Abstract
The intravenous anaesthetic propofol (2, 6-diisopropylphenol) is a widely used hypnotic. As it has some volatility, it can be detected in expired breath of subjects receiving propofol infusion. In this preclinical study we continuously monitored exhaled propofol using ion molecule reaction mass spectrometry (IMR-MS) after administering propofol boli along with continuous infusion. The correlation between blood plasma propofol concentrations and exhaled propofol concentrations was characterized.
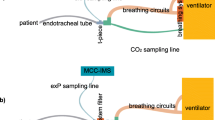
Methods: After approval from the regional authorities for animal research preclinical studies were conducted with twelve pigs. The ion molecule reaction mass spectrometer (IMR-MS) was directly connected to the endotracheal tube with a T-piece. Propofol was applied as a bolus at 0, 30 and 60 min, and simultaneously with the first bolus an infusion of propofol was started. The concentration of propofol was continuously measured using the IMR-MS and compared to blood plasma concentrations.
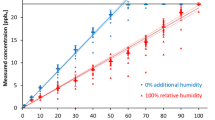
Results: For each bolus application a corresponding peak in exhaled breath was detected and the time to peak duration for each propofol bolus was determined. Linear regression analysis between blood plasma propofol concentrations and breath propofol concentrations yielded the correlation coefficients (R2 values), which varied between 0.28 - 0.74. Conclusions: Changes of blood plasma propofol concentration after application of a bolus can be followed in expired breath. The observed correlation between the blood plasma propofol concentrations and exhaled propofol concentration demonstrates that IMR-MS can be used to monitor propofol bolus application and infusion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Varadarajan, B., Grossherr, M., Meyer, J.U., Dibbelt, L., Gehring, H., Hengstenberg, A. (2009). Monitoring of Propofol Boli in Breathing Gas using Ion Molecule Reaction Mass Spectrometry. In: Dössel, O., Schlegel, W.C. (eds) World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, September 7 - 12, 2009, Munich, Germany. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 25/7. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03885-3_119
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03885-3_119
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-03884-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-03885-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)