Abstract
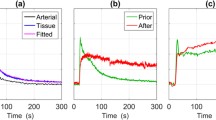
The blood–nerve barrier (BNB) separates the endoneurium from the endovascular space and the epineurial connective tissue. An intact BNB is very important for integrity and functions of the nerve fibers within the endoneurial space. Disruption of the BNB which leads to functional and structural impairment of the peripheral nerve plays an important role in many disorders of the peripheral nerve like Wallerian degeneration, inflammatory nerve disorders, and demyelination. So far, this increased BNB permeability can only be assessed ex vivo. Assessing BNB disruption in vivo would be of great value for studying disorders of the peripheral nervous system. Gadofluorine M (Gf), a new amphiphilic contrast agent for MRI, accumulates in rat nerves with increased permeability of the BNB. After application of Gf, T1-weighted MR images show contrast enhancement of nerves with a disrupted BNB. This new tool of assessing BNB permeability in vivo is described.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi YK, K-W Kim (2008) Blood-neural barrier: its diversity and coordinated cell-to-cell communication. BMB Rep 41:345–352
Seitz RJ, Reiners K, Himmelmann F, Heininger K, Hartung H-P, Toyka KV (1989) The blood-nerve barrier in Wallerian degeneration: a sequential long-term study. Muscle Nerve 12:627–635
Harvey GK, Gold R, Hartung H-P, Toyka KV (1995) Non-neural specific T lymphocytes can orchestrate inflammatory peripheral neuropathy. Brain 118:1263–1272
Hahn AF (1996) Experimental allergic neuritis as a model for the immune-mediated demyelinating neuropathies. Rev Neurol (Paris) 152:328–332
Stoll G, Jander S, Myers RR (2002) Degeneration and regeneration in the peripheral nervous system: from Augustus Waller’s observations to neuroinflammation. J Peripher Nerv Syst 7:13–27
Kristensson K, Olsson Y (1971) The perineurium as a diffusion barrier to protein tracers. Acta Neuropathol 17:127–138
Bendszus M, Wessig C, Solymosi L, Reiners K, Koltzenburg M (2004) MRI of peripheral nerve degeneration and regeneration: correlation with electrophysiology and histology. Exp Neurol 188:171–177
Peled S, Cory DG, Raymond SA, Kirschner DA, Jolesz FA (1999) Water diffusion, T(2), and compartmentation in frog sciatic nerve. Magn Reson Med 42:911–918
Cudlip SA, Howe FA, Griffiths JR, Bell BA (2002) Magnetic resonance neurography of peripheral nerve following experimental crush injury, and correlation with functional deficit. J Neurosurg 96:755–775
Lacour-Petit MC, Lozeron P, Ducreux D (2003) MRI of peripheral nerve lesions of the lower limbs. Neuroradiology 45:166–170
Bendszus M, Wessig C, Schütz A, Horn T, Kleinschnitz C, Sommer C, Misselwitz B, Stoll G (2005) Assessment of nerve degeneration by gadofluorine M-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 57: 388–395
Wessig C, Bendszus M, Stoll G (2007) In vivo visualization of focal demyelination in peripheral nerves by gadofluorine M-enhanced magentic resonance imaging. Exp Neurol 204:14–19
Wessig C, Jestaedt L, Sereda MW, Bendszus M, Stoll G (2008) Gadofluorine M-enhanced magnetic resonance nerve imaging: comparison between acute inflammatory and chronic degenerative demyelination in rats. Exp Neurol 210:137–143
Meding J, Ulrich M, Licha K, Reinhardt M, Misselwitz B, Fayad ZA, Weinmann HJ (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerosis by targeting extracellular matrix deposition with Gadofluorine M. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2:120–129
Acknowledgments
Gf was kindly provided by B. Misselwitz, Bayer-Schering Pharma AG, Berlin, Germany. Studies were supported by the Interdisziplinäre Zentrum für Klinische Forschung, University of Würzburg and the Gemeinnützige Hertie-Stiftung, Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Major contributors to all studies are Guido Stoll, Würzburg, and Martin Bendszus, Heidelberg. Excellent technical assistance was provided by Melanie Glaser, Gabi Köllner, and Virgil Michels.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Wessig, C. (2011). Detection of Blood–Nerve Barrier Permeability by Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In: Nag, S. (eds) The Blood-Brain and Other Neural Barriers. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 686. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-938-3_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-938-3_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-937-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-938-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols