Abstract
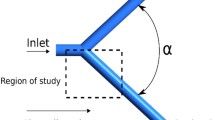
Blood flow at vessel segments with complicated geometry are the objects of fluid-dynamically oriented investigations concerning atherogenesis and thrombosis [1,2]. The development of atherosclerosis in large arteries is determined by two pathogenetic factors: the integrity of the arterial wall and the contents of the vessel, e.g. platelets, white and red blood cells, cholesterol levels [11]. These factors are linked to intimai lipid accumulations and development of fibrous changes in the intima of the arterial wall. In addition, blood is a complex fluid, comprising liquid and flexible cells. How hemodynamic factors like shear stress, high and low velocity gradients, pressure gradients and mass transfer variations play a major role in atherogenesis are not yet understood [13,14], but the areas of predilection for atherosclerosis and thrombosis in the vascular system are characterized by curvature, branding, bifurcation or embanking, where laminar flow is altered and vortices, stagnation points and reverse flows are found [8].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brech R, Bellhouse, BJ: Flow in branching vessels. Cardiovasc Res 7: 593–600, 1973.
Caro CG: Arterial fluid mechanics and atherogenesis. Recent Advances in Cardiovascular Disease, Vol II, Supplement: 6–11, 1981.
Hermann, KH: Platelet aggregation induced in hamster cheek pouch by a photochemical process with exited fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextram. Microvas Res 26: 238–249, 1983.
Krings, WB, Das Verhassuplttchen in der Roh-and verzweigten Kanalstrmung (Durchmesser als 0,1 mm) Med. Diss., Aachen,1984.
Liepsch DW, Moravec St, Zimmer R Enfluß der Hamodynamik auf Gefäßveränderungen (Einfluß der Blutströmung in Arterien auf die Bildung von Thrombosen and Stenosen). Technik 26: 115–122, 1981.
Liepsch, DW: Flow in tubes and arteries-A comparison. Biorheology 23: 395–433, 1986.
Liepsch, DW: Effects of blood flow parameters on flow patterns at arterial bifurcation-Studies in models. Proceedings International Symposium on Biofluid Mechanics: 47–57, 1988.
Marshall M, Hess, H: New findings concerning pathogenesis and non surgical treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Vasa 7: 49–53, 1978.
Naumann, A: Strömung in natüralichen and künstlichen organen and gefßen. Klin Wschr 53: 1007 1019, 1975.
Nerem, RM, Cornhill JF: The role of fluid mechanics in atherogenesis. ASMEY J Biomech Eng. 102: 181–189, 1980.
Schettler G, Nerem, RM, Schmid-Schönbein H, Mohrl H, Siem C: Fluid dynamics as a localizing factor for atherosclerosis. Springer, Berlin, 1983.
Seiffge D, Kremer E: Influence of ADP, blood flow velocity, and vessel diameter on laser-induced thrombus formation. Thromb Res 42: 331–341, 1986.
Stehbens WE: The role of hemodynamics in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Progressive Cardiovascular Diseases 18: 89–103, 1975.
Texon, M: Hemodynamic basis of atherosclerosis. Hemisphere, Washington. 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1990 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Seiffge, D., Kremer, E., Laux, V., Reifert, P. (1990). Investigations Concerning Localization of Induced Thrombus Formation at Arteriolar Bifurcations. In: Liepsch, D.W. (eds) Biofluid Mechanics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-52338-0_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-52338-0_29
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-52730-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-52338-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive