Abstract
This report analyzes the problem of spoken language understanding, how the problem is simplified in the NLPCC shared task, and the properties of the official datasets. It also describes the system we developed for the shared task and provides experimental analysis that explains how promising results could be achieved by careful usage of standard machine learning and natural language processing techniques and external resources.
The authors Meng Li and Jia Wang left the company after the shared task evaluation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
If there were no such name lists, the rules could still rely on some lexical analyzer to identify person names and location names, since these two kinds of names are represented by special part-of-speech labels in most lexical analyzers. Section 4.1 will compare the value of the name lists with that of using a lexical analyzer.
- 2.
B stands for beginning position, I for inside, L for last, O for outside, and U for unit, i.e. both as beginning and last position.
- 3.
n=3 in our usage.
- 4.
That is, if a hypothesis contains N slots, where the i-th slot is assigned a score si by the slot type classifier, then the score of the hypothesis is \( \frac{1}{n}\sum\nolimits_{i} {s_{i} } \).
- 5.
For example, the query in the official training set “
 ” and the query in extra resources “
” and the query in extra resources “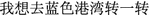 ” are not very similar to each other on their surface forms. Yet because the correct slots “
” are not very similar to each other on their surface forms. Yet because the correct slots “ ” and “
” and “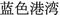 ” are already labeled in both sets, we could convert the queries into patterns “
” are already labeled in both sets, we could convert the queries into patterns “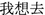 <slot>
<slot>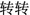 ” and “
” and “ <slot>
<slot> ”. Similarity can be measured on such query patterns.
”. Similarity can be measured on such query patterns.
References
HanLP: Han Language Processing. https://github.com/hankcs/HanLP
Chen, T., Guestrin, C.: XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. arXiv:1603.02754 (2016)
Tur, G., De Mori, R.: Spoken Language Understanding: Systems for Extracting Semantic Information from Speec. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Chen, H., Liu, X., Yin, D., Tang, J.: A survey on dialogue systems: recent advances and new frontiers. arXiv:1711.01731 (2017)
Jeong, M., Lee, G.G.: Triangular-chain conditional random fields. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 16(7), 1287–1302 (2008)
Xu, P., Sarikaya, R.: Convolutional neural network based triangular CRF for joint intent detection and slot filling. In: ASRU (2013)
Zhang, X., Wang, H.: A joint model of intent determination and slot filling for spoken language understanding. In: IJCAI (2016)
Vukotic, V., Raymond, C., Gravier, G.:. Is it time to switch to word embedding and recurrent neural networks for spoken language understanding? In: Interspeech (2015)
Kernighan, M., Church, K., Gale, W.: A spelling correction program based on a noisy channel model. In: COLING (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gong, N. et al. (2018). The Sogou Spoken Language Understanding System for the NLPCC 2018 Evaluation. In: Zhang, M., Ng, V., Zhao, D., Li, S., Zan, H. (eds) Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing. NLPCC 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11108. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99495-6_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99495-6_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-99494-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-99495-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


 ” and the query in extra resources “
” and the query in extra resources “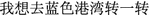 ” are not very similar to each other on their surface forms. Yet because the correct slots “
” are not very similar to each other on their surface forms. Yet because the correct slots “ ” and “
” and “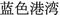 ” are already labeled in both sets, we could convert the queries into patterns “
” are already labeled in both sets, we could convert the queries into patterns “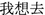 <slot>
<slot>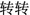 ” and “
” and “ <slot>
<slot> ”. Similarity can be measured on such query patterns.
”. Similarity can be measured on such query patterns.