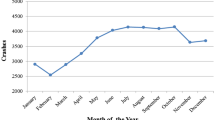
Abstract
The main objective of this paper is to analyze road accidents in Morocco. This analysis could be effective in assessing the level of road insecurity and planning appropriate countermeasures to solve specific road safety problems. The approach adopted for this analysis is based on the deployment of cross-referenced data on road traffic accidents as recorded by the Moroccan National Road Safety Agency as well as data from the Moroccan High Commission for Planning and on data from the International Transport Forum and the World Bank. These different databases were explored because they include official data for the analysis of road accidents in Morocco. The analysis shows that the distribution of road traffic deaths and injuries in Morocco varies according to gender, age, month, time and city. The 15–44 age group is the most likely to be involved in road traffic accidents in Morocco, although men face a higher number of deaths and injuries than women. In addition, road accidents are relatively more numerous in certain extreme weather conditions, during working hours and holiday periods. The Wilaya of grand casa recorded the highest number of fatality risk and mortality rate. Human behavior is the most frequent source of road accidents in Morocco. The most effective way to reduce the number of deaths and injuries would be an integrated approach involving close collaboration between many sectors and focusing on multi-factorial causes: human, vehicular and environmental factors. Taking these factors into consideration helps reducing the risk of a road accident occurrence.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Transport Forum: Road Safety Annual report 2019, irtad, road safety data
Massin, I.: la sécurité routière, 2002/3. No. 103, pp. 451–453. ISSN : 0152-7401
Gilbert, C.: When the act of driving comes down to behaving well. Réseaux, pp. 21–48 (2008)
Loimer, H., Guarnieri, M.: Accidents and acts of God: a history of the terms. Am. J. Public Health 86(1), 101–107 (1996)
Smeed, R.J.: Variations in the patterns of accident rates in different countries and their causes. Traffic Eng. Control 10, 364–371 (1968)
Weber, D.C.: Accident rate potential: An application of multiple regression analysis of a Poisson process. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 66, 285–288 (1971)
Thiran, P., THOMAS, I.: Road accidents and distance from home. a quantitative approach for Brussels. Cahiers scientifiques du transport 32, 105–120 (1997)
Mannering, F.L., Lee, J.: Analysis of roadside accident frequency and severity and roadside safety management. Washington State Transportation Center: Seattle, WA, USA (1999)
Nilsson, G.: Traffic safety dimension and the power model to describe the effect of speed on safety. Bulletin, 221, Lund Institute of Technology (2004)
Latreche, A.: Estimation of the probability of accident by the Probity model in the case of car insurance. Les Annales ROAD 15, 27–53 (2007)
Singh, S.K.: Road traffic accidents in India: issues and challenges. Transp. Res. Proc. 25, 4708–4719 (2017)
Chapelon, J.: The economic impact of road safety. Les Tribunes de la sante (4) 65–70 (2008)
World Health Organization: Global status report on road safety (2018)
Compendiums of road traffic injury statistics (2000, 2006, 2010, 2015 and 2018) published by the Ministry of Equipment, Transport, Logistics and Water of Morocco
World Bank, population data. http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/IS.VEH.NVEH.P3
Bijleveld, F., Churchill, T.: The influence of weather conditions on road safety: an assessment of precipitation and temperature, vol. 2009, no. 9 (2009)
Evans, L.: A new traffic safety vision for the United States, pp. 1384–1386 (2003)
Elvic, R., Vaa, T.: The Handbook of Road Safety Measures. Elsevier Science, Oxford (2004)
Sabine, D.: Accident data and road safety; World Road Association, Routes roads no. 335 (2007)
Guilbot, M.: Accidents de la route, infrastructure et responsabilités. Documentation Française (2008)
Zerka, A., Jawab, F.: Calculation of the costs of health care services for road accident victims in TDABC: a systematic review of the literature. In: 2020 IEEE 13th International Colloquium of Logistics and Supply Chain Management LOGISTIQUA), pp. 1–7. IEEE, December 2020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zerka, A., Jawab, F. (2022). Contribution to the Economic Analysis of Numerical Data of Road Accidents in Morocco. In: Motahhir, S., Bossoufi, B. (eds) Digital Technologies and Applications. ICDTA 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 455. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-02447-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-02447-4_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-02446-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-02447-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)