Abstract
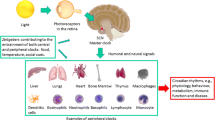
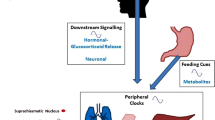
Chronobiology describes the biologic variations of organ systems based on circadian rhythm. The chronobiology of allergic diseases, including asthma and allergic rhinitis, often drives worsening symptoms in the early morning hours. Because of this, much study has gone into the appropriate timing of administration of medications to treat these symptoms when at their worst. However, further work is needed to improve chronotherapy to treat allergic disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin RJ. Chronotherapy of asthma: how to use standard medications for better results. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;15(2):128–35. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1006355.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2015 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) Data. https://www.cdc.gov/asthma/nhis/2015/table3-1.htm. 2017.
Kraft M, Martin RJ. Chronobiology and chronotherapy in medicine. Dis Mon DM. 1995;41(8):506–75.
Hetzel MR, Clark TJ, Branthwaite MA. Asthma: analysis of sudden deaths and ventilatory arrests in hospital. Br Med J. 1977;1(6064):808–11.
Jalaludin BB, Smith MA, Chey T, Orr NJ, Smith WT, Leeder SR. Risk factors for asthma deaths: a population-based, case-control study. Aust N Z J Public Health. 1999;23(6):595–600.
Smolensky MH, Lemmer B, Reinberg AE. Chronobiology and chronotherapy of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59(9–10):852–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.08.016.
Ballard RD, Saathoff MC, Patel DK, Kelly PL, Martin RJ. Effect of sleep on nocturnal bronchoconstriction and ventilatory patterns in asthmatics. J Appl Physiol. 1989;67(1):243–9.
Gervais P, Reinberg A, Gervais C, Smolensky M, DeFrance O. Twenty-four-hour rhythm in the bronchial hyperreactivity to house dust in asthmatics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977;59(3):207–13.
Mohiuddin AA, Martin RJ. Circadian basis of the late asthmatic response. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142(5):1153–7. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1153.
Martin RJ, Cicutto LC, Smith HR, Ballard RD, Szefler SJ. Airways inflammation in nocturnal asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;143(2):351–7. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/143.2.351.
Barnes P, FitzGerald G, Brown M, Dollery C. Nocturnal asthma and changes in circulating epinephrine, histamine, and cortisol. N Engl J Med. 1980;303(5):263–7. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198007313030506.
Postma DS, Keyzer JJ, Koeter GH, Sluiter HJ, De Vries K. Influence of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system on nocturnal bronchial obstruction. Clin Sci. 1985;69(3):251–8.
Beam WR, Weiner DE, Martin RJ. Timing of prednisone and alterations of airways inflammation in nocturnal asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146(6):1524–30. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/146.6.1524.
Pincus DJ, Humeston TR, Martin RJ. Further studies on the chronotherapy of asthma with inhaled steroids: the effect of dosage timing on drug efficacy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;100(6 Pt 1):771–4.
Gagnon M, Cote J, Milot J, Turcotte H, Boulet LP. Comparative safety and efficacy of single or twice daily administration of inhaled beclomethasone in moderate asthma. Chest. 1994;105(6):1732–7.
Noonan M, Karpel JP, Bensch GW, Ramsdell JW, Webb DR, Nolop KB, Lutsky BN. Comparison of once-daily to twice-daily treatment with mometasone furoate dry powder inhaler. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;86(1):36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62353-8.
Fitzpatrick MF, Mackay T, Driver H, Douglas NJ. Salmeterol in nocturnal asthma: a double blind, placebo controlled trial of a long acting inhaled beta 2 agonist. BMJ. 1990;301(6765):1365–8.
Faurschou P, Engel AM, Haanaes OC. Salmeterol in two different doses in the treatment of nocturnal bronchial asthma poorly controlled by other therapies. Allergy. 1994;49(10):827–32.
Martin RJ, Cicutto LC, Ballard RD, Goldenheim PD, Cherniack RM. Circadian variations in theophylline concentrations and the treatment of nocturnal asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;139(2):475–8. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.475.
Morrison JF, Pearson SB, Dean HG. Parasympathetic nervous system in nocturnal asthma. Br Med J. 1988;296(6634):1427–9.
O’Connor BJ, Towse LJ, Barnes PJ. Prolonged effect of tiotropium bromide on methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154(4 Pt 1):876–80. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.154.4.8887578.
Calverley PM, Lee A, Towse L, van Noord J, Witek TJ, Kelsen S. Effect of tiotropium bromide on circadian variation in airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2003;58(10):855–60.
Noonan MJ, Chervinsky P, Brandon M, Zhang J, Kundu S, McBurney J, Reiss TF. Montelukast, a potent leukotriene receptor antagonist, causes dose-related improvements in chronic asthma. Montelukast Asthma Study Group. Eur Respir J. 1998;11(6):1232–9.
Sewlall S, Pillay V, Danckwerts MP, Choonara YE, Ndesendo VM, du Toit LC. A timely review of state-of-the-art chronopharmaceuticals synchronized with biological rhythms. Curr Drug Deliv. 2010;7(5):370–88.
Nicholson PA, Bogie W. Diurnal variation in the symptoms of hay fever: implications for pharmaceutical development. Curr Med Res Opin. 1973;1(7):395–400. https://doi.org/10.1185/03007997309111700.
Storms WW. Pharmacologic approaches to daytime and nighttime symptoms of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(5 Suppl):S146–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.08.045.
Nayak AS, Philip G, Lu S, Malice MP, Reiss TF. Efficacy and tolerability of montelukast alone or in combination with loratadine in seasonal allergic rhinitis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial performed in the fall. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002;88(6):592–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61891-1.
Lavery MJ, Stull C, Kinney MO, Yosipovitch G. Nocturnal pruritus: the battle for a peaceful night’s sleep. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(3):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030425.
Furuta GT, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(17):1640–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1502863.
Gerson LB, Fass R. A systematic review of the definitions, prevalence, and response to treatment of nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(4):372–8; quiz 367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2008.11.021.
Kumar D, Wingate D, Ruckebusch Y. Circadian variation in the propagation velocity of the migrating motor complex. Gastroenterology. 1986;91(4):926–30.
Hatlebakk JG, Katz PO, Kuo B, Castell DO. Nocturnal gastric acidity and acid breakthrough on different regimens of omeprazole 40 mg daily. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998;12(12):1235–40.
Moore JG, Halberg F. Circadian rhythm of gastric acid secretion in men with active duodenal ulcer. Dig Dis Sci. 1986;31(11):1185–91.
Hetzel MR, Clark TJ. Comparison of normal and asthmatic circadian rhythms in peak expiratory flow rate. Thorax. 1980;35(10):732–8.
Bagg LR, Hughes DT. Diurnal variation in peak expiratory flow in asthmatics. Eur J Respir Dis. 1980;61(5):298–302.
Clark TJ, Hetzel MR. Diurnal variation of asthma. Br J Dis Chest. 1977;71(2):87–92.
Lee RE, Smolensky MH, Leach CS, McGovern JP. Circadian rhythms in the cutaneous reactivity to histamine and selected antigens, including phase relationship to urinary cortisol excretion. Ann Allergy. 1977;38(4):231–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Manka, L.A., Martin, R.J. (2019). Chronotherapy. In: Fishbein, A., Sheldon, S. (eds) Allergy and Sleep. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14738-9_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14738-9_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-14737-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-14738-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)