Abstract
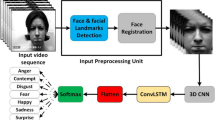
The facial expression recognition (FER) task is widely considered in the modern human-machine platforms (human support robots) and the self-service ones. The important attention given to the FER application is translated by the various architectures and datasets proposed to develop efficient automatic FER frameworks. This paper proposes a new, yet efficient appearance-based deep framework for dynamic FER referred to as Dedicated Encoding-streams based Spatio-Temporal FER (DEST-FER). It considers four input frames where the last presents the peak of the emotion and each input is encoded through a CNN streams. The four streams are joined using LSTM units that perform the temporal processing and the prediction of the dominant facial expression. We considered the challenging FER protocol, which is the person-independent one. To make the DEST-FER more robust to this constraint, we preprocessed the input frames by highlighting 49 landmarks characterizing the emotion’ regions of interest, and applying an edge-based filter. We evaluated 12 CNN architectures for the appearance-based encoders on three benchmarks. The ResNet18 model managed to be the best performing combination with the LSTM units, and led the top FER performance that outperformed the SOTA works.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Chanti, D.A., Caplier, A.: Deep learning for spatio-temporal modeling of dynamic spontaneous emotions. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 12(2), 363–376 (2018)
Bargal, S.A., Barsoum, E., Ferrer, C.C., Zhang, C.: Emotion recognition in the wild from videos using images. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, pp. 433–436 (2016)
Chang, F.J., Tran, A.T., Hassner, T., Masi, I., Nevatia, R., Medioni, G.: ExpNet: landmark-free, deep, 3D facial expressions. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), pp. 122–129. IEEE (2018)
Ding, W., et al.: Audio and face video emotion recognition in the wild using deep neural networks and small datasets. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, pp. 506–513 (2016)
El Hammoumi, O., Benmarrakchi, F., Ouherrou, N., El Kafi, J., El Hore, A.: Emotion recognition in e-learning systems. In: 2018 6th International Conference on Multimedia Computing and Systems (ICMCS), pp. 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMCS.2018.8525872
Gan, C., Yao, J., Ma, S., Zhang, Z., Zhu, L.: The deep spatiotemporal network with dual-flow fusion for video-oriented facial expression recognition. Digit. Commun. Netw. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2022.07.009, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352864822001572
Hasani, B., Mahoor, M.H.: Facial expression recognition using enhanced deep 3D convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 30–40 (2017)
Hasani, B., Mahoor, M.H.: Spatio-temporal facial expression recognition using convolutional neural networks and conditional random fields. In: 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), pp. 790–795. IEEE (2017)
Hu, P., Cai, D., Wang, S., Yao, A., Chen, Y.: Learning supervised scoring ensemble for emotion recognition in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, pp. 553–560 (2017)
Jia, S., Wang, S., Hu, C., Webster, P.J., Li, X.: Detection of genuine and posed facial expressions of emotion: databases and methods. Front. Psychol. 11, 580287 (2021)
Jung, H., Lee, S., Yim, J., Park, S., Kim, J.: Joint fine-tuning in deep neural networks for facial expression recognition. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2983–2991 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.341
Kahou, S.E., et al.: EmoNets: multimodal deep learning approaches for emotion recognition in video. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 10(2), 99–111 (2016)
Kim, D.H., Baddar, W.J., Jang, J., Ro, Y.M.: Multi-objective based spatio-temporal feature representation learning robust to expression intensity variations for facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 10, 223–236 (2019)
Li, S., Deng, W.: Deep facial expression recognition: a survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2020.2981446
Li, W., Huang, D., Li, H., Wang, Y.: Automatic 4D facial expression recognition using dynamic geometrical image network. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), pp. 24–30 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/FG.2018.00014
Lyons, M., Akamatsu, S., Kamachi, M., Gyoba, J.: Coding facial expressions with Gabor wavelets. In: Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 200–205. IEEE (1998)
Martin, C.J., Archibald, J., Ball, L., Carson, L.: Towards an affective self-service agent. In: Kudělka, M., Pokorný, J., Snášel, V., Abraham, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Intelligent Human Computer Interaction (IHCI 2011), Prague, Czech Republic, August, 2011. AISC, vol. 179, pp. 3–12. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31603-6_1
Samadiani, N., et al.: A review on automatic facial expression recognition systems assisted by multimodal sensor data. Sensors 19(8), 1863 (2019)
Topi, M., Timo, O., Matti, P., Maricor, S.: Robust texture classification by subsets of local binary patterns. In: Pattern Recognition, 2000. Proceedings. 15th International Conference on, vol. 3, pp. 935–938. IEEE (2000)
Yu, Z., Liu, Q., Liu, G.: Deeper cascaded peak-piloted network for weak expression recognition. Vis. Comput. 34(12), 1691–1699 (2018)
Zhang, K., Huang, Y., Du, Y., Wang, L.: Facial expression recognition based on deep evolutional spatial-temporal networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(9), 4193–4203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2689999
Zhao, J., Mao, X., Zhang, J.: Learning deep facial expression features from image and optical flow sequences using 3D CNN. Vis. Comput. 34(10), 1461–1475 (2018)
Zhao, X., et al.: Peak-piloted deep network for facial expression recognition. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9906, pp. 425–442. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kas, M., Ruichek, Y., EL-Merabet, Y., Messoussi, R. (2023). Dedicated Encoding-Streams Based Spatio-Temporal Framework for Dynamic Person-Independent Facial Expression Recognition. In: Christensen, H.I., Corke, P., Detry, R., Weibel, JB., Vincze, M. (eds) Computer Vision Systems. ICVS 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14253. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44137-0_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44137-0_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44136-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44137-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)