Abstract
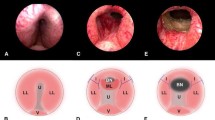
The prostatic urethral lift (PUL) is a minimally invasive device for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) due to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It recently received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval as a treatment for LUTS in September 2013. PUL is mechanically based and does not involve the destruction or physical removal of prostatic tissue. It differs from other mechanically based treatments such as prostatic urethral stents because it does not attempt to conform to the anatomy of the prostatic urethra. Furthermore, the prosthesis becomes incorporated into the prostate and is covered by the urothelium. PUL is performed under endoscopic guidance and prostheses are deployed with the aim of retracting the prostatic urethra towards the prostate capsule to open the prostatic urethral space. In this chapter, we discuss the indication, current studies, and role of PUL in the management of LUTs secondary to BPH.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkin J, Giddens J, Incze P, Casey R, Richardson S, Gange S. UroLift system for relief of prostate obstruction under local anesthesia. Can J Urol. 2012;19:6217–22.
McNicholas TA, Woo HH, Chin PT, et al. Minimally invasive prostatic urethral lift: surgical technique and multinational experience. Eur Urol. 2013;64:292–9.
Woo HH, Chin PT, McNicholas TA, et al. Safety and feasibility of the prostatic urethral lift: a novel, minimally invasive treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int. 2011;108:82–8.
Chin PT, Bolton DM, Jack G, et al. Prostatic urethral lift: two-year results after treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2012;79:5–11.
Roehrborn CG, Gange SN, Shore ND, et al. The prostatic urethral lift for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with prostate enlargement due to benign prostatic hyperplasia: the L.I.F.T. Study. J Urol. 2013;190:2161–7.
Cantwell AL, Bogache WK, Richardson SF, Tutrone RF, Barkin J, Fagelson JE, Chin PT, Woo HH. Multicentre prospective crossover study of the ‘prostatic urethral lift’ for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2014;113:615–22.
Delongchamps NB, Conquy S, Defontaines J, Zerbib M, Peyromaure M. Intra-prostatic UroLift((R)) implants for benign prostatic hyperplasia: preliminary results of the four first cases performed in France. Progres en urologie: journal de l’Association francaise d’urologie et de la Societe francaise d’urologie. 2012;22:590–7.
Garrido Abad P, Coloma Del Peso A, Sinues Ojas B, Fernandez Arjona M. Urolift(R), a new minimally invasive treatment for patients with low urinary tract symptoms secondary to BPH. Preliminary results. Arch Esp Urol. 2013;66:584–91.
Woo HH, Bolton DM, Laborde E, et al. Preservation of sexual function with the prostatic urethral lift: a novel treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Sex Med. 2012;9:568–75.
McVary KT, Gange SN, Shore ND, et al. Treatment of LUTS secondary to BPH while preserving sexual function: randomized controlled study of prostatic urethral lift. J Sex Med. 2014;11(1):279–87. doi:10.1111/jsm.12333. Epub 2013 Sep 30. PMID: 24119101 [PubMed – in process].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Woo, H.H. (2015). Prostatic Tissue Approximation (Urolift). In: Chughtai, B., Te, A., Kaplan, S. (eds) Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Modern Alternative to Transurethral Resection of the Prostate. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1587-3_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1587-3_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-1586-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-1587-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)