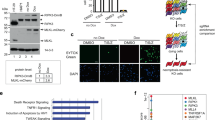
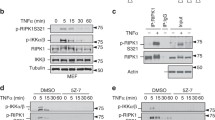
Abstract
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) is a component of the TNFR1 signaling complex (also known as complex I or TNFR-SC), where its ubiquitylation by cIAP1/2 and LUBAC serves to initiate prosurvival and proinflammatory responses through activation of the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. IKKα/β-mediated phosphorylation of RIPK1 in complex I was shown to maintain RIPK1 in a prosurvival modus. Consequently, conditions affecting proper IKKα/β activation perturb IKKα/β-phosphorylation of RIPK1 and switch the TNF response toward RIPK1 kinase-dependent cell death. Methods to study the posttranslational modifications of RIPK1 in complex I are therefore of great value. Here, we describe a detailed protocol to isolate complex I-associated RIPK1 from cells and provide different tools to study the phosphorylation status of RIPK1 in TNFR1 complex I.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger SB, Kasparcova V, Hoffman S, Swift B, Dare L, Schaeffer M, Capriotti C, Cook M, Finger J, Hughes-Earle A, Harris PA, Kaiser WJ, Mocarski ES, Bertin J, Gough PJ (2014) Cutting edge: RIP1 kinase activity is dispensable for normal development but is a key regulator of inflammation in SHARPIN-deficient mice. J Immunol 192(12):5476–5480. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1400499
Dondelinger Y, Jouan-Lanhouet S, Divert T, Theatre E, Bertin J, Gough PJ, Giansanti P, Heck AJ, Dejardin E, Vandenabeele P, Bertrand MJ (2015) NF-kappaB-independent role of IKKalpha/IKKbeta in preventing RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptotic and necroptotic cell death during TNF signaling. Mol Cell 60(1):63–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.032
Vlantis K, Wullaert A, Polykratis A, Kondylis V, Dannappel M, Schwarzer R, Welz P, Corona T, Walczak H, Weih F, Klein U, Kelliher M, Pasparakis M (2016) NEMO prevents RIP kinase 1-mediated epithelial cell death and chronic intestinal inflammation by NF-kappaB-dependent and -independent functions. Immunity 44(3):553–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.020
Newton K, Wickliffe KE, Maltzman A, Dugger DL, Strasser A, Pham VC, Lill JR, Roose-Girma M, Warming S, Solon M, Ngu H, Webster JD, Dixit VM (2016) RIPK1 inhibits ZBP1-driven necroptosis during development. Nature 540(7631):129–133. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20559
Ting AT, Bertrand MJ (2016) More to life than NF-kappaB in TNFR1 signaling. Trends Immunol 37(8):535–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2016.06.002
Brenner D, Blaser H, Mak TW (2015) Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: live or let die. Nat Rev Immunol 15(6):362–374. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3834
Kanayama A, Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Hong M, Shaito A, Chiu YH, Deng L, Chen ZJ (2004) TAB2 and TAB3 activate the NF-kappaB pathway through binding to polyubiquitin chains. Mol Cell 15(4):535–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.008
Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ (2006) Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol Cell 22(2):245–257
Bertrand MJ, Milutinovic S, Dickson KM, Ho WC, Boudreault A, Durkin J, Gillard JW, Jaquith JB, Morris SJ, Barker PA (2008) cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate Cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol Cell 30(6):689–700
Varfolomeev E, Goncharov T, Fedorova AV, Dynek JN, Zobel K, Deshayes K, Fairbrother WJ, Vucic D (2008) c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 are critical mediators of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha)-induced NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 283(36):24295–24299. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C800128200
Haas TL, Emmerich CH, Gerlach B, Schmukle AC, Cordier SM, Rieser E, Feltham R, Vince J, Warnken U, Wenger T, Koschny R, Komander D, Silke J, Walczak H (2009) Recruitment of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex stabilizes the TNF-R1 signaling complex and is required for TNF-mediated gene induction. Mol Cell 36(5):831–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.10.013
Gerlach B, Cordier SM, Schmukle AC, Emmerich CH, Rieser E, Haas TL, Webb AI, Rickard JA, Anderton H, Wong WW, Nachbur U, Gangoda L, Warnken U, Purcell AW, Silke J, Walczak H (2011) Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling. Nature 471(7340):591–596. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09816
Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH, Mrad RL, Plenchette S, Simard C, Enwere E, Arora V, Mak TW, Lacasse EC, Waring J, Korneluk RG (2008) Both cIAP1 and cIAP2 regulate TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(33):11778–11783. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711122105
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM (1996) Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Science 274(5288):787–789
Wang L, Du F, Wang X (2008) TNF-alpha induces two distinct caspase-8 activation pathways. Cell 133(4):693–703
O'Donnell MA, Legarda-Addison D, Skountzos P, Yeh WC, Ting AT (2007) Ubiquitination of RIP1 regulates an NF-kappaB-independent cell-death switch in TNF signaling. Curr Biol 17(5):418–424
Legarda-Addison D, Hase H, O'Donnell MA, Ting AT (2009) NEMO/IKKgamma regulates an early NF-kappaB-independent cell-death checkpoint during TNF signaling. Cell Death Differ 16(9):1279–1288. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.41
Dondelinger Y, Aguileta MA, Goossens V, Dubuisson C, Grootjans S, Dejardin E, Vandenabeele P, Bertrand MJ (2013) RIPK3 contributes to TNFR1-mediated RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis in conditions of cIAP1/2 depletion or TAK1 kinase inhibition. Cell Death Differ 20(10):1381–1392. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.94
Wilson NS, Dixit V, Ashkenazi A (2009) Death receptor signal transducers: nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat Immunol 10(4):348–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1714
O'Donnell MA, Hase H, Legarda D, Ting AT (2012) NEMO inhibits programmed necrosis in an NFkappaB-independent manner by restraining RIP1. PLoS One 7(7):e41238. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041238
Hospenthal MK, Mevissen TET, Komander D (2015) Deubiquitinase-based analysis of ubiquitin chain architecture using ubiquitin chain restriction (UbiCRest). Nat Protoc 10(2):349–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Priem, D., Dondelinger, Y., Bertrand, M.J.M. (2018). Monitoring RIPK1 Phosphorylation in the TNFR1 Signaling Complex. In: Ting, A. (eds) Programmed Necrosis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1857. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8754-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8754-2_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-8753-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-8754-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols