Abstract
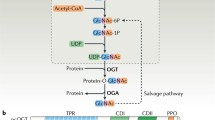
O-GlcNAcylation, which is the cycling of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) on nuclear and cytosolic proteins, has extensive cross talk with phosphorylation to serve as a nutrient sensor that regulates nearly all aspects of cellular metabolism. O-GlcNAc cycling is tightly regulated by only two gene products, O-GlcNAc transferase and O-GlcNAcase that are targeted to substrates by a multitude of binding partners. Research over the past three decades has shown that O-GlcNAcylation is fundamentally important in regulating transcription, modulating signaling pathways, and modifying the activities of metabolic enzymes and kinases in response to nutrients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erickson JR, Pereira L, Wang L, Han G, Ferguson A, Dao K, Copeland RJ, Despa F, Hart GW, Ripplinger CM et al (2013) Diabetic hyperglycaemia activates CaMKII and arrhythmias by O-linked glycosylation. Nature 502:372–376
Gambetta MC, Oktaba K, Muller J (2009) Essential role of the glycosyltransferase sxc/Ogt in polycomb repression. Science 325:93–96
Hart GW, Housley MP, Slawson C (2007) Cycling of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins. Nature 446:1017–1022
Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G, Lagerlof O (2011) Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev Biochem 80:825–858
Lazarus MB, Nam Y, Jiang J, Sliz P, Walker S (2011) Structure of human O-GlcNAc transferase and its complex with a peptide substrate. Nature 469:564–567
Lazarus MB, Jiang J, Kapuria V, Bhuiyan T, Janetzko J, Zandberg WF, Vocadlo DJ, Herr W, Walker S (2013) HCF-1 is cleaved in the active site of O-GlcNAc transferase. Science 342:1235–1239
Macauley MS, Vocadlo DJ (2010) Increasing O-GlcNAc levels: an overview of small-molecule inhibitors of O-GlcNAcase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800(2):107–121
Ranuncolo SM, Ghosh S, Hanover JA, Hart GW, Lewis BA (2012) Evidence of the involvement of O-GlcNAc-modified human RNA polymerase II CTD in transcription in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 287:23549–23561
Sakabe K, Wang Z, Hart GW (2010) Beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) is part of the histone code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:19915–19920
Wang Z, Udeshi ND, O’Malley M, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Hart GW (2010) Enrichment and site mapping of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine by a combination of chemical/enzymatic tagging, photochemical cleavage, and electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:153–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Japan
About this entry
Cite this entry
Hart, G.W. (2014). O-GlcNAcylation: A Nutrient Sensor That Regulates Cell Physiology. In: Endo, T., Seeberger, P., Hart, G., Wong, CH., Taniguchi, N. (eds) Glycoscience: Biology and Medicine. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-54836-2_82-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-54836-2_82-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-54836-2
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences