Abstract
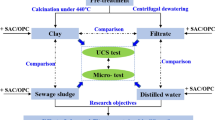
The treatment of organic-rich sludge is significant in geotechnical engineering, which contributes to the resource utilization of sludge and environmental protection. In this paper, several solidifying materials, namely cement, quick lime, potassium ferrate, and super absorbent polymers are selected to treat sludge. Experimental results show that the unconfined compressive strength of treated soil samples is significantly enhanced, and the heavy metal ions concentration measured from the exudation fluid of soil samples is reduced by treatments. Furthermore, the treatment mechanism is investigated by using X-ray diffraction and Scanning Electron Microscopy at the micro scale. The mixing of solidifying materials into sludge leads to the formation of cementitious compounds and the flocculation of clay particles.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tastan, E.O., Edil, T.B., Benson, C.H., et al.: Stabilization of organic soils with fly ash. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 137(9), 819–833 (2011)
Tremblay, H., Duchesne, J., Locat, J., et al.: Influence of the nature of organic compounds on fine soil stabilization. Can. Geotech. J. 39(3), 535–546 (2002)
Hampton, M.B., Edil, T.B.: Strength gain of organic ground with cement-type binders. Geotech. Spec. Publ. 81, 135–148 (1998)
Bell, F.G.: Lime stabilization of clay minerals and soils. Eng. Geol. 42(4), 223–237 (1996)
Jiang, J.Q.: Research progress in the use of ferrate(VI) for the environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 146(3), 617–623 (2007)
Kesenci, K., Say, R., Denizli, A.: Removal of heavy metal ions from water by using poly beads. Eur. Polymer J. 38(7), 1443–1448 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Z., Xiang, W., Liu, Q., Wu, X. (2018). Engineering Properties and Mechanism of Solidifying Materials Treated Sludge. In: Wu, W., Yu, HS. (eds) Proceedings of China-Europe Conference on Geotechnical Engineering. Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97115-5_93
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97115-5_93
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-97114-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-97115-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)