Abstract
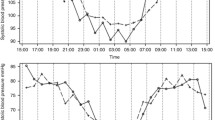
Alcohol abuse increases mortality by cardiovascular disease and relatively high arteriosclerosis process. The effect of alcohol on body can not be noticed even if there are severe cardiac disorders because it paralyzes judgment and perceptual function of people. Also, alcohol uptake could disturb actions of various drugs that are used for angina pectoris and heart failure. In this research, the change of blood flow rate of normal and alcoholic state was investigated as a method to understand the effect of alcohol on human body. The rate of blood flow was measured using a commercial blood flow rate measurement system. The blood flow rate appears higher in alcoholic persons than normal persons from this measurement. This change is considered to investigate indirectly the effects of alcohol uptake on cardiovascular disease like high blood pressure, ischemic heart disease, etc.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keller M, McCormick M, Efron V. A dictionary of words about alcohol. 2nd ed. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Center of Alcohol Studies; 1982.
Orrego H, Carmichael FJ, Israel Y. New insights on the mechanism of the alcohol-induced increase in portal blood flow. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1988;66(1):1
Gorelick DA (1989): Serotonin uptake blockers and the treatment of alcoholism. In: Recent Developments in Alcoholism. Ed by Galanter M. New York, Plenum Press 267–281
Modell JG, Mountz JM (1995): Focal cerebral blood flow change during craving for alcohol measured by SPECT. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 7(1): 15–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jung, Jh., Park, H., Jeon, Ay., Kim, Ch., Ro, Jh., Jeon, Gr. (2007). Research on the change of blood flow rate between normal and alcoholic subjects. In: Magjarevic, R., Nagel, J.H. (eds) World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2006. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 14. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-36841-0_275
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-36841-0_275
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-36839-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36841-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)