Abstract
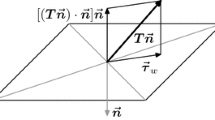
The law of Laplace relates transmural pressure with wall stress. In a (cylindrical) blood vessel and in a (spherical) heart model there exists a simple relation between pressure and circumferential wall stress. The law gives the average stress over the wall, thus how the stress varies over the wall cannot be derived. The law holds only for simple geometries, such as cylindrical blood vessels. Cardiac wall stress estimates require more sophisticated models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huisman RM, Sipkema P, Westerhof N, Elzinga G. Comparison of models used to calculate left ventricular wall force. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1980;18:133–44.
Hefner LL, Sheffield LT, Cobbs GC, Klip W. Relation between mural force and pressure in the left ventricle of the dog. Circ Res. 1962;11:654–63.
Mirsky I, Rankin JS. The effects of geometry, elasticity, and external pressures on the diastolic pressure-volume and stiffness-stress relations. How important is the pericardium? Circ Res. 1979;44:601–11. Review.
Arts T, Bovendeerd HHM, Prinzen FW, Reneman RS. Relation between left ventricular cavity pressure and volume and systolic fiber stress and strain in the wall. Biophys J. 1991;59:93–102.
Torrent-Guasp F, Kocica MJ, Corno AF, Komeda M, Carreras-Costa F, Flotats A, et al. Towards new understanding of the heart structure and function. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;27:191–201. Review.
Arts T, Reneman RS, Veenstra PC. A model of the mechanics of the left ventricle. Ann Biomed Eng. 1979;7:299–318.
Love AEH. A treatise on mathematical elasticity. 3rd ed. London & New York: Cambridge University Press; 1952.
Chirinos JA, Segers P, Gupta AK, Swillens A, Rietzschel ER, De Buyzere ML, et al. Time-varying myocardial stress and systolic pressure-stress relationship: role in myocardial-arterial coupling in hypertension. Circulation. 2009;119:2798–807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Westerhof, N., Stergiopulos, N., Noble, M.I.M., Westerhof, B.E. (2019). Law of Laplace. In: Snapshots of Hemodynamics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91932-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91932-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-91931-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-91932-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)