Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated ERS pathway in Sertoli cells. J Environ Sci. 2015;30:81–9.
Zhang S, Jiang C, Liu H, Guan Z, Zeng Q, Zhang C, et al. Fluoride-elicited developmental testicular toxicity in rats: roles of ERS and inflammatory response. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;271:206–15.
Zhang Y, Zhang K, Ma L, Gu H, Li J, Lei S, et al. Fluoride induced ERS and calcium overload in ameloblasts. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;69:95–101.
Zhou YL, Shi HY, Li XN, Lv P, Li GS, Liu QY, et al. Role of ERS in aberrant activation of fluoride-treated osteoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;154:448–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Xu, H., Guo, FY., Zhang, ZY. (2021). Alteration of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. In: Guan, ZZ. (eds) Coal-burning Type of Endemic Fluorosis. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1498-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1498-9_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-1497-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-1498-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)