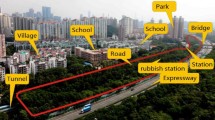
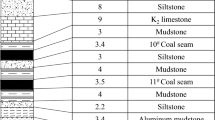
Abstract
Due to the limitation of the terrain and environment condition, two sides of deep foundation pit often appear in different elevation level, which makes foundation pit subjected to asymmetric loadings. The mechanical characteristics of retaining structure with the influence of asymmetric loadings are quite different from that with the influence of symmetric ones. Currently, the relevant code doesn’t present a detailed method for supporting system design of foundation pit under asymmetric loading. Based on Shazitang Station of Changsha Metro Line 4, two sides of them are at different elevation level, the supporting system design scheme and the excavation process was then introduced. Especially, to ensure the safety of foundation pit as well as surrounding buildings, the first supporting was designed as concrete diagonal brace. The horizontal displacement of diaphragm walls and the settlement of surrounding buildings were monitored. Finite element models, which aimed at analyzing the stress and deformation of supporting structures, were then established. With respect to the action of asymmetric load, the horizontal displacement of diaphragm wall on the side of higher elevation level is bigger than the other side. At the top of the wall, the horizontal displacement appears to be a “drift” towards the side of lower elevation level. The horizontal displacement of diaphragm wall and settlement of surrounding ground is relative small and meets requirements of relevant code. In all stages of construction, the deep foundation pit and surrounding buildings remain safety. It can be concluded that the design of supporting system is highly effective in controlling deformation during the foundation pit excavation, which can provide a reference for the design and construction of similar projects.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaqus: Abaqus User’s Manual, Version 6.13. Dassault Simulia Corp., RI (2013)
Hsieh, P.-G., Ou, C.-Y.: Shape of ground surface settlement profiles caused by excavation. Can. Geotech. J. 35(6), 1004–1017 (1998)
Huang, M.S., Liu, Y.H., Sheng, D.C.: Simulation of yielding and stress-strain behaviour of Shanghai soft clay. Comput. Geotech. 38(3), 341–353 (2011)
Liao, S.-M., Wei, S.-F., Tan, Y., et al.: Field performance of large-scale deep excavation in Suzhou. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 37(3), 458–469 (2015). (in Chinese)
Long, M.: Database for retaining wall and ground movements due to deep excavation. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 127(3), 203–224 (2001)
Ou, C.-Y., Hsieh, P.-G., Chiou, D.C.: Characteristics of ground surface settlement during excavation. Can. Geotech. J. 30(5), 758–767 (1993)
Shi, Y.-F., Yang, J.-S., Bai, W., et al.: Analysis of field testing for deformation and internal force of unsymmetrical loaded foundation pit’s enclosure structure close to railway. Chinese J. Rock Mech. Eng. 30(4), 826–833 (2011) (in Chinese)
Tan, Y., Li, M.: Measured performance of a 26 m deep top-down excavation in downtown Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 48(5), 704–719 (2011)
Tan, Y., Wang, D.L.: Characteristics of a large-scale deep foundation pit excavation by the central-island technique in Shanghai soft clay.I: bottom-up construction of the central cylindrical shaft. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 139(11), 1875–1893 (2013a)
Tan, Y., Wang, D.L.: Characteristics of a large-scale deep foundation pit excavation by the central-island technique in Shanghai soft clay.II: top-down construction of the peripheral rectangular pit. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 139(11), 1894–1910 (2013b)
Wang, J.H., Xu, Z.H., Wang, W.D.: Wall and ground movements due to deep excavations in Shanghai soft soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 136(7), 985–994 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The research was conducted with funding provided by the transverse project of SINOHYDRO BUREAU 8 CO., LTD. (Grant NO.SDBJ-CSDT-JS-2017-001). The first and second authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by SINOHYDRO BUREAU 8 CO., LTD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, S., Yang, J., Liu, W., Wang, J. (2019). Mechanical and Deformation Properties of Deep Foundation Pit Supporting System Subjected to Asymmetric Loadings. In: Khabbaz, H., Youn, H., Bouassida, M. (eds) New Prospects in Geotechnical Engineering Aspects of Civil Infrastructures. GeoChina 2018. Sustainable Civil Infrastructures. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95771-5_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95771-5_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-95770-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-95771-5
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)