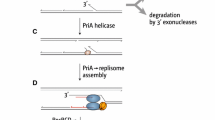
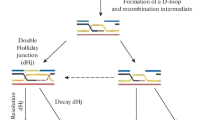
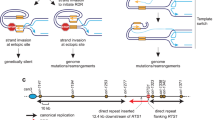
Abstract
Progress in understanding the basis of recombination has lagged behind the related and overlapping areas of replication and repair for a number of reasons. For instance, the most favorable organisms for genetic analysis of recombination have not coincided with those most suitable for molecular studies. E. coli and its phages have been the prime source of molecular information, but some fairly obscure fungi have been instrumental in providing crucial genetic information about recombination. Furthermore, the phages of E. coli that were used most extensively for analysis of recombination were so different in their life cycles that it was not at all clear, at least in the beginning, that conclusions from any one of them could be generalized. Finally, recombination has not lent itself easily to dissection by biochemists because for a long time nobody could think of an adequate way to study the process. The problem was, if essentially identical chromosomes were crossed, what biochemical property could be exploited to measure the progress of the reaction?
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi M, Das Gupta C, Radding CM (1983) Synapsis and the formation of paranemic joints by E. coli rec A protein. Cell 34:931–939
Brahms S, Vergue J, Brahms JG, Di Capua E, Bucher P, Koller T (1982) Natural DNA sequences can form left-handed helices in low salt solution under conditions of to-pological constraint. J Mol Biol 162:473–493
Bullock P, Miller J, Botchan M (1986) Effects of poly [d(pGpT)•d(pApC)] and poly-[d(pCpG) •d(pCpG)] repeats on homologous recombination in somatic cells. Mol Cell Biol 6:3948–3953
Champoux JJ (1977) Renaturation of complementary single-stranded DNA circles: complete rewinding facilitated by the DNA untwisting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5329–5332
Cohen JB, Effron K, Rechavi G, Ben-Neriah Y, Zakut R, Gival D (1982) simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in interaction? Nucl Acids Res 10:3352–3370
Cox MM, Lehman IR (1987) Enzymes of general recombination. Biochemistry 56:225–262
Di Capua E, Stasiak A, Koller T, Brahms S, Thomae R, Pohl FM (1983) Torsional stress induces left-handed helical stretches in DNA of natural base sequence: circular dichroism and antibody binding. EMBO J 2:1531–1535
Flanagan JG, Lefranc MP, Rabbitts TH (1984) Mechanism of divergence and convergence of the human immunoglobulin α1 and α2 constant region gene sequences. Cell 36:681–688
Gonda DK, Shibata T, Radding CM (1985) Kinetics of homologous pairing promoted by rec A protein: effect of ends and internal sites in DNA. Biochemistry 24:413–420
Hamada H, Petrino MG, Kakunaga T (1982) A novel repeated element with Z-DNA priming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6465–6469
Haniford DB, Pulleyblank DE ( 1986) The in vivo occurrence of Z-DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn 1:593–609
Holliday R (1964) A mechanism for gene conversion in fungi. Genet Res Camb 5:282–304
Holliday R (1967) Altered recombination frequencies in radiation sensitive strains of Ustilago. Mutat Res 4:275–288
Holloman WK, Wiegand R, Hoessli C, Radding CM (1975) Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA: a possible mechanism for initiation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:2394–2398
Kilpatrick MW, Klysik J, Singleton CK et al. (1984) Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem 259:7268–7274
Klysik J, Stirdivant SM, Wells RD (1982) Left-handed DNA: cloning, characterization and instability of inserts containing different lengths of (dC-dG) in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 257:10152–10158
Kmiec E, Holloman WK (1982) Homologous pairing of DNA molecules promoted by a protein from Ustilago. Cell 29:367–374
Kmiec E, Holloman WK (1983) Heteroduplex formation and polarity during strand transfer promoted by Ustilago rec 1 protein. Cell 33:857–864
Kmiec EB, Holloman WK (1984) Synapsis promoted by Ustilago rec 1 protein. Cell 36:593–598
Kmiec EB, Angelides KJ, Holloman WK (1985) Left-handed DNA and the synaptic pairing reaction promoted by Ustilago rec 1 protein. Cell 40:139–145
Kmiec EB, Holloman WK (1986) Homologous pairing of DNA molecules by Ustilago rec 1 protein is promoted by sequences of Z-DNA. Cell 44:545–554
Lafer EM, Moller A, Nordheim A, Stolar BD, Rich A (1981) Antibodies specific for left-handed Z-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3546–3550
Meselson MS, Radding CM (1975) A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:359–361
Nordheim A, Rich A (1983) The sequence (dC-dA)n (dG-dT)n forms left-handed Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:1821–1825
Nordheim A, Lafer EM, Peck LJ, Wang JC, Stollar BD, Rich A (1982) Negatively super-coiled plasma contain left-handed Z-DNA segments as detected by specific antibody binding. Cell 31:309–318
Pohl FM (1969) Ein Modell der DNS-Struktur. Naturwissenschaften 54:616
Riddles PW, Lehman IR (1985) The formation of paranemic and plectonemic joints between DNA molecules by the rec A protein and single stranded DNA-binding proteins of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 260:165–169
Shen S, Slightom JL, Smithies O (1981) A history of the human fetal globin gene duplication. Cell 26:191–203
Shibata T, DasGupta C, Cunningham RP, Radding CM (1979) Purified E. coli rec A protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1638–1642
Skowronski J, Plucienniczak A, Bednarek A, Jaworski J (1984) Bovine 1.709 Satellite: recombination hotspots and dispersed repeated sequences. J Mol Biol 177:399–416
Stettler UH, Weber H, Koller T, Weissman C (1979) Preparation and characterization of form V DNA, the duplex DNA resulting from association of complementary, circular single-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol 131:21–20
Stringer JR (1985) Recombination between poly [d(GT)•d(CA)] sequences in simian virus 40-infected cultured cells. Mol Cell Biol 5:1247–1259
Szostak JW, Orr-Weaver TL, Rothstein RB, Stahl FW (1983) The double strand break model for recombination. Cell 33:25–35
Treco D, Arnheim N (1986) The evolutionary conserved repetitive sequence d(TG′ AC)n promotes reciprocal exchange and generates unusual recombinant tetrads during yeast meiosis. Mol Cell Biol 6:3934–3947
Weinstock GM, McEntee K, Lehman IR (1979) ATP-dependent renaturation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:126–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1988 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Holloman, W.K. (1988). Homologous Pairing Promoted by Ustilago Rec 1 Protein. In: Eckstein, F., Lilley, D.M.J. (eds) Nucleic Acids and Molecular Biology. Nucleic Acids and Molecular Biology, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-83384-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-83384-7_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-83386-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-83384-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive