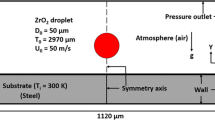
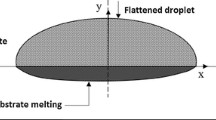
Abstract
Most of the studies reported for droplet impact and spreading on a substrate in a thermal spray coating process assume that droplet material solidifies as a pure substance, i.e., phase change occurs at a fixed temperature. The alloy-type behavior of the droplet impact where it solidifies within liquidus and solidus temperature is not well reported. The role of formation of mushy zone and species composition variation during the coating layer formation while using a multi-constituent alloy material is not established. This work investigates the spreading and solidification characteristics of an alloy droplet impacting on a substrate. Two-dimensional axisymmetric model has been used to simulate the transient flow and alloy solidification dynamics during the droplet impingement process. Volume of fluid (VOF) surface tracking method coupled with the alloy solidification model within a one-domain continuum formulation is developed to describe the transport phenomena during the droplet impact, spreading, and solidification of an alloy droplet on a flat substrate. Using the model, the characteristics of alloy solidification in coating formation are highlighted.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Specific heat capacity (m2 s−2 K−1)
- C :
-
Solute concentration (kg kg−1)
- D :
-
Solute mass diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- D o :
-
Initial droplet diameter (mm)
- f l :
-
Weight fraction of liquid (kg kg−1)
- f s :
-
Weight fraction of solid (kg kg−1)
- F :
-
Volume of fluid function
- F vol :
-
Continuum surface tension force source term (N m−3)
- \(\vec{g}_{r}\) :
-
Acceleration due to gravity vector (m s−2)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- k p :
-
Equilibrium partition coefficient
- K :
-
Permeability of mushy zone (m2)
- L :
-
Latent heat of fusion (J kg−1)
- m L :
-
Liquidus slope (°C wt%−1)
- p :
-
Pressure (N m−2)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- T m :
-
Melting point of pure substance (K)
- \(\vec{u}\) :
-
Continuum velocity vector (m s−1)
- U 0 :
-
Initial droplet velocity (m s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- d:
-
Droplet
- subs:
-
Substrate
- air:
-
Air
- alloy:
-
Alloy
- eff:
-
Effective
- l:
-
Liquid
- s:
-
Solid
- 0:
-
Initial
References
Ahmed AM, Rangel RH (2002) Metal droplet deposition on non-flat surfaces: effect of substrate morphology. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:1077–1091
Attinger D, Poulikakos D (2001) Melting and resolidification of a substrate caused by molten micro droplet impact. ASME J Heat Transf 123:1110–1122
Aziz SD, Chandra S (2000) Impact, recoil and splashing of molten metal droplets. Int J Heat Mass Transf 43:2841–2857
Bellet M, Combeau H, Fautrelle Y, Gobin D, Rady M, Arquis E, Budenkova O, Dussoubs B, Duterrail Y, Kumar A, Gandin CA, Goyeau B, Mosbah S, Zaloznik M et al (2009) Call for contributions to a numerical benchmark problem for 2D columnar solidification of binary alloys. Int J Therm Sci 48:2013–2016
Bennett T, Poulikakos D (1994) Heat transfer aspects of Splat-Quench solidification: modeling and experiment. J Mater Sci 29:2025–2039
Bussmann M, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J et al (2000) Modeling the splash of a droplet impacting a solid surface. Phys Fluids 12:3121–3132
Chandra S, Fauchais P (2009) Formation of solid splats during thermal spray deposition. J Therm Spray Technol 18:148–180
Fukumoto M, Huang Y (1999) Flattening mechanism in thermal sprayed Ni particles impinging on flat substrate surface. J Therm Spray Technol 8(3):427–432
Fukumoto M, Yang K, Tanaka K, Usami T, Yasui T, Yamada M et al (2011) Effect of substrate temperature and ambient pressure on heat transfer at interface between molten droplet and substrate surface. J Therm Spray Technol 20:48–58
Hong FJ, Qiu HH (2005) Modeling of substrate remelting, flow, and resolidification in microcasting. Numer Heat Transfer, Part A 48:987–1008
Inada S, Yang WJ (1994) Solidification of molten metal droplets impinging on a cold surface. Exp Heat Transfer 7:93–100
Kamnis S, Gu S (2005) Numerical modelling of droplet impingement. J Phys D Appl Phys 38:3664–3673
Kamnis S, Gu S, Lu TJ, Chen C et al (2008) Numerical modelling of sequential droplet impingements. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:165303 (7 pp)
Kang B, Zhao Z, Poulikakos D et al (1994) Solidification of liquid metal droplets impacting sequentially on a solid surface. ASME J Heat Transfer 116:436–445
Kumar A, Gu S, Tabbara H, Kamnis S et al (2012a) Study of impingement of hollow ZrO2 droplets onto a substrate. Surf Coat Technol 220:164–169
Kumar A, Gu S, Kamnis S et al (2012b) Simulation of impact of a hollow droplet on a flat surface. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 109:101–109
Li L, Wang XY, Wei G, Vaida A, Zhang H, Sampath S et al (2004) Substrate melting during thermal spray splat quenching. Thin Solid Films 468:113–119
Liu H, Lavernia EJ, Rangel RH et al (1993) Numerical simulation of substrate impact and freezing of droplets in plasma spray processes. J Phys D Appl Phys 26:1900–1908
Madejski J (1976) Solidification of droplets on a cold surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 19:1009–1013
Rangel RH, Bian X (1997) Metal-droplet deposition model including liquid deformation and substrate remelting. Int J Heat Mass Transf 40:2549–2564
Shakeri S, Chandra S (2002) Splashing of molten tin droplets on a rough steel surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:4561–4575
Tabbara H, Gu S (2012) Modelling of impingement phenomena for molten metallic droplets with low to high velocities. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:2081–2208
Waldvogel JM, Poulikakos D, Wallace DB, Marusak R et al (1996) Transport phenomena in picoliter size solder droplet dispersion. J Heat Transfer 118:148–156
Wang SP, Wang GX, Matthys EF et al (1999) Deposition of a molten layer of high melting point material: substrate melting and solidification. Mater Sci Eng A 262:25–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer India
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shukla, R.K., Yadav, S.K., Shete, M.H., Kumar, A. (2015). Numerical Modeling of Impact and Solidification of a Molten Alloy Droplet on a Substrate. In: Narayanan, R., Dixit, U. (eds) Advances in Material Forming and Joining. Topics in Mining, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering. Springer, New Delhi. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2355-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2355-9_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New Delhi
Print ISBN: 978-81-322-2354-2
Online ISBN: 978-81-322-2355-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)