Abstract
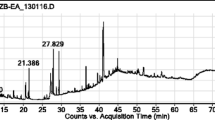
The objective of this study is to measure the toxicity of acaricidal of Mentha piperita extracts, and to isolate and identify the chemical compounds of the extracts. This experiment uses three kinds of solvents - petroleum ether, chloroform, and methanol in extraction with the. Liquid-liquid partition technique. The acaricidal substance was isolated and purified by silica gel column, chromatography, and thin layer chromatography (TLC) together with iodine chromo test; it is traced with the slide retting method. Finally the experiment employs UV photo spectrum, HPLC, RI, and MS, and other techniques in identifying the active substance. The study finds that part of the crude petroleum ether extract from the Mentha piperita land shows significant acaricidal effect to Tetranychus cinnabarinus-when its density reaches 1 mg/ml, lethal rate of mature mites is 87.05 % within 24 hours, and mites’ eggs 93.16 %. According to Duncan’s inspection, three kinds of solvents of crude extracts display great differences in the lethal rate of mature mites and mite eggs (P < 0.05). The study also finds that chloroform extract and methanol extract from the upper menthe lands has relatively weak acaricidal effect - their lethal rates to mature mites comes at 28.51% in 24 hours, and mites eggs 10.73 %. Based on a liquid-liquid extraction of petroleum ether by methanol, the crucial components of the acaricidal substance appear to exist in petroleum ether of lower polar whose lethal rate of mature mites reaches 93.75 % within 24 hours. The study gains eight fractions from the isolation of the petroleum ether extracts. With bioactive tracing, one of them provides a sample compound V which possesses higher acaricidal effect. Its lethal concentration (LC50) reaches 0.5464 mg/mL. Its credible interval is 0.3268 - 0.9134 mg/mL. The purity of the sample compound was 89.16 % based on HPLC. MS shows its molecular ion peak being 414 which reveals its sterol ring structure according to the corresponding data base. IR reflects that the substance shows notable characteristic peaks at 1160 cm-1, 1450 cm-1, 1380 cm-1 and 1700 cm-1. It is thus determined that the substance isolated from Mentha piperita in this study is a β-sitosterol.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, W.S.: A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. Economic Entomology 18, 265–267 (1925)
Ahmed, S.M., Eapen, M.: Vapour toxicity and repellency of some essential oils to insect pests. Indian Perfumer 30, 273–278 (1986)
Chiasson, H.L.N., Langer, A.B., Bostanian, N.: Acaricidal Properties of Artemisia absinthium and Tanacetum vulgare(Asteraceae) Essential Oils Obtained by Three Methods of Extraction. Journal of Economic Entomology 94, 167–171 (2001)
Clanahan, R.H., Thomassen, D., Slattery, J.T.: Metabolic activation of (R)2(+)2pulegone to are activeen on althatcova 2 lentlybinds to mouse liver proteins. Chemical Research Toxicology 2, 349–355 (1989)
Edris, A.E., Farrag, E.S.: Antifungal activity of peppermint an sweet basil essential oils and their majority constituents of some plant pathogenic fungi from the vaporphase. Nahrung 47, 117–121 (2003)
Engel, W.: In vivo studies on the metabolism of the monoterpene pulegone in humans using the metabolism of ingestion correlated amounts(MICA) approach:explanation for the toxicity differences between (S)-(2)- and (R)2(+)-pulegone. Journal of Agriculture Food Chemcal 51, 6589–6597 (2003)
Grange, M., Ahmed, S.: Handbook of plants with pest control properties, pp. 202–203. Wiley Interscience (1988)
Grigoleit, H.G., Grigoleit, P.: Pharmacology and preclinical pharmacokinetics of peppermint oil. Phytomedicine 12, 612–616 (2005)
Hays, J.B., Laws, E.R.: Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology, p. 496. Academic Press, San Diego (1991)
He, L., Yang, Y., Fu, J.Z.: Resistance selection and relative fitness of Tetranychus cinnabarinus(Boisduval)to abamectin. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica 31, 395–400 (2004)
Hou, H., Zhao, L.L.: Studies on the acaricidic activity of the extracts of Kochia scoparia. Planrt Protection 30, 42–45 (2004)
Kim, E.H., Kim, H.K., Choi, D.H., Ahn, Y.J.: Acaricidal activity of clove bud oil compounds against Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Acari: Acaridae). Applied Entomology Zoolology 38, 261–266 (2003)
Liang, C.Y., Li, W.L., Zhang, H.Q., Ren, B.R.: The advance on the reseach of chemical constituants and pharmacological activities of Mentha haplocalyx. Chinese Wild Plant Resources 22, 9–12 (2003)
Luo, W.C.: Research in the Bioactivity of Botanical Alkaloids against Insects. Pesticides 36, 11–15 (1997)
Madyastha, K.M., Raj, C.P.: Studies on the metabolism of amonoterpeneketone, R2(+) 2pulegoneahepa to toxin in rat: isolation and characterization of new metabolites. Xenobiotica 23, 509–518 (1993)
Mansour, F., Ravid, U., Putievsky, E.: Studies on the effects of essential oils isolated from 14 species of Labiatae on the carmine spider mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus. Phytoparasitica 14, 137–142 (1986)
Masatoshi, H., Hiroaki, K.: Repellency of rosemary oil and its components against the onion, aphid Neotoxoptera formosana (Takahashi) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Applied Entomology Zoolology 32, 303–310 (1997)
Moorthy, B., Madyastha, P., Madyastha, K.M.: Hepatotoxicity of pulegoneinrats: its effects on microsomalenzymes, invivo. Toxicology 55, 327–337 (1989)
Mucciarelli, M., Camusso, W., Maffei, M.: Volatile terpenoids of endophyte-free and infected peppermint (Mentha piperita L.): Chemical partitioning of a symbiosis. Microbial Ecology 54, 685–696 (2007)
Pamo, T.E., Tendonkeng, T.: The acaricidal effect of the essential oil of Ageratum houstonianum Mill. flowers on ticks (Rhipicephalus lunulatus) in Cameroon South Africa. Journal of Animal Science 34, 244–247 (2004)
Raja, N., Albert, S., Ignacimuthu, S.: Effect of plant volatile oils in protecting stored cowpea Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walpers against Callosobruchus maculates (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) infestation. Journal of Stored Products Research 37, 127–132 (2001)
Schuhmacher, A., Reichling, J., Schnitzler, P.: Virucidal effect of peppermint oil on the developed viruses herpess implex virus type and type in vitro. Phytomedicine 10, 504–510 (2003)
Shi, G.L., Zhao, L.L., Liu, S.Q.: Acaricidal Activities of Extracts of Kochia scoparia against Tetranychus urticae, Tetranychus cinnabarinus, and Tetranychus viennensis (Acari: Tetranychidae). Journal of Economic Entomology 99, 858–863 (2006)
Stables, L.M.: Effect of pesticides on three species of Tyrophagus, and detection of resistance to pirimiphosmethyl. In: Palmarum, T., Putrescentiae, T. (eds.) Acarology, pp. 1026–1033. Ellis Horwood, Chichester (1984)
Tak, J.H., Kim, H.K., Lee, S.H.: Acaricidal activities of paeonol and benzoic acid from Paeonia suffruticosa root bark and monoterpenoids against Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Acari: Acaridae). Pest Management Science 62, 551–557 (2006)
Thomassen, D., Knebel, N., Slattery, J.T.: Reactive intermediates in the oxidation of menthofuranby cytochromes. Chemical Research Toxicology 5, 123–130 (1992)
Wang, Y.N., Shi, G.L.: Acaricidal activity of Juglans regia leaf extracts on Teranychus viennensis and Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Acari:Tetranychidae). Journal of Economic Entomology 100, 1298–1303 (2007)
Wang, Y.W., Zhang, G.Z., Xu, H.H.: The effect of compounds such as β-sitosterol on gut esterase activity of insects. Journal of Qinghai University (Natural Science) 18, 1–2 (2000)
Wilkin, D.R.: The control of mites in cheese stores. In: Recent Advances in Acarology, New York, pp. 221–229 (1979)
Yao, K.: Research profile of foreign plant grain protectants The second national grain storage professional academic exchange yindong literature, pp. 28–38 (1981)
Zeng, J.W., Qian, S.H., Wu, J.Z.: Studies on antiviral constituents in stems and leaves of Pithecellibium clypearia. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medical 31, 400–402 (2006)
Zhang, H., Meng, L.: Current status of application, development and prospect of agricultural acaricides. Pesticides 42, 14–17 (2003)
Zheng, H.C., Cai, S.Q.: Pharmaceutical Botany and Pharmacognosy, p. 383. People’s medical publishing house, Beijing (2003)
Zhou, S.Y., Li, Q., Yang, Q.F.: Effect of Paris Polyphylla Smith-synergistic Substances Mixtures on Panoychus Citri (Mc Gregor). Journal of Anhui. Agri. Sci. 35, 458–459 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag GmbH Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ren, Jj., Ma, Lq., Liu, Yb., Shi, Gl., Wang, Yn. (2012). The Isolation and Identification of the Acaricidal Principal Extracted from Mentha Piperita. In: Zhu, E., Sambath, S. (eds) Information Technology and Agricultural Engineering. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 134. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27537-1_71
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27537-1_71
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-27536-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-27537-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)