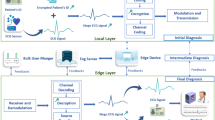
Abstract
The increasing global focus on health protection issues draws attention to the importance of point-of-care (POC) technologies. Its ability to provide cost-effective solutions for health maintenance points out their importance. However, against the obvious benefits, POC does not provide any primary diagnosis at the patient side. So, this work aims at a primary diagnosis of cardiac diseases at patient side itself by detecting the electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality. For perfect diagnosis, confidential data of patients are also required. However, transmission of this confidential data through public network may cause many security concerns. Also, wide privacy problems may occur as private data may be revealed to illicit servers. This paper uses support vector machine (SVM)-based technique for detecting abnormality in ECG signals. And Fast Walsh–Hadamard transform-based steganographic method is used for providing privacy, security and confidentiality of the transferred data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yager P, Domingo GJ, Gerdes J (2008 Aug) Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 10:107–144
Wang H et al (2010) Resource-aware secure ecg healthcare monitoring through body sensor network. Wirel Commun IEEE 17(1):12–19
Yang S, Yang G (2010) ECG pattern recognition based on wavelet transform and BP neural network, pp 246–249
Vijaya V, KishanRao K, Rama V (2011) Arrhythmia detection through ECG feature extraction using wavelet analysis. Eur J Sci Res 66:441–448
Castro B, Kogan D, Geva AB (2000)ECG feature extraction using optimal mother wavelet. In: The 21st IEEE convention of the electrical and electronic engineers in Israel, pp 346–350
Venkateswarlu D et al (2007) e health networking to cater to rural health care and health care for the aged. In: 2007 9th international conference on e-health networking, application and services, pp 273–276. IEEE (2007)
Zheng K, Qian X (2008) Reversible data hiding for electrocardiogram signal based on wavelet transforms. In: International conference on computational intelligence and security, 2008 CIS’08, vol 1, pp 295–299. IEEE
Ibaida A, Khalil I, Sufi F (2010) Cardiac abnormalities detection from compressed ECG in wireless telemonitoring using principal components analysis (PCA). In: Proceedings of 5th international conference on intelligent sensors, sensor networks and information processing, Dec 2010, pp 207–212
Abuadbba A, Khalil I (2017) Walsh–Hadamard-based 3-D steganography for protecting sensitive information in point-of-care. IEEE Trans Bio-med Eng
Abuadbba A et al (2015) Robust privacy preservation and authenticity of the collected data in cognitive radi network Walsh–Hadamard based steganographic approach. Pervasive Mob Comput
Ibaida A, Khalil I (2013) Wavelet based ECG steganography for protecting patient confidential information in point-of-care systems. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60:3322–3330
Goldberger A et al (2000) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):e215–e220
Clifford G, Liu C, Moody B, Lehman H, Silva I, Li Q et al (2017) AF classification from a short single lead ECG recording. The PhysioNet computing in cardiology challenge
Beevi KS, Nair MS, Bindu GR (2019) Automatic mitosis detection in breast histopathology images using convolutional neural network based deep transfer learning. Biocybern Biomed Eng 39(1):214–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Akhila, N.S., Sabeena Beevi, K. (2020). Anomaly Detection and Safe Transmission of ECG Signals in Point-of-Care Systems. In: Jayakumari, J., Karagiannidis, G., Ma, M., Hossain, S. (eds) Advances in Communication Systems and Networks . Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 656. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3992-3_66
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3992-3_66
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3991-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3992-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)