Abstract
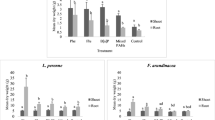
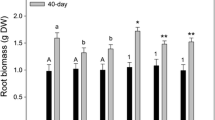
To understand the effect of rice root activities on PAHs bound with humic acid in rhizosphere, we conducted a glasshouse study using rhizoboxes to build rhizosphere gradient with 1–5 mm from root surface of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and measured for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) bound with humic acid. The concentration of humic acid-bound PAHs was varied with distance from root surface. In soils with high PAH concentrations, the proportion of humic acid-bound PAHs was lower in rhizosphere near root surface, whereas the proportion of humic acid-bound PAHs was higher in rhizosphere near root surface in soils with low PAH concentrations. When evaluating the effect of root on humic acid-bound PAHs with toxicity, the concentration of PAHs were transferred into benzo[a]pyrene concentration with equivalency toxicity. Total toxicity of PAHs in rhizosphere decreased with time. The toxicity of humic acid-bound PAHs in soils with different spiked concentrations was similar. The toxicity concentration of PAHs bound with humic acid was significantly higher near root surface. The results suggest that rice root activities promoted the bound between PAHs and humic acid in low concentration, but inhibited the bound in high concentration. However, the toxicity of PAHs bound with humic acid was higher near root surface.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, Y., J.M. Xu, C.X. Tang, and Y.P. Wu. 2005. Facilitation of pentachlorophenol degradation in the rhizosphere of ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Soil Biology and Biochemistry 37: 2017–2024.
He, L., J. Song, and P. Peng. 2008. Characterization of extractable and non-extractable polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils and sediments from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Pollution 156: 769–774.
Ma, B., H. Chen, Y. He, H. Wang, and J. Xu. 2010. Evaluation of toxicity risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in crops rhizosphere of contaminated field with sequential extraction. Journal of Soil Sediments 10: 955–963.
Ma, B., J.J. Wang, M.M. Xu, Y. He, H.Z. Wang, H.J. Di, and J.M. Xu. 2012. Evaluation of dissipation gradients of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rice rhizosphere utilizing a sequential extraction procedure. Environmental Pollution 162: 413–421.
Macleod, C.J.A., and K.T. Semple. 2003. Sequential extraction of low concentrations of pyrene and formation of non-extractable residues in sterile and non-sterile soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 35: 1443–1450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Zhejiang University Press and Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ma, B., Xu, J. (2013). Humic Acid-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Rhizosphere of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). In: Xu, J., Wu, J., He, Y. (eds) Functions of Natural Organic Matter in Changing Environment. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5634-2_102
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5634-2_102
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-5633-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-5634-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)