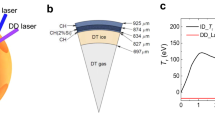
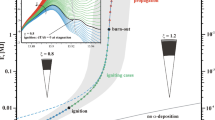
Abstract
Essential ingredients of inertial confinement fusion (ICF) are fuel compression to very high density and hot spot ignition. In the conventional approach to ICF both fuel compression and hot spot formation are produced by the implosion of a suitable target driven by a time-tailored pulse of laser light or X-rays. This scheme requires an implosion velocity of 350–400 km/s. In advanced ignition schemes, instead, the stages of compression and hot spot heating are separated. First, implosion at somewhat smaller velocity produces a compressed fuel assembly. The hot spot is then generated by a separate mechanism in the pre-compressed fuel. The reduced implosion velocity relaxes issues concerning hydrodynamic instabilities, laser-plasma instabilities and preheat control. In addition, it can lead to higher target energy gain (ratio of fusion energy to driver energy). Fast ignition and shock ignition are promising advanced ignition schemes. In fast ignition the hot spot is created by either relativistic electrons or multi-MeV protons or light-ions, produced by a tightly focused ultra-intense laser beam. In shock ignition, intense laser pulses drive a converging shock wave that helps creating a hot spot at the centre of the fuel. These advanced schemes are illustrated in the present chapter. Motivation, potential advantages and issues are described. Research needs and perspective are also briefly discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Atzeni, J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, The Physics of Inertial Fusion (Clarendon, Oxford, 2004)
J.D. Lindl, Phys. Plasmas 2, 3933 (1995)
J.D. Lindl, Inertial Confinement Fusion: The Quest for Ignition and High Gain Using Indirect Drive (Springer and AIP, New York, 1997)
J.W. Hogan (ed.), Energy from Inertial Fusion (International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1995)
M.E. Cuneo et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 48, R1 (2006)
C. Olson et al., Fusion Sci. Technol. 47, 633 (2005)
B.G. Logan, L.J. Perkins, J.J. Barnard, Phys. Plasmas 15, 072701 (2008)
J.H. Nuckolls, L. Wood, A. Thiessen, G.B. Zimmermann, Nature 239, 139 (1972)
S.W. Haan et al., Phys. Plasmas 18, 051001 (2011)
J.D. Lindl, E.I. Moses, Phys. Plasmas 18, 050901 (2011)
G.H. Miller, E.I. Moses, C.R. Wuest, Nucl. Fusion 44, S228 (2004)
L.J. Suter et al., Phys. Plasmas 7, 2092 (2000)
M. Tabak et al., Phys. Plasmas 1, 1626 (1994)
R. Betti et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 155001 (2007)
S.E. Bodner et al., Phys. Plasmas 7, 2298 (2000)
S. Atzeni, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51, 124029 (2009)
M. Lafon, J. Ribeyre, G. Schurtz, Phys. Plasmas 17, 052704 (2010)
M.C. Herrmann, M. Tabak, J.D. Lindl, Nucl. Fusion 41, 99 (2001)
J.D. Lindl et al., Phys. Plasmas 11, 339 (2004)
S.E. Bodner, J. Fusion Energy 1, 221 (1981)
M.D. Rosen, Phys. Plasma 6, 1690 (1999)
C. Garban-Labaune et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 1018 (1982)
W.L. Kruer, The Physics of Laser Plasma Interactions (Addison Wesley, Redwood City, 1988)
Ya.B. Zel’dovich, Yu.P. Raizer, Physics of Shock Waves and High Temperature Hydrodynamic Phenomena (Academic, New York, 1967)
J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, C. Schalk, Z. Naturf. 37a, 955 (1982)
G.I. Taylor, Proc. R. Soc. (London) A201, 159 (1950)
K. Anderson, R. Betti, Phys. Plasmas 11, 5 (2004)
V.N. Goncharov et al., Phys. Plasmas 10, 1906 (2003)
R. Betti, C. Zhou, Phys. Plasmas 12, 110702 (2005)
S. Atzeni, A. Schiavi, C. Bellei, Phys. Plasmas 14, 052702 (2007)
X. Ribeyre et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 50, 025007 (2008)
X. Ribeyre et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51, 015013 (2009)
S. Atzeni, A. Schiavi, A. Marocchino, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53, 035010 (2011)
S. Atzeni, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1980 (1995)
J.D. Lawson, Proc. R. Soc. (London) 70, 6 (1957)
J. Wesson, Tokamaks, 3rd edn. (Clarendon, Oxford, 2003)
J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, Nucl. Fusion 22, 561 (1982)
M.D. Rosen, J.D. Lindl, Laser Program Annual Report, Report UCRL-520021-83, 3.5 (1984)
S. Atzeni, Phys. Plasmas 6, 3316 (1999)
J.C. Fernandez et al., Nucl. Fusion 49, 065004 (2009)
S. Atzeni, M. Tabak, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47, B769 (2005)
M. Tabak et al., Fusion Sci. Technol. 49, 254 (2006)
D. Strickland, G. Mourou, Opt. Commun. 55, 447 (1985)
M. Perry, G. Mourou, Science 264, 917 (1994)
M.H. Key, Phys. Plasmas 14, 055502 (2007)
E.M. Campbell, R.R. Freeman, K.A. Tanaka (guest editors), Fusion Sci. Technol. 49, 249 (2006)
J.R. Davies, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51, 014006 (2009)
P.M. Nilson et al., Phys. Rev. Lett 105, 235001 (2010)
S.C. Wilks et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 1383 (1992)
G. Malka, J.L. Miquel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 75 (1996)
J.S. Green et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 0150032 (2010)
F.N. Beg et al., Phys. Plasmas 4, 448 (1997)
S.C. Wilks, W.L. Kruer, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 33, 1954 (1997)
B. Chrisman, Y. Sentoku, A.J. Kemp, Phys. Plasmas 15, 056309 (2008)
R. Kodama et al., Nature 418, 933 (2002)
H. Shiraga et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53, 124029 (2011)
S.P. Hatchett et al., Fusion Sci. Technol. 49, 327 (2006)
S. Atzeni, A. Schiavi, J.R. Davies, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51, 015016 (2009)
S. Atzeni et al., Phys. Plasmas 15, 056311 (2008)
A. Debayle, J.J. Honrubia, E.D. D’Humieres, V.T. Tikhonchuk, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53, 124024 (2011)
J.J. Honrubia, J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51, 014008 (2009)
D.J. Strozzi et al., EPJ Web of Conf. Preprint: arXiv:1111.5089v1 (2012)
R.R. Freeman, Presentation at the National Academy Review on Prospects for Inertial Confinement Fusion Energy Systems (2011); fire.pppl.gov/IFE_NAS3_Fast_Ignite_Freeman.pdf
B. Ramakrishna et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 135001 (2010)
M. Tabak, D. Callahan, Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A544, 48 (2005)
M. Roth et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 436 (2001)
M.H. Key et al., Fusion Sci. Technol. 49, 440 (2006)
V.Yu. Bychenkov et al., Plasma Phys. Rep. 27, 1017 (2001)
M. Borghesi et al., Fusion Sci. Technol. 49, 412 (2006)
S. Atzeni, M. Temporal, J.J. Honrubia, Nucl. Fusion 42, L1 (2002)
L. Yin, B.J. Albright, B.M. Hegelich, J. Fernandez, Laser Part. Beams 24, 291 (2006)
B.J. Albright et al., Phys. Plasmas 14, 094502 (2007)
B.M. Hegelich et al., Nucl. Fusion 51, 083011 (2011)
A. Kemp, J. Meyer-ter-Vehn, S. Atzeni, Phys. Rev. Lett 86, 3336 (2001)
L.J. Perkins et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 045004 (2009)
A.J. Schmitt et al., Phys. Plasmas 17, 042701 (2010)
X. Ribeyre et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 51, 124030 (2009)
S. Atzeni, G. Schurtz, Proc. SPIE 8080, 808022 (2011)
S. Atzeni et al., Nucl. Fusion 49, 055008 (2009)
S. Atzeni et al., Comput. Phys. Commun. 169, 153 (2005)
A.R. Bell, M. Tzoufras, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53, 045010 (2011)
W. Theobald et al., Phys. Plasmas 15, 056306 (2008)
W.L. Kruer et al., Phys. Plasmas 3, 382 (1996)
O. Klimo et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 52, 055013 (2010)
S. Depierreux et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53, 124034 (2011)
J. Ebrardt, J.M. Chaput, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 244, 032017 (2010)
S. Skupsky et al., Phys. Plasmas 11, 2763 (2004)
J.A. Marozas et al., Phys. Plasmas 13, 056311 (2006)
Acknowledgements
Work partially supported by the Italian project PRIN 2009FCC9MS and by HiPER project and Preparatory Phase Funding Agencies (EC, MSMT and STFC). I thank A. Schiavi and A. Marocchino for continuous collaboration on several topics discussed in this paper. I also thank G. Schurtz for many discussions on advanced ignition schemes and, particularly, for communicating me a few results on shock ignition prior to publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Atzeni, S. (2013). Inertial Confinement Fusion with Advanced Ignition Schemes: Fast Ignition and Shock Ignition. In: McKenna, P., Neely, D., Bingham, R., Jaroszynski, D. (eds) Laser-Plasma Interactions and Applications. Scottish Graduate Series. Springer, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00038-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00038-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-00037-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-00038-1
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)