Abstract
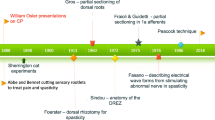
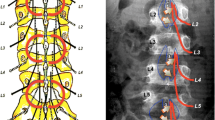
Surgery in the dorsal root entry zone (DREZ) was introduced in 1972 [1,2] to treat intractable pain. Because of its inhibitory effects on muscular tone, it has been applied to patients with focalized hyperspasticity [3–6]. This method – named microsurgical DREZotomy (MDT) – attempts to selectively interrupt the small nociceptive and the large myotatic fibers (situated laterally and centrally, respectively), while sparing the large lemniscal fibers which are regrouped medially. It also enhances the inhibitory mechanisms of Lissauer’s tract and dorsal horn [7] (Figure 116-1 ).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sindou M. Etude de la jonction radiculo-médullaire postérieure: la radicellotomie postérieure sélective dans la chirurgie de la douleur. Lyon: These med; 1972.
Sindou M, Quoex C, Baleydier C. Fiber organization at the posterior spinal cord-rootlet junction in man. J Comp Neurol 1974;153:15–26.
Sindou M, Fisher G, Goutelle A, et al. La radicellotomie postérieure sélective dans le traitement des spasticités. Rev Neurol 1974;130:201–15.
Sindou M, Millet MF, Mortamais J, et al. Results of selective posterior rhizotomy in the treatment of painful and spastic paraplegia secondary to multiple sclerosis. Appl Neurophysiol 1982;45:335–40.
Sindou M, Abdennebi B, Sharkey P. Microsurgical selective procedures in the peripheral nerves and the posterior root-spinal cord junction for spasticity. Appl Neurophysiol 1985;48:97–104.
Sindou M, Pregelj R, Boisson D, et al. Surgical selective lesions of nerve fibers and myelotomies for the modifications of muscle hypertonia. In: Sir Eccles J, Dimitrijevic, MR, editors. Recent achievements in restorative neurology: upper motor neuron functions and dysfunctions. Basel: S. Karger; 1985. p. 10–26.
Eccles J, Eccles R, Magni F. Central inhibitory action attributable to presynaptic depolorization produced by muscle afferent volleys. J Physiol 1961;159:147–66.
Sindou M, Jeanmonod D, Mertens P. Surgery in the DREZ: microsurgical DREZotomy for treatment of spasticity. In: Sindou M, Abbott R, Keravel Y, editors. Neurosurgery for spasticity. Wien: Springer; 1991. p. 165–82.
Sindou M, Jeanmonod D. Microsurgical DREZ-tomy for the treatment of spasticity and pain in the lower limbs. Neurosurgery 1989;24:655–70.
Sindou M, Mifsud JJ, Boisson D, et al. Selective posterior rhizotomy in the dorsal root entry zone for treatment of hyperspasticity and pain in the hemiplegic upper limb. Neurosurgery 1986;18:587–95.
Beneton C, Mertens P, Leriche, et al. The spastic bladder and its treatment. In: Sindou M, Abbott R, Keravel Y. Neurosurgery for spasticity: a multidisciplinary approach. New York: Springer; 1991. p. 193–9.
Willis WD. Pain system. Basel: Karger; 1985.
Rand R. Further observations on Lissauer’s tractolysis. Neurochirurgica 1960;3:151–68.
Denny-Brown D, Kirk EJ, Yanagisawa N. The tract of Lissauer in relation to sensory transmission in the dorsal horn of spinal cord in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol 1973;151:175–200.
Ramon y Cajal S. Histologie du systéme nerveux, vol. 1. Paris: Maloine; 1901.
Szentagothai J. Neuronal and synaptic arrangement in the substantia gelatinosa. J Comp Neurol 1964;122:219–39.
Wall PD. Presynaptic control of impulses at the first central synapse in the cutaneous pathway. In: Eccles JC, Schadé JP, editors. Physiology of spinal neurons. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1964. p. 92–118.
Jeanmonod D, Sindou M, Magnin M, et al. Intra-operative unit recordings in the human dorsal horn with a simplified floating microelectrode. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1989;72:450–4.
Guenot M, Hupe JM, Mertens P, et al. New type of microelectrode for obtaining unitary recordings in the human spinal cord. J Neurosurg (Spine) 1999;91:25–32.
Guenot M, Bullier J, Rospars J, et al. Single-unit analysis of the spinal dorsal horn in patients with neuropathic pain. J Clin Neurophysiol 2003;20:142–50.
Loeser JD, Ward AA, Jr, White LE, Jr. Some effects of deafferentation of neurons. J Neurosurg 1967;17:629–36.
Albe-Fessard D, Lombard MC. Use of an animal model to evaluate the origin of and protection against deafferentation pain. In: Bonica JJ, et al. editors. Advances in pain research and therapy, vol. 5. New York: Raven Press; 1983. p. 691–700.
Guenot M, Bullier J, Sindou M. Clinical and electrophysiological expression of deafferentation pain alleviated by dorsal root entry zone lesions in rats. J Neurosurg 2002;97:1402–9.
Mertens P, Ghaemmaghami C, Bert L, et al. Microdialysis study of amino-acid neurotransmitters in the spinal dorsal horn of patients undergoing microsurgical dorsal root entry zone lesioning. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 2001;94:165–73.
Jeanmonod D, Sindou M. Somatosensory function following dorsal root entry zone lesions in patients with neurogenic pain or spasticity. J Neurosurg 1991;74:916–32.
Sindou M, Fischer G, Mansuy L. Posterior spinal rhizotomy and selective posterior rhizidiotomy. In: Krayenbühl H, Maspes PE, Sweet WH, editors. Progress in neurological surgery, vol. 7. Basel: Karger; 1976. p. 201–50.
Sindou M, Goutelle A. Surgical posterior rhizotomies for the treatment of pain. In: Krayenbühl H, editor. Advances and technical standards in neurosurgery, vol. 10. Vienna: Springer; 1983. p. 147–85.
Mertens P, Guénot M, Hermier M, et al. Radiologic anatomy of the spinal dorsal horn at the cervical level (anatomy – MRI correlations). Surg Radiol Anat 2000;22:81–8.
Sindou M. Microsurgical DREZotomy (MDT) for pain, spasticity and hyperactive bladder: a 20 year experience. Acta Neurochir 1995;137:1–5.
Sindou M, Abbott R, Keravel Y (eds.). “Neurosurgery for spasticity.” Wien: Springer; 1991.
Decq P, Mertens P. La Neurochirurgie de la Spasticité, Neurochirurgie. Masson: Paris; 2003.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this entry
Cite this entry
Sindou, M.P., Mertens, P. (2009). Surgery in the Dorsal Root Entry Zone for Spasticity. In: Lozano, A.M., Gildenberg, P.L., Tasker, R.R. (eds) Textbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69960-6_116
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69960-6_116
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-69959-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-69960-6
eBook Packages: MedicineReference Module Medicine