Abstract
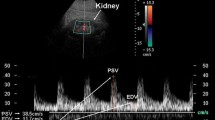
Cyclosporin (CyA) has been demonstrated to increase the vascular resistance of renal allografts (RVR), whereas calcium channel blocking agents like nifedipine may counteract this effect. In this study RVR was calculated from renal blood flow (RBF), measured by the clearance of para-aminohippurate (PAH), and mean arterial pressure (MAP). Analysis of Doppler spectra obtained under ultrasonographic guidance was used as a non-invasive method of assessing renal haemodynamics. A comparison was made between these two methods to detect changes in renal haemodynamics which were caused by the administration of 10 mg nifedipine orally to 11 renal transplant recipients treated with CyA. RBF increased significantly (444 ± 176 vs 559 ± 192 ml/min per 1.73 m2; P<0.05) despite a decrease in MAP (116 ± 10 vs 101 ± 11 mm Hg; P<0.05) after administration of nifedipine. Calculated RVR decreased from 0.31 ± 0.17 to 0.20 ± 0.07 mmHg × min/ml (P<0.05). Results of Doppler spectrum analysis were in concordance with these observations. Resistance index (RI) in interlobar arteries decreased from 0.60 ± 0.04 to 0.56 ± 0.06 (P < 0.05) and acceleration time (Tmax) of the Doppler spectrum decreased from 133 ± 32 to 98 ±32 ms (P<0.05). Theoretically, a lower RI and decreased Tmax indicate a reduced vascular resistance and changes in vascular wall compliance, respectively. Analysis of Doppler spectra may thus become a useful device for non-invasive assessment of acute changes in RVR.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams JS, Bentley FR, Garrison RN, Cryer HM (1991) Cyclosporin A directly constricts intrarenal arterioles. Transplant Proc 23:356–359
Adamson SL, Morrow RJ, Bascon PAJ, Mo LYL, Ritchie JWK (1989) Effect of placental resistance arterial diameter, and blood pressure on the uterine arterial velocity waveform: a computer modeling approach. Ultrasound Med Biol 15:437–442
Allen KS, Jorkasky DK, Arger PH, Velchik MG, Grumbach K, Coleman BF, Mintz MC, Betsch SE, Perloff LJ (1988) Renal allografts: prospective analysis of Doppler sonography. Radiology 169:371–376
Arima M, Ishibashi M, Usami M, Sagawa S, Mizutani S, Sonoda T, Ichikawa S, Ihara H, Nagano S (1979) Analysis of the arterial blood flow patterns of normal and allografted kidneys by the directional ultrasonic Doppler technique. J Urol 122:587–591
Curtis JJ, Dubovsky E, Whelchel JD, Luke RG, Diethelm AG, Jones P (1986) Cyclosporin in therapeutic doses increases renal allograft vascular resistance. Lancet i: 477–479
Dawidson I, Rooth P, Fry WR, Sandor Z, Willms C, Coorpender L, Alway C, Reisch J (1989) Prevention of acute cyclosporine induced renal blood flow inhibition and improved immunosuppression with verapamil. Transplantation 48:575–580
Don S, Kopecky KK, Fili RS, Leapman SB, Thomalla JV, Jones JA, Klatte EC (1989) Duplex Doppler US of renal allografts: causes of elevated resistive index. Radiology 171:709–712
English J, Evan A, Houghton DC, Bennett WM (1987) Cyclosporine induced acute renal dysfunction in the rat. Evidence of ar-teriolar vasoconstriction with preservation of tubular function. Transplantation 44:135–141
Gosling RC, Dunbar G, King DH (1971) The quantitative analysis of occlusive peripheral arterial disease by a non-intrusive ultrasonic technique. Angiology 22:52–55
Hoitsma AJ, Wetzels JFM, Van Lier HJJ, Berden JHM, Koene RAP (1987) Cyclosporin treatment with conversion after three months versus conventional immunosuppression in renal allograft recipients. Lancet i: 584–586
Merkus JWS, Asten van WNJC, Hoitsma AJ, Koene RAP, Skot-nicki SH (1991) Doppler spectrum analysis can detect immediate haemodynamic effects of cyclosporine infusion on human kidney grafts. Transplant Proc 23:972–973
Morales JM, Andres A, Preto C, Ortuno B, Ortuno T, Patermina ER, Hernandez Pablete G, Praga M, Ruilope LM, Rodicio JL (1989) Calcium antagonist treatment of recipients minimizes cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in renal transplantation. A prospective randomized trial. Transplant Proc 21:1537–1539
Perella RR, Duerinckx AJ, Tessler FN, Danovitch GM, Wilkinson A, Gonzalex S, Cohen A, Grant EG (1990) Evaluation of renal transplant dysfunction by duplexJDoppler sonography: a prospective study and review of the literature. Am J Kidney Dis 15:544–550
Planiol T, Pourcelot L (1974) Doppler effect study of the carotid circulation, in: White D, McCready V, Vlieger M (eds) Ultrasonics in medicine. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 104–111
Rigsby CM, Burns PM, Weltin GG, Chen B, Bia M, Taylor KJW (1987) Doppler signal quantitation in renal allografts: Comparison in normal and rejecting transplants with pathologic correlation. Radiology 162:39–42
Skidmore R, Woodcock JP (1980) Physiological interpretation of Doppler shift waveforms-I. Theoretical considerations. Ultrasound Med Biol 6:7–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Merkus, J.W.S., van Asten, W.N.J.C., Skotnicki, S.H., Hilbrands, L.B., Hoitsma, A.J., Koene, R.A.P. (1992). Haemodynamic changes in human kidney allografts following administration of nifedipine: assessment with doppler spectrum analysis. In: Kootstra, G., Opelz, G., Buurman, W.A., van Hooff, J.P., MacMaster, P., Wallwork, J. (eds) Transplant International Official Journal of the European Society for Organ Transplantation. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-77423-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-77423-2_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-55342-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-77423-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive