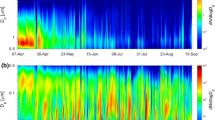
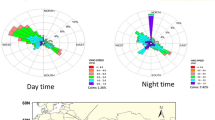
Abstract
This study examines the chemical composition of aerosols over Athens. To achieve this, particulate matter sampling has been conducted on a 6–24 h basis from January 2013 until now. More than 700 aerosol samples were collected at downtown Athens, in Thissio and after mass quantification, were analyzed for major ions (Cl−, Br−, \( {\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } \), \( {\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - } \), \( {\text{PO}}_{4}^{ - 3 } \), \( {\text{C}}_{2} {\text{O}}_{4}^{ - 2 } \), \( {\text{NH}}_{4}^{ + } \), K+, Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+), trace elements (Al, As, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, V, Zn, Mn, Ni, Pb, P, S, Sb), organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC). Aerosol chemical mass closure calculations indicated that carbonaceous aerosol constitutes a major component, along with nitrate and sulfate anions, dust, cations and EC. Principal component analysis (PCA) was also applied to better constrain the aerosol sources over Athens with specific emphasis during the winter time, period characterized by intense biomass burning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birch ME, Cary RA (1996) Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposures to particulate diesel exhaust. Aerosol Sci Technol 25:221–41
Paraskevopoulou D, Liakakou E, Gerasopoulos E, Theodosi C, Mihalopoulos N (2014) Long term characterization of organic and elemental carbon in the PM2.5 fraction: the case of Athens, Greece. Atmos Chem Phys 14:13313–13325
Remoundaki E, Kassomenos P, Mantas E, Mihalopoulos N, Tsezos M (2013) Composition and mass closure of PM2.5 in urban environment (Athens, Greece). Aerosol Air Qual Res 13:72–82
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (1998) Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to cli-mate change. Wiley, New York
Theodosi C, Im U, Bougiatioti A, Zarmpas P, Yenigun O, Mihalopoulos N (2010) Chemical composition of aerosols over Istanbul, Turkey. Sci Total Environ 408(12):2482–2491
Acknowledgments
CT acknowledges support by the State Scholarship Foundation (“IKY Fellowships of Excellence for Postgraduate Studies in Greece—Siemens Programme”) in the framework of the Hellenic Republic–Siemens Settlement Agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Theodosi, C. et al. (2017). Aerosol Chemical Mass Closure in Athens, Greece: Towards a Better Understanding of the Seasonal Variation of Aerosol Sources in the Area. In: Karacostas, T., Bais, A., Nastos, P. (eds) Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences. Springer Atmospheric Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-35095-0_122
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-35095-0_122
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-35094-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-35095-0
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)