Abstract
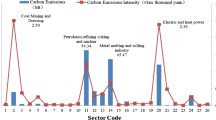
Guangxi’s economic development mainly relies on major industries such as electric power, steel, cement, nonferrous metallurgy, papermaking, sugar, starch, and glass industry. With continuous development of the economy, the situation of carbon emission reduction of these industries is not optimistic. In this paper, carbon emission of Guangxi’s major industries in 2012 was calculated using Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) method, and then, the situation of carbon emissions was analyzed. The results showed that carbon emission of Guangxi’s major industries mainly came from energy consumption, but carbon emissions in the technological process also should not be ignored; carbon emissions were mainly from industries such as steel, cement, thermal power, and nonferrous metallurgical and chemical industry where energy consumption is high and energy efficiency is low. The key factors that influence carbon emissions of these industries included irrational energy consumption structure and energy processing, the overall low utilization efficiency, and the increasing demand with the rapid economic growth. In order to realize a low-carbon economy and sustainable development in these major industries, the following measures were proposed such as formulation of low-carbon development planning and regulatory standards in these industries, management strengthening of the energy consumption in existing enterprises, optimization of the industrial and energy structure, and actively carrying out industrial upgrade, vigorous promotion of the use of new energy, establishment of the financing and policy guaranteeing system, and improvement of the processing and utilization of energy resources.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Energy Research Institute National Development and Reform Commission (2003) Study on the sustainable development of China’s energy and carbon emissions scenario. Energy research institute national development and reform commission, Beijing, pp 20–39 (in Chinese)
IPCC (2006) IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories: vol II (EB/OL). The Institute for Global Environmental Strategies, Japan 2008. http://www.ipcc.ch/ipccreports/Methodology-reports.htm
Li YY, Xian YN (2014) The current situation and prediction of energy consumption and carbon emissions, and way choice of low-carbon development in Beijing. J Central Univ Finance Econ 6:105–112 (in Chinese)
ORNL (1990) Estimate of CO2 emission from fossil fuel burning and cement manufacturing. ORNL/CD IAC-25. Carbon Dioxide Information. Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA
Schimel DS (1995) CO2 and carbon cycle. In: Climate change 1994: radioactive forcing of climate change (IPCC). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 35–71
Su QY, Wu SX (2008) Some thinking of the energy situation and energy industry in Guangxi. Energy Environ 2008(6):20–22 (in Chinese)
Tang YQ, Chen J, Ran T (2010) Study on the status quo of carbon emission and the strategy to develop low-carbon economy in Chongqing. Sichuan Environ 29(1):87–90 (in Chinese)
Zhao M, Zhang WG, Yu LZ (2009) Carbon emissions from energy consumption in Shanghai city. Res Environ Sci 22(8):984–989 (in Chinese)
Zhu Y, Qiu SF (2010) Calculation and analysis of carbon emissions from energy consumption in Fujian province. Fujian BBS, Humanit Soc Sci 10:145–148 (in Chinese)
Zhu Y, Zhou H, He XW (2010) Study on CO2 emission investigation and reduction measure in Liaoning Province. J Anhui Agric Sci 38(23):12357–12360 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, Lx., Zhang, Lh., Song, Xw., Qin, Nj., Zhang, J. (2015). Carbon Emission of Guangxi’s Major Industries and Measures for Low-carbon Economic Development. In: Feng, S., Huang, W., Wang, J., Wang, M., Zha, J. (eds) Low-carbon City and New-type Urbanization. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45969-0_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45969-0_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-45968-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-45969-0
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)