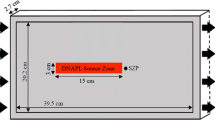
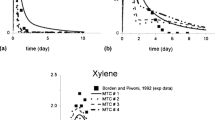
Abstract
Nonaqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) such as gasoline and halogenated solvents enter the subsurface after a spill, or from leaking underground storage tanks. NAPLs trapped by capillary forces in subsurface environments pose a long-term threat to drinking water supplies. The main challenge in site remediation lies in dealing with the dissolving NAPL source (Corapcioglu and Baehr 1987). An understanding and quantification of the NAPL dissolution process at pore scale are of utmost importance in estimating the source of existing dissolved compounds and in evaluating the efficiency of in situ remediation of NAPL-contaminated aquifers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- θ :
-
porosity of porous medium
- Ana :
-
interfacial area between the NAPL and the aqueous phase
- ana :
-
specific interfacial area between the NAPL and the aqueous phase
- A r :
-
surface area (two-dimensional) of residual NAPL blob or ganglia
- C:
-
aqueous concentration of NAPL
- CSAT :
-
saturation concentration of NAPL
- k:
-
mass transfer coefficient
- k*:
-
mass transfer rate coefficient
- PNA :
-
total (two-dimensional) interfacial perimeter of residual NAPL
- pN :
-
density of NAPL
- S:
-
degree of saturation of NAPL
- t:
-
time
- Vr :
-
volume of residual NAPL blob or ganglia
References
Brusseau ML (1992) Rate-limited mass transfer and transport of organic solutes in porous media that contain immobile immiscible organic liquids. Water Resour Res 28:33–45
Buckley J (1992) Multiphase displacement in micromodels. In: Morrow N (ed) Interfacial phenomena in petroleum technology. Marcel Decker, New York, pp 157–189
Chatzis I, Morrow N, Lim HT (1983) Magnitude and detailed structure of residual oil saturation. Soc Petrol Eng J 23:311–325
Conrad SH, Wilson JL, Mason WR, Peplinski WJ (1992) Visualization of residual organic liquid trapped in aquifers. Water Resour Res 28:467–478
Corapcioglu MY, Baehr AL (1987) A compositional multiphase model for groundwater contamination by petroleum products. Water Resour Res 23:191–200
Corapcioglu MY, Chowdhury S, Roosevelt SE (1997) Micromodel visualization and quantification of solute transport in porous media, Water Resour Res: 33(11)
Dawe RA, Mahers EG, Williams JK (1987) Pore-scale physical modeling of transport phenomena in porous media. In: Bear J, Corapcioglu MY (eds) Advances in transport phenomena in porous media. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 49–76
Hatfield K, Stauffer TB (1993) Transport in porous media containing residual hydrocarbon. I. Model. J Environ Eng 119:540–558
Hunt JR, Sitar N, Udel KS (1988) Nonaqueous phase liquid transport and cleanup, experimental studies. Water Resour Res 24:1259–1269
Imhoff PT, Jaffe PR, Pinder GF (1994) An experimental study of complete dissolution of a nonaqueous phase liquid in saturated porous media. Water Resour Res 30:307–320
Kennedy CA, Lennox WC (1997) A pore-scale investigation of mass transport from dissolving DNAPL ganglia. J Contam Hydrol, 24:221–246
McKeller M, Wardlaw N (1982) A method of making two-dimensional glass micromodels of pore systems. J Can Petrol Technol 21:39–41
Media Cybernetics (1992) Image-Pro PlusTM image processing system version 2.0. Silver Springs, Maryland
Miller CT, Poirier-McNeill MM, Mayer AS (1990) Dissolution of trapped nonaqueous phase liquids: mass transfer characteristics. Water Resour Res 26:2783–2796
Morrow NR, Lim HT, Ward JS (1986) Effect of crude-oil induced wettability changes on oil recovery. SPE Formation Evaluation 1:89–103
Powers SE, Loureiro CO, Abriola LM, Weber WJ Jr (1991) Theoretical study of the significance of nonequilibrium dissolution of nonaqueous phase liquids in subsurface systems. Water Resour Res 27:463–477
Powers SE, Abriola LM, Weber WJ Jr (1992) An experimental investigation of nonaqueous phase liquid dissolution in saturated subsurface systems. Steady state mass transfer rates. Water Resour Res 28:2691–2705
Powers SE, Abriola LM, Weber WJ Jr (1994) An experimental investigation of nonaqueous phase liquid dissolution in saturated subsurface systems. Transient mass transfer rates. Water Resour Res 30:321–332
Soll WE, Celia MA, Wilson JL (1993) Micromodel studies of three-fluid porous media systems: porescale processes relating to capillary pressure-saturation relationships. Water Resour Res 29:2963–2974
Wardlaw N (1982) The effects of geometry, wettability, viscosity and interfacial tension on trapping in single pore-throat pairs. J Can Petrol Technol 21:21–27
Wilson JL (1994) Visualization of flow and transport at the pore level. In: Dracos TH, Stauffer F (eds) Transport and reactive processes in aquifers. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 19–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Corapcioglu, M.Y., Chowdhury, S., Roosevelt, S.E. (1998). Residual Nonaqueous Phase Liquid Dissolution in Micromodels. In: Rubin, H., Narkis, N., Carberry, J. (eds) Soil and Aquifer Pollution. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-03674-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-03674-7_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-08294-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-03674-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive