Abstract
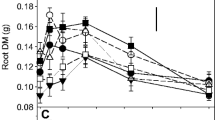
The aim of this study was to relate root system structure to function in Betula pendula. Knowledge of root system type and response to nitrogen and phosphorus is important in selecting genotypes for optimising tree establishment on upland soil. From an initial screening experiment where 30 genotypes were assessed, 2 were selected with contrasting root characteristics. Genotype 1 had few fine roots whereas genotype 2 had many fine roots. The two genotypes did not differ significantly in their growth response to contrasting levels of N supply, but genotype 1 appeared to be more responsive to mycorrhizal infection under conditions of low P supply. Root: shoot ratio and the proportion of roots less than 1 mm diameter may be useful traits for screening birch genotypes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson D 1990. The influence of root system morphology and development on the need for fertilisers and the efficiency of use. In Crops as Enhancers of Nutrient Use. Eds. VC Baliger and RR Duncan, pp 411–457. Academic Press, London.
Bernston GM, Farnsworth EJ and Bazzaz FA. 1995. Allocation, within and between organs, and the dynamics of root length changes in two birch species. Oecologia 101, 439–447.
Callaghan TV, Headley AD and Lee JA. 1991. Root function related to the morphology, life history and ecology of tundra plants. In Plant Root Growth, An Ecological Perspective. Ed D Atkinson. Special Publication No 11 of the British Ecological Society pp 311–340. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford.
Ericsson T. 1995. Growth and shoot-root ratio of seedlings in relation to nutrient availability. Plant and Soil. 169, 205–214.
Estáun V, Calvet C. and Hayman DS. 1987. Influence of plant genotype on mycorrhizal infection: response of three pea cultivars. Plant and Soil. 103, 295–298.
Fitter AH. 1985. Functional significance of root morphology and root system architecture. In Ecological Interactions in Soil. Eds AH Fitter, D Atkinson, DJ Read and MB Usher. pp 87–106. Blackwell, Oxford.
Genstat 5 Committee (1993) Genstat 5 Release 3 Reference manual, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Harley JL and Smith SE. 1983. Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic Press, London.
Ingestad T and Lund AB. 1979. Nitrogen stress in birch seedlings 1. Growth technique and growth. Physiologia Plantarum, 45, 137–148.
Last FT, Mason PA, Pelham J and Ingleby K. 1984. Fruitbody production by the sheathing mycorrhizal fungi: effects of host genotypes and propagating soils. Forest Ecology and Management, 9, 221–227.
Last FT, Mason PA, Wilson S and Deacon JW. 1983. Fine roots and sheathing mycorrhizas: their formation, function and dynamics. Plant and Soil, 71, 9–21.
Lavender EA, Atkinson D and Mackie-Dawson LA. 1993. Variation in root development in genotypes of Betula pendula. Aspects of Applied Biology, 34, 183–192.
Mason PA. 1975. The genetics of mycorrhizal associations between Amanita muscaria and Betula verrusoca Ehrh. In The Development and Function of Roots. Eds JG Torrey and DC Clarkson. pp 567–574. Academic Press, London.
Mason PA, Pelham J. 1976. Genetic factors affecting the response of trees to mineral nutrients. In Tree physiology and yield improvement. Eds MGR Cannell and FT Last. pp 437–448. HMSO, London.
Mason PA, Last FT, Pelham J and Ingleby K. 1982. Ecology and some fungi associated with an aging stand of birches. Forest Ecology and Management, 4, 19–39.
Murphy J and Riley JP. 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36.
Newman EI. 1966. A method of estimating the total length of root in a sample. Journal of Applied Ecology 3, 139–145.
Paakkonen E and Holopainen T. 1995. Influence of nitrogen supply on the response of clones of birch (Betula pendula Roth.) to ozone. New Phytologist, 129, 595–603.
Pelham J and Mason PA. 1981. Nutritional variants of birch. In Forest and Woodland Ecology. Eds. FT Last and AS Gardner. pp 78–81. HMSO, London.
Tennant D. 1975. A test of a modified line intersect method of estimating root length. Journal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mackie-Dawson, L.A., Lavender, E.A., Atkinson, D. (1998). The effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and mycorrhizal infection on root and shoot growth of two contrasting genotypes of Betula pendula Roth. In: Box, J.E. (eds) Root Demographics and Their Efficiencies in Sustainable Agriculture, Grasslands and Forest Ecosystems. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, vol 82. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5270-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5270-9_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-6218-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-5270-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive