Abstract
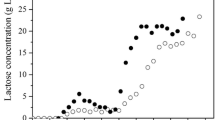
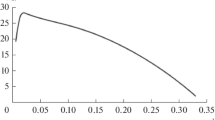
Mathematical models of organism growth help in designing and scaling-up bioreactors and in predicting how microorganisms will respond to changes in growth conditions so that an appropriate process control system can be devised Models also guide the analysis of experimental data and help in understanding biochemical growth mechanisms. Filamentous organisms which form pellets can be modelled using a cube root model or a modified logistic model. The cube root model allows detecting lag phases and stationary phases easily. The modified logistic model is a versatile model which can be used to model the entire growth cycle and which includes an adjustable inflection point for the rapid growth period These two models were tested by studying the growth of Acidothermus cellulolyticus in glucose and cellulose media in batch culture. The pH was maintained at 5.3 and the temperature was controlled at 45, 55, or 65°C. Cell biomass was determined by protein assay. The biomass productivity for the growth in a batch process shows that 55°C is the optimum temperature for biomass productivity. The growth data were used to evaluate the model parameters for the two models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bailey, J. F. and D. F. 011is, Biochemical Engineering,2nd ed., pp.403–405 McGraw-Hill, New York(1986).
Metz, B.and N. W. F. Kossen, The Growth of Molds in the Form of Pellets-A Literature Review, Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 19, 781 (1977).
Hubbard, D. W. and T. B. Co, Modeling the Growth of CellullaseProducing Organisms, in Hurst, C. J., ed., Modelling the Metabolic and Physiologic Activities of Microorganisms,pp. 89–113 John Wiley and Sons, New York(1992)
Mohagheghi, A., K. Grohmann, M. Himmel, L. Leighton, and D. M. Updegraff, Isolation and characterization of Acidothermus cellulolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus of thermophilic, acidophilic, cellulolytic bacteria. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology,36 435(1986).
Markwell, M. A. R., S. Hass, N. Tolbert, and L. Bieber, Protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples: Manual and automated procedures, Methods in Enzymology, 72, 296 (1981).
Co, T. B. and B. E. Ydstie, System Identification Using Modulating Functions and Fast Fourier Transforms, Computers in Chemical Engineering, 14, 1051 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hubbard, D.W., Co, T.B., Murthy, P.P.N., Mandalam, R. (1994). Modelling the Growth of Acidothermus cellulolyticus . In: Galindo, E., Ramírez, O.T. (eds) Advances in Bioprocess Engineering. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-0641-4_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-0641-4_34
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-4459-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-0641-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive