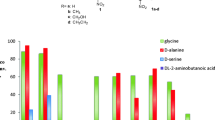
Abstract
Aminotransferases are key enzymes of the metabolism of proteinogenic amino acids. These ubiquitous biocatalysts show high specific activities and relaxed substrate specificities making them valuable tools for the stereoselective synthesis of unnatural amino acids. We describe here the application of aspartate aminotransferase and branched chain aminotransferase from E. coli for the synthesis of various glutamate analogues, molecules of particular interest regarding the neuroactive properties of glutamic acid.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, B Y et al. (2005) Revisit of aminotransferase in the genomic era and its application to biocatalysis. J Mol Cat B, Enzymatic 37, 47–55.
Ager, D J et al. (2001) Novel biosynthetic routes to non-proteinogenic amino acids as chiral pharmaceutical intermediates. J Mol Cat B, Enzymatic 11, 199–205.
Yun, H et al. (2004) Kinetic resolution of (R, S)-sec-butylamine using omega-transaminase from Vibrio fluvialis JS17 under reduced pressure. Biotechnol Bioeng 87, 772–778.
Shin, J S, Kim B G (2001) Comparison of the omega-transaminases from different microorganisms and application to production of chiral amines. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65, 1782–1788.
Iwasaki, A et al. (2003) Microbial synthesis of (R)- and (S)-3,4-dimethoxyamphetamines through stereoselective transamination. Biotechnol Lett 25, 1843–1846.
Yun, H et al. (2004) ω-Amino acid: pyruvate transaminase from Alcaligenes denitrificans Y2k-2: a new catalyst for kinetic resolution of β-amino acids and amines. Appl Environ Microbiol 70, 2529–2534.
Alaux, S et al. (2005) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of a series of 4-substituted glutamate analogues and pharmacological characterization at human glutamate transporters subtypes 1–3. J Med Chem 48, 7980–7992.
Sagot, E et al. (2008) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of (2S,4R)-2-amino-4-(3-(2,2-diphe-nylethylamino)-3-oxopropyl)pentanedioic acid: a novel selective inhibitor of human excitatory amino acid transporter subtype 2. J Med Chem 51, 4085–4092.
Sagot, E et al. (2008) Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of a series of 2,4-syn-functionalized (S)-glutamate analogues: new insight into the structure-activity relation of ionotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 5, 6, and 7. J Med Chem 51, 4093–4103.
Xian, M et al. (2007) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of glutamic acid analogues: substrate specificity and synthetic applications of branched chain aminotransferase from Escherichia coli. J Org Chem 72, 7560–7566.
Kamitori, S. et al. (1987) Overproduction and preliminary X-Ray characterization of Asparatate aminotransferase from Escherichia coli. J Biochem 101, 813–816.
Kagamiyama, H, Hayashi, H (2000) Branched-chain amino-acid aminotransferase of Escherichia coli. Meth Enzymol 324, 103–113.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS). We are grateful to Kagamiyama’s group (Osaka Medical College) for providing us with the AspAT and BCAT overexpressing E. coli strains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Gefflaut, T., Assaf, Z., Sancelme, M. (2012). Preparation of Glutamate Analogues by Enzymatic Transamination. In: Pollegioni, L., Servi, S. (eds) Unnatural Amino Acids. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 794. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-331-8_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-331-8_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-330-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-331-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols