Abstract
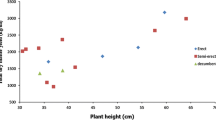
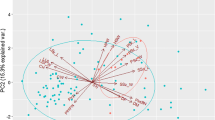
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is an important perennial legume for animal feeding. A basic requirement for the successful breeding of this species is variability of the initial material. The collection under study consisted of 37 cultivars of different origin. The current study aimed to determine the genetic variability of the most important traits, including disease resistance, seed yield, fresh and dry matter yield, plant height during spring regrowth and at flowering stage and stem density. The statistical analysis of the data (ANOVA) revealed significant variability among the cultivars for all traits investigated. The highest variability was found for the seed yield (46.5%), while the lowest one (5.9%) was estimated for resistance to spring black stem and leaf spot. A cluster analysis was used to graphically illustrate the genetic diversity of alfalfa cultivars. The high level of genetic variability among the alfalfa cultivars in this collection highlights their potential for being used in the future breeding schemes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2012) Fodder plants. Medicago sativa L. Off J Eur Union 31:132–140. Common catalogue of varieties of agricultural plant species
Bodzon Z (2004) Correlations and heritability of the characters determining the seed yield of the long-raceme alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). J Appl Genet 45:49–59
Bouton JH (2012) Breeding Lucerne for persistence. Crop Pasture Sci 63:95–106
Campbell CL, Madden LV (1990) Introduction to plant disease epidemiology. Wiley, New York
Castell-Miller CV, Zeyern RJ, Samac DA (2007) Infection and development of Phoma medicaginis on moderately resistant and susceptible alfalfa genotypes. Can J Plant Pathol 29:290–298
Ellwood SR, Kamphuis LG, Oliver RP (2006) Infection of sources of resistance to Phoma medicaginis isolates in Medicago truncatula SARDI core collection accessions, and multigene differentiation of isolates. Phytopathology 96:1330–1336
Herrmann D, Flajoulot S, Julier B (2010) Sample size for diversity studies in tetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa) based on co-dominantly coded SSR markers. Euphytica 171:441–446
Kanbe M, Mizuikami Y, Fujimoto F (2002) Improvement of resistance to Sclerotinia crown and stem rot of alfalfa through phenotypic recurrent selection. Jpn Agr Res Q 36:1–5
Lamb JFS, Sheaffer CC, Rhodes LH, Sulc RM, Undersander DJ, Brummer EC (2006) Five decades of alfalfa cultivars improvement: impact on forage yield, persistence, and nutritive value. Crop Sci 46:902–906
Liatukienė A, Žilvinas L (2010) Lucerne complex resistance to diseases. Scripta Hort Bot Univ Vyt Mag 14:98–104
Nagl N, Taski-Ajdukovic K, Barac G, Baburski A, Seccareccia I, Milic D, Katic S (2011) Estimation of genetic diversity in tetraploid alfalfa populations based on RAPD markers for breeding purpose. Int J Mol Sci 12:5449–5460
Rashidi M, Zang B, Cholami M (2009) Effect of different seedling rates on seed yield and same seed yield components of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Int J Agric Biol 11:779–782
Sabanci CO, Ertus MM, Zorer Celebi S (2013) Collection, conservation and evaluation for forage yield of alfalfa landraces grown in East Anatolia. Turkish J Field Crops 18(1):46–51
Touil L, Guesmi F, Fares K, Zagrouba C, Ferchichi A (2009) Mineral composition and genetic variability of some Mediterranean populations of the cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) supported by morphological markers. Asian J Plant Sci 8:1–10
Yaege JR, Stuteville DL (2000) Reaction in the annual Medicago core germplasm collection to two isolates of Peronospora trifoliorum from alfalfa. Plant Dis 84:521–524
Acknowledgments
This study was funded through the long-term research program “Genetics and purposeful change of genotypes of agricultural and forest plants” implemented by Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liatukienė, A. (2018). Genetic Variability of the Most Important Traits in Alfalfa Cultivars Under Lithuanian Conditions. In: Brazauskas, G., Statkevičiūtė, G., Jonavičienė, K. (eds) Breeding Grasses and Protein Crops in the Era of Genomics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89578-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89578-9_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-89577-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-89578-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)