Abstract
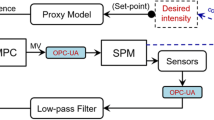
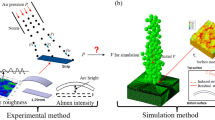
Peening velocity (shot velocity) is one of the key parameters in shot peening process, which directly relates to intensity and coverage area. A desired intensity and/or coverage area can be attained by controlling the peening velocity to the right value. However, this is a challenging task as the peening velocity is the function of many different variables (peening system, nozzle design, air pressure, media (shot) flow rate, shot size, etc.). In this study, we develop a process model that links the input/operating parameters of the peening machine to the average shot stream velocity upon impact. In particular, the formulation of shot stream velocity is derived as the function of input air pressure and media flow rate, which also accounted for the peening system and nature of the flow inside (e.g., nozzle shape, pressure loss, energy transfer, and turbulence, etc.). The model is validated against the experimental data for different inlet pressure as well as the media flow rates. The calculated results are in good agreement with experimental data. Furthermore, the model validity and reliability are examined for the wide range of input parameters and the system parameter. The results also indicated that the developed process model can be applied for different peening machines with different nozzle design by defining relevant model constants. There are a few key applications for the process model; which are (1) the model can support the operators to rapidly estimate and setup the working conditions of the machine to attain the desired peening intensity and coverage area to avoid the cost and time in doing experiments based on trials and errors, and (2) The model also can be used in model predictive control (MPC) to develop the controller for the peening machine.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrison, J.: Controlled shot-peening: cold working to improve fatigue strength. Heat Treat. 19, 16–18 (1987)
David, K.: Quantification of shot peening coverage. The Shot Peener, Fall (2014). https://www.electronics-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/QuantificationOfShotPeeningCoverage.pdf
Nguyen, V.B., Poh, H.J., Zhang, Y.W.: Predicting shot peening coverage using multi-phase computational fluid dynamics simulations. Powder Technol. 256, 100–112 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.01.097
David, K.: Variability of a shot stream’s measured peening intensity. The Shot Peener, Summer (2011). https://www.shotpeener.com/library/pdf/2011120.pdf
David, K.: Peening intensity: true meaning and measurement Strategy. The Shot Peener, Summer (2016). https://www.shotpeener.com/library/detail.php?anc=2016030
David, K.: Curve fitting for shot peening data analysis. The Shot Peener, 6. Spring (2002). https://www.shotpeener.com/library/pdf/2002091.pdf
David, K., Abyaneh, M.Y.: Theoretical basis of shot peening coverage control. Shot Peener, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 5–70 (1999). https://www.shotpeener.com/library/pdf/1995043.pdf
David, K.: Theoretical principal of shot peening coverage. Shot Peener, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 24–26 (2005). https://www.shotpeener.com/library/detail.php?anc=2005145
Bill, B., Kevin, Y.: Particle velocity sensor for improving shot peening process control. Shot Peener, Technological aspects (2005). https://www.shotpeener.com/library/pdf/2005114.pdf
Brunton, S.L., Joshua, L.P., Kutz J.N.: Discovering governing equations from data by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 113, no. 15, pp. 3932–3937 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1517384113
Tobias, G.: Model Predictive Control of High Power Converters and Industrial Drives. Wiley, London (2016). ISBN 978-1-119-01090-6
Wang, L.: Model Predictive Control System Design and Implementation Using MATLAB®, p. xii. Springer Science & Business Media, London (2009)
Kaiser, E., Kutz, J.N., Brunton, S.L.: Sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics for model predictive control in the low-data limit, 474. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2018.0335
Zhang, L., Schaeffer H.: On the convergence of the SINDy algorithm. Journal CoRR (2018). http://arxiv.org/abs/1805.06445
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the project entitled: “Machine Learning Assisted Control of Shot Peening Process” under Grant number A1894a0032, which is lead by Dr. Kang Chang Wei (IHPC, A*STAR) and Dr. Ampara (ARTC, A*STAR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Van Bo, N., Te, B., Teo, A., Ahluwalia, K., Aramcharoen, A., Chang Wei, K. (2020). Process Model for Evaluating the Peen Velocity in Shot Peening Machine. In: Itoh, S., Shukla, S. (eds) Advanced Surface Enhancement. INCASE 2019. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0054-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0054-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0053-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0054-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)