Abstract
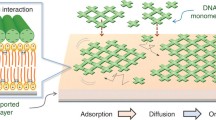
RNA architectonics offers the possibility to design and assemble RNA into specific shapes, such as nanoscale 3D solids or nanogrids. Combining the minute size of these programmable shapes with precise positioning on a surface further enhances their potential as building blocks in nanotechnology and nanomedicine. Here we describe a bottom-up approach to direct the arrangement of nucleic acid nanostructures by using a supported fluid lipid bilayer as a surface scaffold. The strong attractive electrostatic interactions between RNA polyanions and cationic lipids promote RNA adsorption and self-assembly. Protocol steps for the characterization of assembled RNA complexes via several complementary methods (QCM-D, ellipsometry, confocal fluorescence microscopy, AFM) are also provided. Due to their tunable nature, lipid bilayers can be used to organize RNA laterally on the micrometer scale and thus facilitate the building of more complex 3D structures. The bilayer-based approach can be extended to other programmable RNA or DNA objects to construct intricate structures, such as 2D grids or 3D cages, with high precision.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Severcan I, Geary C, Chworos A et al (2010) A polyhedron made of tRNAs. Nat Chem 2:772–779. doi:10.1038/nchem.733
K a A, Bindewald E, Yaghoubian AJ et al (2010) In vitro assembly of cubic RNA-based scaffolds designed in silico. Nat Nanotechnol 5:676–682. doi:10.1038/nnano.2010.160
Nasalean L, Baudrey S, Leontis NB, Jaeger L (2006) Controlling RNA self-assembly to form filaments. Nucleic Acids Res 34:1381–1392. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl008
Geary C, Chworos A, Jaeger L (2011) Promoting RNA helical stacking via A-minor junctions. Nucleic Acids Res 39:1066–1080. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq748
Severcan I, Geary C, Verzemnieks E et al (2009) Square-shaped RNA particles from different RNA folds. Nano Lett 9:1270–1277. doi:10.1021/nl900261h
Grabow WW, Zakrevsky P, Afonin KA et al (2011) Self-assembling RNA nanorings based on RNAI/II inverse kissing complexes. Nano Lett 11:878–887. doi:10.1021/nl104271s
Chworos A, Severcan I, Koyfman AY et al (2004) Building programmable jigsaw puzzles with RNA. Science 306:2068–2072. doi:10.1126/science.1104686
Alivisatos AP, Johnsson KP, Peng X et al (1996) Organization of “nanocrystal molecules” using DNA. Nature 382:609–611. doi:10.1038/382609a0
Mirkin C, Letsinger RL, Mucic RC, Storhoff JJ (1996) A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature 382:607–609
Aldaye FA, Sleiman HF (2007) Dynamic DNA templates for discrete gold nanoparticle assemblies: control of geometry, modularity, write/erase and structural switching. J Am Chem Soc 129:4130–4131. doi:10.1021/ja070017i
Michanek A, Björklund M, Nylander T, Sparr E (2012) ssRNA base pairing at a bilayer interface can be controlled by the acyl chain order. Soft Matter 8:10428. doi:10.1039/c2sm06700e
Dabkowska AP, Michanek A, Jaeger L et al (2015) Assembly of RNA nanostructures on supported lipid bilayers. Nanoscale 7:583–596. doi:10.1039/C4NR05968A
Suzuki Y, Endo M, Sugiyama H (2015) Lipid-bilayer-assisted two-dimensional self-assembly of DNA origami nanostructures. Nat Commun 6:8052. doi:10.1038/ncomms9052
Kocabey S, Kempter S, List J et al (2015) Membrane-assisted growth of DNA origami nanostructure arrays. ACS Nano 9:3530–3539. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b00161
Harke M, Teppner R, Schulz O et al (1997) Description of a single modular optical setup for ellipsometry, surface plasmons, waveguide modes and their corresponding imaging techniques including Brewster angle microscopy. Rev Sci Instrum 68:3130
Vandoolaeghe P, Rennie AR, Campbell RA et al (2008) Adsorption of cubic liquid crystalline nanoparticles on model membranes. Soft Matter 4:2267. doi:10.1039/b801630e
Kern W, Puotinen D (1970) Cleaning solutions based on hydrogen peroxide for use in silicon semiconductor technology. RCA Rev 31:187–206
Jönsson P, Jonsson MP, Tegenfeldt JO, Höök F (2008) A method improving the accuracy of fluorescence recovery after photobleaching analysis. Biophys J 95:5334–5348. doi:10.1529/biophysj.108.134874
Keller CA, Kasemo B (1998) Surface specific kinetics of lipid vesicle adsorption measured with a quartz crystal microbalance. Biophys J 75:1397–1402. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(98)74057-3
Richter R, Mukhopadhyay A, Brisson A (2003) Pathways of lipid vesicle deposition on solid surfaces: a combined QCM-D and AFM study. Biophys J 85:3035–3047. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74722-5
Cho NJ, Frank CW, Kasemo B, Hook F (2010) Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring of supported lipid bilayers on various substrates. Nat Protoc 5:1096–1106. doi:10.1038/Nprot.2010.65
Kasemo B, Fant C, Sott K et al (2001) Variations in coupled water, viscoelastic properties, and film thickness of a Mefp-1 protein film during adsorption and cross-linking: a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring, ellipsometry, and surface plasmon. Anal Chem 73:5796–5804
Azzam RMA, Bashara NM (1996) Ellipsometry and polarized light. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam
Tiberg F, Landgren M (1993) Characterization of thin nonionic surfactant films at the silica/water interface by means of ellipsometry. Langmuir 9:927–932. doi:10.1021/la00028a009
de Feijter A, Benjamins J, Veer FA (1978) Ellipsometry as a tool to study the adsorption behavior of synthetic and biopolymers at the air–water interface. Biopolymers 17:1759. doi:10.1002/bip.1978.36017071
Ainalem M-L, Kristen N, Edler KJ et al (2010) DNA binding to zwitterionic model membranes. Langmuir 26:4965–4976. doi:10.1021/la9036327
Nieuwenhuysen P, De Voeght F, Clauwaert J (1981) The molecular weight of Artemia ribosomes, as determined from their refractive-index increment and light-scattering intensity. Biochem J 197:689
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Dabkowska, A.P., Michanek, A., Jaeger, L., Chworos, A., Nylander, T., Sparr, E. (2017). Supported Fluid Lipid Bilayer as a Scaffold to Direct Assembly of RNA Nanostructures. In: Bindewald, E., Shapiro, B. (eds) RNA Nanostructures . Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1632. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7138-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7138-1_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7137-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7138-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols