Abstract
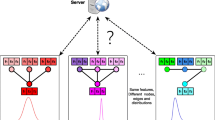
Graph learning has a wide range of applications in many scenarios, which require more need for data privacy. Federated learning is an emerging distributed machine learning approach that leverages data from individual devices or data centers to improve the accuracy and generalization of the model, while also protecting the privacy of user data. Graph-federated learning is mainly based on the classical federated learning framework i.e., the Client-Server framework. However, the Client-Server framework faces problems such as a single point of failure of the central server and poor scalability of network topology. First, we introduce the decentralized framework to graph-federated learning. Second, determine the confidence among nodes based on the similarity of data among nodes, subsequently, the gradient information is then aggregated by linear weighting based on confidence. Finally, the proposed method is compared with FedAvg, Fedprox, GCFL, and GCFL+ to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengio, Y., Courville, A., Vincent, P.: Representation learning: a review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(8), 1798–1828 (2013)
Caldarola, D., Mancini, M., Galasso, F., Ciccone, M., Rodolà, E., Caputo, B.: Cluster-driven graph federated learning over multiple domains. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2749–2758 (2021)
Coulouris, G.F., Dollimore, J., Kindberg, T.: Distributed systems: concepts and design. Pearson Education (2005)
Covert, I.C., et al.: Temporal graph convolutional networks for automatic seizure detection. In: Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, pp. 160–180. PMLR (2019)
Diao, C., Zhang, D., Liang, W., Li, K.C., Hong, Y., Gaudiot, J.L.: A novel spatial-temporal multi-scale alignment graph neural network security model for vehicles prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 24(1), 904–914 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3140229
Guo, T., et al.: Graduate employment prediction with bias. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 670–677 (2020)
Hamilton, W., Ying, Z., Leskovec, J.: Inductive representation learning on large graphs. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Jiang, H., Cao, P., Xu, M., Yang, J., Zaiane, O.: Hi-GCN: a hierarchical graph convolution network for graph embedding learning of brain network and brain disorders prediction. Comput. Biol. Med. 127, 104096 (2020)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Zaheer, M., Sanjabi, M., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. Proc. Mach. Learn. Syst. 2, 429–450 (2020)
Lv, M., Hong, Z., Chen, L., Chen, T., Zhu, T., Ji, S.: Temporal multi-graph convolutional network for traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(6), 3337–3348 (2020)
Maly, R.J., Mischke, J., Kurtansky, P., Stiller, B.: Comparison of centralized (client-server) and decentralized (peer-to-peer) networking. Semester thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 1–12 (2003)
McMahan, B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., y Arcas, B.A.: Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In: Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 1273–1282. PMLR (2017)
Müller, M.: Dynamic time warping. Information retrieval for music and motion, pp. 69–84 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74048-3_4
Pilkington, M.: Blockchain technology: principles and applications. In: Research handbook on digital transformations, pp. 225–253. Edward Elgar Publishing (2016)
Qiu, H., Zheng, Q., Msahli, M., Memmi, G., Qiu, M., Lu, J.: Topological graph convolutional network-based urban traffic flow and density prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(7), 4560–4569 (2020)
Raval, S.: Decentralized applications: harnessing Bitcoin’s blockchain technology. O’Reilly Media, Inc. (2016)
Scarselli, F., Gori, M., Tsoi, A.C., Hagenbuchner, M., Monfardini, G.: The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20(1), 61–80 (2008)
Wang, T., et al.: MORONET: multi-omics integration via graph convolutional networks for biomedical data classification. bioRxiv, pp. 2020–07 (2020)
Xia, F., Ahmed, A.M., Yang, L.T., Luo, Z.: Community-based event dissemination with optimal load balancing. IEEE Trans. Comput. 64(7), 1857–1869 (2014)
Xia, F., Ahmed, A.M., Yang, L.T., Ma, J., Rodrigues, J.J.: Exploiting social relationship to enable efficient replica allocation in ad-hoc social networks. IEEE Trans. Parall. Distrib. Syst. 25(12), 3167–3176 (2014)
Xie, H., Ma, J., Xiong, L., Yang, C.: Federated graph classification over non-IID graphs. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 18839–18852 (2021)
Xu, K., Hu, W., Leskovec, J., Jegelka, S.: How powerful are graph neural networks? arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.00826 (2018)
Zhang, J., Wang, W., Xia, F., Lin, Y.R., Tong, H.: Data-driven computational social science: a survey. Big Data Res. 21, 100145 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, P., Tang, Y., Zhang, M., Chen, W. (2023). Graph Federated Learning Based on the Decentralized Framework. In: Iliadis, L., Papaleonidas, A., Angelov, P., Jayne, C. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2023. ICANN 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14256. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44213-1_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44213-1_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44212-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44213-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)