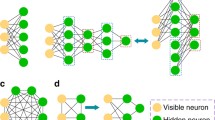
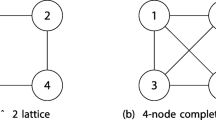
Abstract
Machine learning architectures provide a novel perspective on the study of quantum many body states. Restricted Boltzmann machines (RBM) tool is used to represent quantum many-body states in order to find connections to tensor network tools for studying quantum many-body physics, for a deeper understanding of the origin of entanglement entropy in quantum systems. Here, we seek the conditions for the optimal mapping of RBMs into Matrix Product States (MPS), with the aim to show that machine learning methods are a powerful tool for quantum state representations. We here showcase an efficient algorithm for translating RBMs into MPS, with a particular proof for Ising model. We also study the upper entropy bound condition and the entanglement properties of such mapping.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015)
Howard, E.M.: Machine learning algorithms in Astronomy. In: Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems XXV, Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems ADASS XXV, vol. 512, p. 245 (2017)
Le Roux, N., Bengio, Y.: Representational power of restricted Boltzmann machines and deep belief networks. Neural Comput. 20, 1631–1649 (2008)
Carleo, G., Troyer, M.: Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks. Science 355, 602 (2017)
Nomura, Y., Darmawan, A.S., Yamaji, Y., Imada, M.: Restricted Boltzmann machine learning for solving strongly correlated quantum systems. Phys. Rev. B 96, 205152 (2017)
Saito, H., Kato, M.: Machine learning technique to find quantum many-body ground states of bosons on a lattice. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 87, 014001 (2018)
Amico, L., Fazio, R., Osterloh, A., Vedral, V.: Entanglement in many-body systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 517 (2008)
Gao, X., Duan, L.-M.: Efficient representation of quantum many-body states with deep neural networks. Nat. Commun. 8, 662 (2017)
Vidal, G.: Class of quantum many-body states that can be efficiently simulated. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 110501 (2008)
Verstraete, F., Murg, V., Cirac, J.I.: Matrix product states, projected entangled pair states, and variational renormalization group methods for quantum spin systems. Adv. Phys. 57(2), 143–224 (2008)
Howard, E.: Holographic renormalization with machine learning arXiv:1803.11056 [physics.gen-ph] (2018)
Tagliacozzo, L., Evenbly, G., Vidal, G.: Simulation of two-dimensional quantum systems using a tree tensor network that exploits the entropic area law. Phys. Rev. B 80, 235127 (2009)
Hastings, M.B.: An area law for one-dimensional quantum systems. J. Stat. Mech. 2007, P08024 (2007)
Vidal, G., Latorre, J.I., Rico, E., Kitaev, A.: Entanglement in quantum critical phenomena. Phys. Rev. Lett 90, 227902 (2003)
Carleo, G., Nomura, Y., Imada, M.: Constructing exact representations of quantum many-body systems with deep neural networks. arXiv:1802.09558 (2018)
Chen, J., Cheng, S., Xie, H., Wang, L., Xiang, T.: Equivalence of restricted Boltzmann machines and tensor network states. Phys. Rev. B 97, 085104 (2018)
Bottou, L.: Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computational Statistics, pp. 177–187 (2010)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.L.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Eisert, J., Cramer, M., Plenio, M.B.: Colloquium: area laws for the entanglement entropy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 277 (2010)
McCulloch, I.P.: Infinite size density matrix renormalization group, revisited, arXiv:0804.2509 (2008)
Vidal, G.: Efficient simulation of one-dimensional quantum many-body systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(4), 040502 (2004)
Jastrow, R.: Many-Body Problem with Strong Forces. Phys. Rev. 98(5), 1479–1484 (1955)
Gutzwiller, M.C.: Correlation of electrons in a narrow \(s\) band. Phys. Rev. 137(6A), A1726–A1735 (1965)
Huang, Y., Moore, J.E.: Neural network representation of tensor network and chiral states arXiv:1701.06246 (2017)
Clark, S.R.: Unifying neural-network quantum states and correlator product states via tensor networks. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 51, 135301 (2018)
Bottou, L., Curtis, F.E., Nocedal, J.: Optimization methods for large-scale machine learning. Siam Rev. 60(2), 223–311 (2018)
Carrasquilla, J., Melko, R.G.: Machine learning phases of matter. Nat. Phys. 13, 431–434 (2017)
Wang, L.: Discovering phase transitions with unsupervised learning. Phys. Rev. B 94, 195105 (2016)
Deng, D.-L., Li, X., Sarma, S.D.: Quantum entanglement in neural network states. Phys. Rev. X 7, 021021 (2017)
Deng, D.-L., Li, X., Sarma, S.D.: Machine learning topological states. Phys. Rev. B 96, 195145 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Howard, E., Chowdhury, I.S., Nagle, I. (2021). Matrix Product State Representations for Machine Learning. In: Silhavy, R. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Intelligent Systems. CSOC 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 229. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77445-5_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77445-5_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-77444-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-77445-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)