Abstract
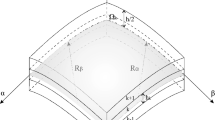
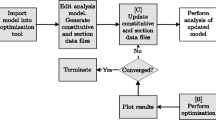
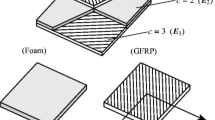
A numerical model for the optimal design of thin plate-shell laminated type structures, made of composite materials, is presented . The model is based on a plate-shell finite element with 18 degrees of freedom, using the discrete Kirchhoff theory. Sensitivity analysis with respect to fiber orientation and ply thickness is obtained through analytical formulation which is directly included in the finite element code. The model is applied to the optimal design of test cases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. L. Batoz, K. J. Bathe and L. W. Ho (1980) ‘A study of three node triangular plate bending elements’, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 15, 1771 –1812.
K. J. Bathe and L, W. Ho (1981) ‘A simple and effective element for analysis of general shell structures’, Computers & Structures 13, 673 –681.
P. Pedersen (1987) ‘On sensitivity analysis and optimal design of specially orthotropic laminates3’, Engineering Optimization 11, 305–316.
R. Reiss and S. Ramachandran (1987) ‘Maximum frequency design of symmetric angle-ply laminates’, Composite Structures 1, 1476 –1487.
S. S. Rao and K. Singh, ‘Optimum design of laminates with frequency’ (1979), Journal of Sound and Vibration 67, 101–112.
L. A. Schmit and B. Farshi, (1977) ‘Optimum design of laminated fibre composite plates’, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 11, 623 –640.
S. Adali, (1984), ‘Design of shear-deformable antisymmetric angle-ply laminates to maximize the fundamental frequency and frequency separation’ Composite Structures 2, 349 –369.
T. Y. Kam and M. D. Lai (1989), ‘Multilevel optimal design of laminated composite plate structures’, Computers & Structures 31, 197 –202.
Miraveti (1990) ‘Analysis and optimization of simple composite structures’ in Wilde W. P. and Blaim W. R. (eds.), Composite Materials Design and Analysis, Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 529 –547.
R. Haftka and M. Kamat (1987), ‘Finite elements on optimal structural design’, in C. A. Mota Soares (ed.), Computer Aided Optimal Design:Structural and Mechanical Systems, Springer - - Verlag, Berlin.
G. N. Vanderplaats (1984), Numerical Optimization Techniques for Engineering Design, McGraw Hill, USA.
G. N. Vanderplaats, ‘ADS-A Fortran Program for Automated Design Synthesis, Version 1.14’, Engineering Design Optimization, Inc. , St. Barbara, California.
J. R. Vinson and R. L. Sierakowski (1986), The Behaviour of Structures Composed of Composite Materials, Martinus Nijhoff Pub., Dordrecht.
O. C. Zienkiewich (1987), The Finite Element Method in Engineering Design, McGraw Hill 3rd Ed., UK.
C. M. Mota Soares, V. F. Correia and J. Herskovits (1990), ‘Sensitivity analysis of laminate structures’ in G. N. Pande and Middleton (eds.), Numeta 90, Numerical Methods in Engineering: Theory and Applications, Elsevier Applied Science, London, pp. 431–438 (volume 1).
A. K. Noor, I. Elishakoff, G. Hulbert (1990), Symbolic Computations and Their Impact on Mechanics, ASME 205, Dallas.
H. C. Mateus, C. M. Mota Soares and C. A. Mota Soares (1991), ‘Sensitivity analysis and optimal design of thin laminated composites structures’, Computers & Structures 41, 501–508.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1993 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mota Soares, C.M., Mota Soares, C.A., Correia, V.F., Mateus, H.C. (1993). Optimal Design of Thin Laminated Composite Structures. In: Bendsøe, M.P., Soares, C.A.M. (eds) Topology Design of Structures. NATO ASI Series, vol 227. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1804-0_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1804-0_22
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-4795-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-1804-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive