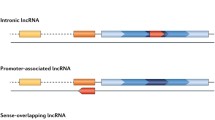
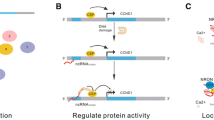
Abstract
Until somewhat recently, the complexity of the human genome has not been well understood. With advancements in sequencing technology, we now know that nearly the whole genome is transcribed but a very small portion of those transcripts code for proteins. As the research of non-coding genes and transcripts has evolved rapidly in the last decade, it has become clear that many of them serve important biological functions in many previously well-studied cell processes. As the previous chapters in this book have reviewed, the field of noncoding RNA research has provided new insights into specific disease states, especially those driven by inflammation. Understanding the basic mechanisms of non-coding RNAs in the context of inflammation has led to prospective therapeutics that may overcome many of the challenges faced in diagnosing and treating inflammatory diseases. In this final chapter we discuss the current state of the field of non-coding RNA therapeutics and how it may evolve to overcome the short cummings we currently face with diagnosing and treating inflammatory diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnig C, Bezema T, Calder PC, Charloux A, Frossard N, Garssen J, Haworth O, Dilevskaya K, Levi-Schaffer F, Lonsdorfer E, Wauben M, Kraneveld AD, te Velde AA (2019) Activation of resolution pathways to prevent and fight chronic inflammation: lessons from asthma and inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol 10:1699. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01699
Zuo L, Prather ER, Stetskiv M, Garrison DE, Meade JR, Peace TI, Zhou T (2019) Inflammaging and oxidative stress in human diseases: from molecular mechanisms to novel treatments. Int J Mol Sci 20(18):4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184472
Franceschi C, Garagnani P, Parini P, Giuliani C, Santoro A (2018) Inflammaging: a new immune–metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14(10):576–590. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0059-4
Lin T, Liu GA, Perez E, Rainer RD, Febo M, Cruz-Almeida Y, Ebner NC (2018) Systemic inflammation mediates age-related cognitive deficits. Front Aging Neurosci 10:236. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00236
Renz H, von Mutius E, Brandtzaeg P, Cookson WO, Autenrieth IB, Haller D (2011) Gene-environment interactions in chronic inflammatory disease. Nat Immunol. 12(4):273–277. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0411-273
Xue C, Zhang X, Zhang H, Ferguson JF, Wang Y, Hinkle CC, Li M, Reilly MP (2017) De novo RNA sequence assembly during in vivo inflammatory stress reveals hundreds of unannotated lincRNAs in human blood CD14+ monocytes and in adipose tissue. Physiol Genomics. 49(6):287–305
Napoli M, Li X, Ackerman HD, Deshpande AA, Barannikov I, Pisegna MA, Bedrosian I, Mitsch J, Quinlan P, Thompson A, Rajapakshe K, Coarfa C, Gunaratne PH, Marchion DC, Magliocco AM, Tsai KY, Flores ER (2020) Pan-cancer analysis reveals TAp63-regulated oncogenic lncRNAs that promote cancer progression through AKT activation. Nat Commun 11(1):5156. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18973-w
Liu SJ et al (2017) CRISPRi-based genome-scale identification of functional long noncoding RNA loci in human cells. Science 355:eaah7111
Covarrubias S et al (2017) CRISPR/Cas-based screening of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in macrophages with an NF-κB reporter. J Biol Chem 292:20911–20920
Huang Y, Gulshan K, Nguyen T, Wu Y (2017) Biomarkers of cardiovascular disease. Dis Markers 2017:1–2
Pearson TA et al (2003) Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: application to clinical and public health practice: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation 107:499–511
Li P, Zheng Y, Chen X (2017) Drugs for autoimmune inflammatory diseases: from small molecule compounds to anti-TNF biologics. Front Pharmacol 8:460
Her M, Kavanaugh A (2016) Alterations in immune function with biologic therapies for autoimmune disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137:19–27
Dugger SA, Platt A, Goldstein DB (2018) Drug development in the era of precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17:183–196
Damase TR et al (2021) The limitless future of RNA therapeutics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:628137
Everaert C et al (2019) Performance assessment of total RNA sequencing of human biofluids and extracellular vesicles. Sci Rep 9:17574
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M, Glavač D (2017) Long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers. 2017:7243968. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7243968
Yuan L et al (2020) Long non-coding RNAs towards precision medicine in gastric cancer: early diagnosis, treatment, and drug resistance. Mol Cancer 19:96
Micheletti R et al (2017) The long noncoding RNA Wisper controls cardiac fibrosis and remodeling. Sci Transl Med 9:eaai9118
Roy D, Tiirikainen M (2020) Diagnostic power of DNA methylation classifiers for early detection of cancer. Trends Cancer 6:78–81
Larson MH et al (2021) A comprehensive characterization of the cell-free transcriptome reveals tissue- and subtype-specific biomarkers for cancer detection. Nat Commun 12:2357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Halasz, H., Carpenter, S. (2022). Challenges and Future Directions for LncRNAs and Inflammation. In: Carpenter, S. (eds) Long Noncoding RNA. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1363. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92034-0_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92034-0_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92033-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92034-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)