Abstract
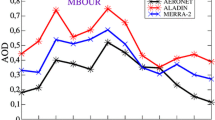
Initial and boundary conditions of dust are still a missing component in atmospheric modeling. In this context, dust models are usually initialized based on their own previous forecasting cycle. As it is obvious, even at the idealized hypothesis of a perfect model run, this approach implies the propagation of numerical diffusion errors. However, recent improvements in remote sensing retrievals of dust optical depth allow the timely generation of dust fields that can be used for assimilation in forecasting atmospheric modeling systems. In this work we present the methodology and preliminary results for the application of MSG/SEVIRI dust retrievals in the atmospheric model NMME-DREAM. First results of the assimilation method are compared with ground photometers (AERONET) and LIDAR (PollyXT) systems during Charadmexp campaign (15 June–15 July 2014). Significant improvement is found mainly over dust sources in Africa and Arabia deserts. The introduction of satellite assimilation methods in dust models provides an additional tool for the improvement of our understanding on the dust-atmosphere interactions and on their possible implications for climate change.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baklanov A et al (2014) Online coupled regional meteorology chemistry models in Europe: current status and prospects. Atmos Chem Phys 14:317–398. doi:10.5194/acp-14-317-2014
Basart S, Pérez C, Nickovic S, Cuevas E, Baldasano J (2012) Development and evaluation of the BSCDREAM8b dust regional model over northern Africa, the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Tellus B 64:18539. doi:10.3402/tellusb.v64i0.18539
Brindley HE, Russell JE (2009) An assessment of Saharan dust loading and the corresponding cloud-free longwave direct radiative effect from geostationary satellite observations. J Geophys Res 114:148–227
Nickovic S, Papadopoulos A, Kakaliagou O, Kallos G (2001) Model for prediction of desert dust cycle in the atmosphere. J Geophys Res 106:18113–18129
Nickovic S, Solomos S, Pejanovic G, Pradhan Y, Marenco F, Amiridis V, Marinou E, Petkovic S, Cvetkovic B (2016) Effects of MSG-SEVIRI dust assimilation on NMME-DREAM model. (in preparation)
Pejanovic G, Vukovic A, Vujadinovic M, Dacic M, (2010) Assimilation of satellite information on mineral dust using dynamic relaxation approach. Geophysical Research Abstracts Vol. 12, EGU2010-7353, EGU General Assembly 2–7 May 2010, Vienna, Austria
Pejanovic G, Nickovic S, Petkovic S, Vukovic A, Djurdjevic V, Vujadinovic M, Dacic M (2012) Dust operational forecast system with assimilation of dust analysed data. In: regional conference on dust and dust storms, Kuwait, 20–22 Nov 2012
Pérez C, Nickovic S, Pejanovic G, Baldasano JM, Ozsoy E (2006) Interactive dust-radiation modeling: a step to improve weather forecasts. J Geophys Res 111:D16206. doi:10.1029/2005JD006717
Schepanski K, Knippertz P, Fiedler S, Timoukc F, Demartyd J (2015) QJR Meteorol Soc B 141:1442–1456. doi:10.1002/qj.2453
Solomos S, Kallos G, Mavromatidis E, Kushta J (2012) Density currents as a desert dust mobilization mechanism. Atmos Chem Phys 12:11199–11211. doi:10.5194/acp-12-11199-2012
Acknowledgments
The model development was performed under support of the Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia. In addition the study was supported by the European Union Seventh Framework Program (FP7-REGPOT-2012-2013-1), in the framework of the project BEYOND, under Grant Agreement No. 316210 (BEYOND—Building Capacity for a Centre of Excellence for EO-based monitoring of Natural Disasters, http://ocean.space.noa.gr/BEYONDsite) and by the ESA-ESTEC project “CHARADMEXP—Characterization of Aerosol mixtures of Dust And Marine origin”; contract no. IPL-PSO/FF/lf/14.489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Solomos, S. et al. (2017). Development of a Dust Assimilation System for NMM-DREAM Model Based on MSG-SEVIRI Satellite Observations. In: Karacostas, T., Bais, A., Nastos, P. (eds) Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences. Springer Atmospheric Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-35095-0_115
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-35095-0_115
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-35094-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-35095-0
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)