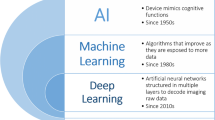
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence applications have recently demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy and increased workflow efficiency in radiology. Machine learning models, particularly deep learning, can perform complex tasks in medical imaging, especially when they are trained with a large amount of high-quality data. For effective realization of the potential of artificial intelligence in interventional radiology, some unique challenges involving data storage, interoperability, adoption of standards, and conflict of interest between physicians and developers need to be addressed. With immense innovation and technological breakthrough, the scope of interventional radiology is continuously increasing in both width and breadth, and so are the opportunities of AI to revolutionize the sector. Artificial intelligence can complement the efforts of the interventional radiologist through decision support, triaging and screening of patients, prevention of error, procedural and periprocedural support, patient monitoring, prognostication of diseases, outcome prediction, image acquisition, image processing, etc. In conjunction with augmented reality systems, it can also help in improving procedural skills of interventional radiology residents and fellows through superior simulation training. Artificial intelligence has a tremendous potential to boost the productivity of radiologists. However, they are unlikely to replace them as there are significant apprehensions regarding the legal accountability, transparency, fairness, equality, bias, or potential misuse by an artificial intelligence system which prevent any independent action or clinical application without the oversight of an expert radiologist.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seldinger SI. Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous arteriography; a new technique. Acta Radiol. 1953;39(5):368–76.
Baum RA, Baum S. Interventional radiology: a half century of innovation. Radiology. 2014;273(2S):S75–91.
Taslakian B, Georges Sebaaly M, Al-Kutoubi A. Patient evaluation and preparation in vascular and interventional radiology: what every interventional radiologist should know (Part 1: Patient assessment and laboratory tests). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2016;39(3):325–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1228-7.
Hosny A, Parmar C, Quackenbush J, Schwartz LH, Aerts HJWL. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(8):500–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0016-5.
Meskó B, Görög M. A short guide for medical professionals in the era of artificial intelligence. npj Digit Med. 2020;3:126.
Yadav SS, Jadhav SM. Deep convolutional neural network based medical image classification for disease diagnosis. J Big Data. 2019;6:113.
Morris MA, Saboury B, Burkett B, Gao J, Siegel EL. Reinventing radiology: big data and the future of medical imaging. J Thorac Imaging. 2018;33(1):4–16.
Persons KR, Nagels J, Carr C, Mendelson DS, Fischer B, Doyle M. Interoperability and considerations for standards-based exchange of medical images: HIMSS-SIIM Collaborative white paper. J Digit Imaging. 2020;33(1):6–16.
Oren O, Gersh BJ, Bhatt DL. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging: switching from radiographic pathological data to clinically meaningful endpoints. Lancet Digit Health. 2020;2(9):e486–8.
Lee LI, Kanthasamy S, Ayyalaraju RS, Ganatra R. The current state of artificial intelligence in medical imaging and nuclear medicine. BJR| Open. 2019;1:20190037.
Choy G, Khalilzadeh O, Michalski M, Do S, Samir AE, Pianykh OS, Geis JR, Pandharipande PV, Brink JA, Dreyer KJ. Current applications and future impact of machine learning in radiology. Radiology. 2018;288(2):318–28.
Meek RD, Lungren MP, Gichoya JW. Machine learning for the interventional radiologist. Am J Roentgenol. 2019;213(4):782–4.
Kaufman JA, Lee MJ. Vascular and interventional radiology: the requisites e-book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013.
Baerlocher MO, Kennedy SA, Ward TJ, Nikolic B, Bakal CW, Lewis CA, Winick AB, Niedzwiecki GA, Haskal ZJ, Matsumoto AH. Society of interventional radiology: resource and environment recommended standards for IR. J Vasc Interven Radiol: JVIR. 2017;28(4):513.
Taslakian B, Ingber R, Aaltonen E, Horn J, Hickey R. Interventional radiology suite: a primer for trainees. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):1347.
Annarumma M, Withey SJ, Bakewell RJ, Pesce E, Goh V, Montana G. Automated triaging of adult chest radiographs with deep artificial neural networks. Radiology. 2019;291(1):196–202.
Mafeld S, Musing EL, Conway A, Kennedy S, Oreopoulos G, Rajan D. Avoiding and managing error in interventional radiology practice: tips and tools. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2020;71:528–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0846537119899215.
Mafeld S, Oreopoulos G, Musing EL, Chan T, Jaberi A, Rajan D. Sources of error in interventional radiology: how, why, and when. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2020;71:518–27. https://doi.org/10.1177/0846537119899226.
Hashimoto DA, Rosman G, Rus D, Meireles OR. Artificial intelligence in surgery: promises and perils. Ann Surg. 2018;268(1):70.
Flin R, Youngson G, Yule S. How do surgeons make intraoperative decisions? BMJ Qual Saf. 2007;16(3):235–9.
Navarrete-Welton AJ, Hashimoto DA. Current applications of artificial intelligence for intraoperative decision support in surgery. Front Med. 2020;14:369–81.
Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, Dong Y, Li H, Ma S, Wang Y, Dong Q, Shen H, Wang Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2017;2(4):230–43.
McCollough CH, Leng S. Use of artificial intelligence in computed tomography dose optimisation. Ann ICRP. 2020;49:113–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146645320940827.
Blanco Sequeiros R, Ojala R, Kariniemi J, Perälä J, Niinimäki J, Reinikainen H, Tervonen O. MR-guided interventional procedures: a review. Acta Radiol. 2005;46(6):576–86.
Johnson PM, Recht MP, Knoll F. Improving the speed of MRI with artificial intelligence. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2020;24(1):12. NIH Public Access.
Mirchi N, Bissonnette V, Yilmaz R, Ledwos N, Winkler-Schwartz A, Del Maestro RF. The virtual operative assistant: an explainable artificial intelligence tool for simulation-based training in surgery and medicine. PLoS One. 2020;15(2):e0229596.
Chander Mohan SM. Artificial intelligence in radiology–are we treating the image or the patient? Indian J Radiol Imag. 2018;28(2):137.
Geis JR, Brady AP, Wu CC, Spencer J, Ranschaert E, Jaremko JL, Langer SG, Kitts AB, Birch J, Shields WF, van den Hoven van Genderen R. Ethics of artificial intelligence in radiology: summary of the joint European and North American multisociety statement. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2019;70(4):329–34.
European Society of Radiology (ESR). Impact of artificial intelligence on radiology: a EuroAIM survey among members of the European Society of Radiology. Insights Imag. 2019;10(1):105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Datta, S. (2022). AIM in Interventional Radiology. In: Lidströmer, N., Ashrafian, H. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64573-1_283
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64573-1_283
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-64572-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-64573-1
eBook Packages: MedicineReference Module Medicine