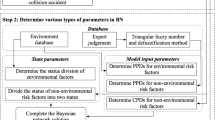
Abstract
The accident mechanism is established to strengthen the safety management and reduce accidents of waterborne transport projects combined with security science. Basing on “2-4” model theory, this mechanism analyzes the influences on the security of waterborne projects construction. The impact factors include personal behaviors, project management and environment. We calculate the probability of each factor with Bayesian network and rank them as they contribute the accident. According to the probability, prevention measure and security management methods can be made to reduce accidents.
This paper is based on National Key R&D Program: 2017YFC0805300.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu G, Yin W, Dong J et al (2013) Behavior-based accident causation: the “2-4” model and its safety implications in coal mines. J China Coal Soc 38(7):1123–1129
Reason J, Hollnagel E, Paries JS (2006) Revisiting the “Swiss Cheese” model of accidents. Euro Control Experimental Center, Brussels
Stroeve SH, Sharpanskykh A, Kirwan B (2011) Agent-based organizational modeling for analysis of safety culture at an air navigation service provider. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 96:515–533
Park H (2011) Man-made disasters: a cross-national analysis. Int Bus Rev 20:466–476
Hollnagel E (2004) Barriers and accident prevention. Ashgate Publishing Group, Burlington, pp 21–50
Qureshi ZH (2008) A review of accident modelling approaches for complex critical socio-technical systems. Defence Science and Technology Organization
Reason J (1990) Human error. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 173–188
Fan Y, Guo Y (2014) Csusal factor analysis of Chinese coal mining accident based on HFACS frame. Disaster Adv 7(4):19–26
Geoff C, Hussein S (1998) A project specific risk management concept. Int J Proj Manage 16(6):353–366
Everson (2004) A systems-theoretic approach to safety engineering. In: Monograph of the ESD Symposium, pp 41–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, J., Wen, Y. (2020). Research on Accident Causing Chains with Bayesian Networks on Waterborne Engineering. In: Wang, W., Baumann, M., Jiang, X. (eds) Green, Smart and Connected Transportation Systems. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 617. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0644-4_70
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0644-4_70
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0643-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0644-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)