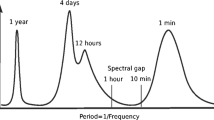
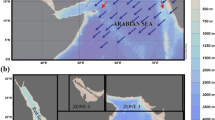
Abstract
A survey of the literature was conducted to review historical and current regime of the Etesian (Etesiae) winds pattern as it was described by Aristotle in his work called Meterologica (around 330 B.C.) up to the current observations and models which investigate the origin of these winds, their behavior and their relation to the climate of Eastern Mediterranean. Since UNESCO dedicated the year 2016 to Aristotle it worth evaluating Aristotle’s conception of the Etesian in the perspective of recent research, studying also the trends and the possible changes of this most stable and persistent wind field.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggelis DE (2010) Contribution to the study of tropospheric ozone changes over Europe. Dissertation (in Greek), National and Kapodistrian University of Athens doi:10.12681/eadd/26331
Aristotle (1994) Hapanta, Vol 13, meteorologica A, B (in Greek) ancient greek literature, the greek. Cactus Editions, ISBN 960-352-224-4; Athens
Anagnostolpoulou C et al (2014) Recent past and future patterns of the Etesian winds based on regional scale climate model simulations Climate Dynamic. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-1936-0
Carapiperis L (1951) On the periodicity of the Etesian in Athens. Weather 6:378–379
Chronis T et al (2011) The summer North Atlantic Oscillation influence on the eastern Mediterranean. J. Climate 24:5584–5596. doi:10.1175/2011JCLI3839.1
Climate Change Impacts Study Committee (2011) The Environmental. Economic and Social Impacts of Climate Change in Greece, Bank of Greece. ISBN 978-960-7032-58-4, Athens
Dafka S et al (2015) The Etesian: from observations to reanalysis. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2920-7
Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K, Lalas D (2001) The effect of the island of Crete on the Etesian winds over the Aegean Sea. Q J R Meteorol Soc 127:1917–1937. doi:10.1002/qj.49712757604
Metaxas DA, Bartzokas A (1994) Pressure covariability over the Atlantic, Europe and N. Africa. Application: centers of action for temperature, winter precipitation and summer winds in athens. Greece. Theor Appl Climatol 49:9–18. doi:10.1007/BF00866284
Poupkou A et al (2011) Present climate trend analysis of the Etesian winds in the Aegean Sea. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 106:459–472
Prezerakos NG (1984) Does the extension of the Azores’ anticyclone towards the Balkans really exist? Meteor. Atmos. Phys. 33:217–227. doi:10.1007/BF02257726
Rizou D et al (2013) On the link between summer Indian monsoon and the etesian pattern over the Aegean sea. In: 13th Conference on environmental science and technology, 5–7 September 2013, Athens, Greece
Tyrlis E, Lelieveld J (2013) Climatology and dynamics of the summer Etesian winds over the Eastern Mediterranean. J Atmos Sci 70:3374–3396. doi:10.1175/JAS-D-13-035.1
Zanis P et al (2013) Summertime free tropospheric ozone pool over the Eastern Mediterranean/Middle East. Atmos Chem Phys Discuss 13, 22 025–22 058, doi:10.5194/acpd-13-22025-2013
Ziv B, Saaroni H, Alpert P (2004) The factors governing the summer regime of the eastern Mediterranean. Int J Climatol 24:1859–1871. doi:10.1002/joc.1113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Aggelis, D.E. (2017). Etesiae Winds: From Aristotle to the 21st Century. In: Karacostas, T., Bais, A., Nastos, P. (eds) Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences. Springer Atmospheric Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-35095-0_178
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-35095-0_178
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-35094-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-35095-0
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)