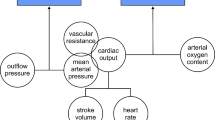
Abstract
The traditional concepts of haemodynamic responses to harmorrhage have been derived primarily from studies in anaesthetized animals, often by using indirect techniques for measuring blood flow. It is, however, well recognized that general anaesthetic agents exert a variety of influences on the cardiovascular system and its control by the autonomic nervous system(1–6). Moreover, the effects of the anaesthetic agents can be modified further by concomitant surgical trauma(7).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vatner SF (1978) Effects of anesthesia on cardiovascular control mechanisms. Environ Health Perspect 26: 193
Merin RG, Kumazawa T and Luka NL (1976) Enflurane depresses myocardial function, perfusion and metabolism in the dog. Anesthesiology 45: 501
Horan BF, Prys-Roberts C, Hamilton WK and Roberts JG (1977) Haemodynamic responses to enflurane anesthesia and hypovolaemia in the dog, and their modification by propranolol. Br J Anaesth 49: 1189
Zimpfer M, Gilly H, Krosl P, Schlag G and Steinbereithner K (in press) Importance of myocardial loading conditions in determining the effects of enflurane on left ventricular function in the intact and isolated canine heart. Anesthesiology
Beck A, Zimpfer M, Raberger G (in press) Inhibition of the carotid chemoreflex by enflurane in chronically instrumented dogs. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol
Zimpfer M, Manders WT, Barger AC, Vatner SF (in press) Pentobarbital alters compensatory neural and humoral mechanisms in response to haemorrhage. Am J Physiol
Fray JCW, Siwek LG, Strull WM, Steller RN and Wilson JM (1976) Influence of dietary sodium on renin activity and arterial pressure during anesthesia. Am J Physiol 231: 1185
Armitage P (1971) Statistical methods in medical research. Oxford, Blackwell Sci-entific Publications
Chien S (1967) Role of the sympathetic nervous system in haemorrhage. Physiol Ref 47: 214
Haddy FJ, Overbeck HW, Daugherty RM Jr (1968) Peripheral Vascular resistance. Ann Rev Med 19: 167
Guyton AC (1976) Textbook of medical physiology. Philadelphia London Toronto, WB Saunders
Morton M, Duke PC and Ong B (1980) Baroreflex control of heart rate in man awake and during enflurane and enflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology 52: 221
Weiskopf RB, Townsley MI, Riordan KK, Chadwick K, Baysinger M and Mahoney E (1981) Comparison of cardiopulmonary responses to graded haemorrhage during enflurane, halothane, isoflurane, and ketamine anesthesia. Anaesth Analg 60: 481
Schumacher IG and Arndt JO (1978) Der Effekt von Methohexital, Fentanyl, De- hydrobenzperidol sowie von Chloralone auf die Aktivitat des Aortenbogens decere- brierter Katzen. Anaesthetist 27: 10
Zimpfer M, Beck A, Mayer N, Raberger G and Steinbereithner K (in press) Einfluft von Morphium auf die Kontrolle des kardiovaskularen Systems durch den Carotis- Sinus-Reflex und den Carotis-Chemoreflex. Anaesthesist
Marta JA, Davis HS and Eisele JH (1973) Vagomimetic effects of morphine and In- novar in man. Anaesth Analg 52: 817
Hug CC Jr (1982) Anesthetic agents and the patient with cardiovascular disease. In: Ream AK, Fogdall RP (eds) Acute cardiovascular management. Philadelphia Toronto, J.B. Lippincott, p 247
Eger II EI (1976) Anesthetic uptake and action. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins
Biscoe TJ, Bardley GW and Purves MJ (1970) The relation between carotid body chemoreceptor discharge, carotid sinus pressure, and carotid body venous flow. J Physiol 208: 99
Zimpfer M, Beck A, Raberger G, Mayer N and Steinbereithner K (1982) Effects of fentanyl on the carotid chemoreflex. Anesthesiology 57: A296
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1983 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zimpfer, M., Kotae, E., Mayer, N., Placheta, P., Steinbereithner, K. (1983). Effects of Anaesthesia on Haemodynamic Responses to Haemorrhage. In: Vickers, M.D., Lunn, J.N. (eds) Mortality in Anaesthesia. European Academy of Anaesthesiology, vol 3. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69355-7_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69355-7_28
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-12824-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-69355-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive