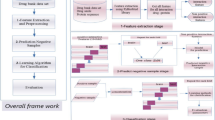
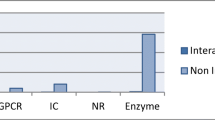
Abstract
Drug target interaction is one of the most significant fields of research for drug discovery. The laboratory experiments conducted to identify the drug target interactions are tedious, delayed, and costly. Hence, there is an urgent need to develop highly efficient computational methods for identifying potential drug target interactions that can limit the search space of these laboratory experiments. The existing computational techniques for drug target interaction have been broadly classified into similarity-based methods and feature-based methods. In this paper, a novel feature-based technique to predict drug target interactions has been proposed. The technique uses ensemble learning to determine drug target interactions. Ensemble learning offers greater accuracy in comparison with the traditional classifiers. Thus, the proposed technique aims to improve accuracy using ensemble learning. Also, dimensionality reduction of drug target features is performed using principal component analysis so that the computational time of the method can be reduced. The results indicate an improved performance in comparison with the state-of-the-art methods in the field.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, X., et al.: Drug–target interaction prediction: databases, web servers and computational models. Briefings Bioinf. 17(4), 696–712 (2016)
Paul, S.M., et al.: How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 9(3), 203 (2010)
Ezzat, A., et al.: Computational prediction of drug-target interactions using chemogenomic approaches: an empirical survey. Briefings Bioinf. bby002–bby002 (2018)
Cheng, F., et al.: Prediction of drug-target interactions and drug repositioning via network-based inference. PLoS. Comput. Biol. 8(5), e1002503 (2012)
Emig, D., et al.: Drug target prediction and repositioning using an integrated network-based approach. PLoS. One. 8(4), e60618 (2013)
Jin, G., Wong, S.T.: Toward better drug repositioning: prioritizing and integrating existing methods into efficient pipelines. Drug Discov. Today 19(5), 637–644 (2014)
Atias, N., Sharan, R.: An algorithmic framework for predicting side-effects of drugs. In: Annual International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology. Springer (2010)
Pauwels, E., Stoven, V., Yamanishi, Y.: Predicting drug side-effect profiles: a chemical fragment-based approach. BMC Bioinf. 12(1), 169 (2011)
Yamanishi, Y., Pauwels, E., Kotera, M.: Drug side-effect prediction based on the integration of chemical and biological spaces. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 52(12), 3284–3292 (2012)
Bolton, E.E., et al.: PubChem: integrated platform of small molecules and biological activities. In: Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry, pp. 217–241. Elsevier (2008)
Jacob, L., Vert, J.-P.: Protein-ligand interaction prediction: an improved chemogenomics approach. Bioinformatics 24(19), 2149–2156 (2008)
Li, H., et al.: TarFisDock: a web server for identifying drug targets with docking approach. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 34(suppl_2), W219-W224 (2006)
Xie, L., et al.: Drug discovery using chemical systems biology: weak inhibition of multiple kinases may contribute to the anti-cancer effect of nelfinavir. PLoS. Comput. Biol. 7(4), e1002037 (2011)
Mousavian, Z., Masoudi-Nejad, A.: Drug–target interaction prediction via chemogenomic space: learning-based methods. Expert. Opin. Drug. Metabol. Toxicol. 10(9), 1273–1287 (2014)
van Laarhoven, T., Nabuurs, S.B., Marchiori, E.: Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug–target interaction. Bioinformatics 27(21), 3036–3043 (2011)
Bleakley, K., Yamanishi, Y.: Supervised prediction of drug–target interactions using bipartite local models. Bioinformatics. 25(18), 2397–2403 (2009)
Zheng, X., et al.: Collaborative matrix factorization with multiple similarities for predicting drug-target interactions. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, ACM (2013)
Gönen, M.: Predicting drug–target interactions from chemical and genomic kernels using Bayesian matrix factorization. Bioinformatics 28(18), 2304–2310 (2012)
Wang, W., Yang, S., Li, J.: Drug target predictions based on heterogeneous graph inference. In: Biocomputing, pp. 53–64. World Scientific (2013)
Tabei, Y., Yamanishi, Y.: Scalable prediction of compound-protein interactions using minwise hashing. BMC. Syst. Biol. 7(6), S3 (2013)
Mei, J.-P., et al.: Drug–target interaction prediction by learning from local information and neighbors. Bioinformatics 29(2), 238–245 (2012)
Nagamine, N., Sakakibara, Y.: Statistical prediction of protein–chemical interactions based on chemical structure and mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics 23(15), 2004–2012 (2007)
He, Z., et al.: Predicting drug-target interaction networks based on functional groups and biological features. PloS. one. 5(3), e9603 (2010)
Perlman, L., et al.: Combining drug and gene similarity measures for drug-target elucidation. J. Comput. Biol. 18(2), 133–145 (2011)
Yamanishi, Y., et al.: Prediction of drug–target interaction networks from the integration of chemical and genomic spaces. Bioinformatics 24(13), i232–i240 (2008)
Safavian, S.R., Landgrebe, D.: A survey of decision tree classifier methodology. IEEE. Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 21(3), 660–674 (1991)
Cristianini, N., Taylor, J.: Support vector machines and other Kernel-based learning algorithms. Technical Report (2000)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., Geladi, P.: Principal component analysis. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2(1–3), 37–52 (1987)
Dietterich, T.G.: Ensemble methods in machine learning. In: International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems. Springer (2000)
Cao, D.-S., et al.: Rcpi: R/Bioconductor package to generate various descriptors of proteins, compounds and their interactions. Bioinformatics 31(2), 279–281 (2014)
Li, Z.-R., et al.: PROFEAT: a web server for computing structural and physicochemical features of proteins and peptides from amino acid sequence. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 34(suppl_2), W32–W37 (2006)
Dietterichl, T.G.: Ensemble learning (2002)
Law, V., et al.: Drugbank 4.0: shedding new light on drug metabolism. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 42(D1), D1091–D1097 (2013)
Fawcett, T.: An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern. Recogn. Lett. 27(8), 861–874 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sachdev, K., Gupta, M.K. (2020). Predicting Drug Target Interactions Using Dimensionality Reduction with Ensemble Learning. In: Singh, P., Kar, A., Singh, Y., Kolekar, M., Tanwar, S. (eds) Proceedings of ICRIC 2019 . Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 597. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29407-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29407-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-29406-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-29407-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)