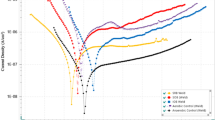
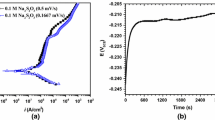
Abstract
Stainless steels (SS) are frequently used in a variety of industrial applications, where good corrosion resistance is needed. SS are usually in contact with waters of very dissimilar nature that generally, are favorable environments for microbial growth. Thus, they are susceptible to microbiologically influenced corrosion MIC (Pope et al., 1989).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beech, I.B., and Gaylarde, C.C. (1989). Adhesion of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Pseudomonas fluorescens to mild steel surfaces. J. Appl. Bacteriol., 67, 201–207.
Benbouzid-Rollet, N.D., Guezennec, J., Conte, M., and Prieur, D. (1991). Experimental biofilms containing sulphate-reducing and fermentative bacteria on stainless steel in a laboratory tubular flow-system. In: Microbiallv Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 3/ pp. 47–54 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Borenstein, S. (1988). Microbially influenced corrosion failures of austenitic stainless steels welds. Mat. Perf., 27 (8), 62–66.
Borenstein, S.W. (1991). Microbiologically influenced corrosion of austenitic stainless steel weldments. Mat. Perf., 30 (1), 52–54.
Borenstein, S.W., and Lindsay, P.B. (1987). Planning and conducting microbiologically influenced corrosion failure analyses. Corrosion/87, paper no. 381, Houston, NACE.
Borenstein, S.W., and White, D.C. (1989). Influence of welding variables on microbiologically influenced corrosion of austenitic stainless steel weldments. Corrosion/89, paper no. 183, Houston, NACE.
Buchanan, R.A., Xiao Zhang, Ping Li, Stansbury, E.E., Dowling, N.J.E., Hall, T., and Lindberg, A. (1991). Effects of surface condition on susceptibility to microbially influenced corrosion: stainless steel weldments and carbon steel. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 3/ pp. 99102 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Cristofaro, N.B. de, Acosta, C.A., Salvarezza, R.C., and Videla, H.A. (1986). The effect of sulfides on the electrochemical behavior of AISI 304 stainless steel in neutral buffered solutions. Corrosion, 42 (4), 240–242.
Das, C.R., and Mishra, K.G. (1986). Biological corrosion of welded steel due to marine algae. In: Biologically Induced Corrosion, pp. 1 14–1 17 (S.C. Dexter, ed.), NACE-8, International Corrosion Conferences Series, Houston, NACE.
Dexter, S.C., and Gao, G.Y. (1988). Effect of seawater biofilms on corrosion potential and oxygen reduction of stainless steel. Corrosion, 44 (10), 717–723. Discussion on this paper by F. Mansfeld and B. Little in Corrosion, 45 (10), 786–789.
Dexter, S.C., and Lin, S. (1990). Effect of marine bacteria on calcareous deposition. Corrosion/90, paper no. 157, Houston, NACE.
Dexter, S.C., Lucas, K.E., and Gao, G.Y. (1986). The role of marine bacteria in crevice corrosion initiation. In: Biologically Induced Corrosion, pp. 144–153 (S.C. Dexter, ed.), NACE-8, International Corrosion Conferences Series, Houston, NACE.
Dexter, S.C., Duquette, D.J., Siebert, O.W., and Videla, H.A. (1991). Use and limitations of electrochemical techniques for investigating microbiological corrosion. Corrosion, 47 (4), 308–318.
Dowling, N.J.E., Guezennec, J., and White, D.C. (1986). Facilitation of corrosion of stainless steel exposed to aerobic seawater by microbial biofilms containing both facultative and absolute anaerobes. In: Microbial Problems in the Offshore Oil Industry, pp. 27–38 ( E.C. Hill, J.L. Shennan and R.J. Wilkinson, eds.), Institute of Petroleum, London.
Dowling, N.J.E., Guezennec, J., and White, D.C. (1988). Methods for insight into mechanisms of microbially influenced metal corrosion. In: Biodeterioration 7, pp. 404–410 ( D.R.Houghton, R.N.Smith and H.O.W.Eggins, eds.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Dowling, N.J.E., Franklin, M., White, D.C., Lee, C.H., and Lundin, C. (1989). The effect of microbiologically influenced corrosion on stainless steel weldments in artificial seawater. Corrosion/89, paper no. 187, Houston, NACE.
Dowling, N.J.E., White, D.C., Buchanan, R.A., Danko, J.C., Vass, A., Brooks, S., and Ward, G.L. (1990). Microbiologically influenced corrosion of 6% molybdenum stainless steels and AISI 316: comparison with ferric chloride testing. Corrosion/90, paper no. 532, Houston, NACE.
Erauzkin, E. (1988). Biocorrosion of AISI stainless steel by sulphate reducing bacteria. In: Microbial Corrosion 1, pp. 412–430 ( C.A.C. Sequeira and A.K. Tiller, eds.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Fera, P., Siebel, M.A., Characklis, W.G., and Prieur, D. (1988). Seasonal variations in bacterial colonization of stainless steel, aluminum and polycarbonate surfaces in a seawater flow system. Biofoulinq, 1 (3), 251–261.
Feron, D. (1991). Chemical and electrochemical aspects of the corrosion of stainless steels in the presence of sulphate reducing bacteria. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 5/ pp.73–83 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Franklin, M.J., Guckert, J.B., White, D.C., and Isaacs, H.S. (1991). Spatial and temporal relationships between localized microbial metabolic activity and electrochemical activity of steel. Corrosion/91, paper no. 115, Houston, NACE.
Gaylarde, C.C., and Cook, P.E. (1987). ELISA techniques for the detection of sulphate-reducing bacteria. In: Immunoassay Techniques for the Detection of Bacteria, pp. 231–244 ( J.M. Grange, A. Fox and N.L. Morgan, eds.), Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Gaylarde, C.C., Edyvean, R.G.J., and Videla, H.A. (1992). Biologically Induced Corrosion, Research Studies Press, London, in press.
Geesey G.G., and Bremer P.J., (1992). Properties of a bacterium that causes pitting corrosion. In: Proceedings of the International Marine Biotechnology Conference ‘81, Society for Industrial Microbiology, Annandale, Va, in press.
Gendron, T.S., Cleland, R.D., and Lavoie, P.A. (1991). The role of chloride and SRB in underdeposit corrosion of alloy 800 in fresh water. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 2/ pp. 1–7 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Gilbert, P.D., and Herbert, B.N. (1987). Monitoring microbial fouling in flowing systems using coupons. In: Industrial Microbiological Testing, pp. 79–98 ( J.W.Hopton and E.C.Hill, eds.), Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Griffin, R.B., Cornwell, L.R., Seitz, W., and Estes, E. (1988). Localized corrosion under biofouling. Corrosion/88, paper no. 400, Houston, NACE.
Guezennec, J., Scotto, V., and Alabiso, G. (1988). Biocorrosion of stainless steels in natural seawater comparison tests in field and in lab. In: Microbial Corrosion 1, pp. 183–187 ( C.A.C. Sequeira and A.K. Tiller, eds.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Gundersen, R., Johansen, B., Gartland, P.O., Vintermyr, I., Tunold, R., and Hagen, G. (1989). The effect of sodium hypochlorite on the electrochemical properties of stainless steels and on the bacterial activity in seawater. Corrosion/89, paper no. 108, Houston, NACE.
Hernandez, G., Lemaitre, C., Guezennec, J., Audouard, J.P., and Beranger, G. (1988). Etude de l’influence d’elements poisons sur la resistance a la corrosion bacterienne d’aciers inoxydables en milieu marin. In: Proc. 7th Intl. Congr. on Marine Corrosion and Fouling, Valencia, Spain, in press.
bars, J.R., Moreno, D.A., Lloret, M., and Ranninger, C. (1988). Microstructural effects on the electrochemical behaviour of AISI 410 in microbiological media. In: Microbial Corrosion 1, pp. 287–289 (C.A.C. Sequeira and A.K. Tiller, eds.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Johnsen, S., and Bardai, E. (1986). The effect of a microbiological slime layer on stainless steel in natural sea water. Corrosion/86, paper no. 227, Houston, NACE.
Juanas, F., de la Cruz, M., and Ranninger, C. (1988). Corrosión por bacterias de acero inoxidable AISI 304L. Rev. Iberoamer. Corros. Prot., 19 (2), 84–85.
Kearms, J.R., and Borenstein, S.W. (1991). Microbially influenced corrosion testing of welded stainless alloys for nuclear power plant service water systems. Corrosion/91, paper no. 279, Houston, NACE.
Licina, G.J. (1989). An overview of microbiologically influenced corrosion in nuclear power plants. Mat. Perf., 28 (10), 55–60.
Licina, G.J., Pytel, M.L., and Hirota, N.S. (1990). An innovative method for mitigation of MIC in stainless steel weldments. Corrosion/90, paper no. 114, Houston, NACE.
Licina, G.J., Anderson, S., Maner, M.K., and Ward, G.L. (1991). In-plant electrochemical studies of service water system materials. Corrosion/91, paper no. 277, Houston, NACE.
Little, B.J., Wagner, P.A., Gerchakov, S.M., Walch, M. and Mitchell, R. (1986). The involvement of a thermophilic bacterium in corrosion processes. Corrosion, 42 (9), 533–536.
Little, B.J., Wagner, P., and Duquette, D. (1988). Microbiologically induced increase in corrosion current density of stainless steel under cathodic protection. Corrosion, 44 (5), 270–274.
Little, B., Ray, R., Wagner, P., Lewandowski, Z., Lee, W.C., Characklis, W.G., and Mansfeld, F. (1990). Electrochemical behavior of stainless steels in natural seawater. Corrosion/90, paper no. 150, Houston, NACE.
Little, B., Wagner, P., and Mansfeld, F. (1991a). An electrochemical evaluation of biofilms and calcareous deposits formed in natural seawater. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 5/ pp. 9–15 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Little, B., Ray, R., Wagner, P., Lewandowski, Z., Chee Lee, W., Characklis, W.G., and Mansfeld, F. (1991 b),Impact of biofouling on the electrochemical behaviour of 304 stainless steel in natural seawater. Biofoulinq, 3 (1), 45–59.
Lloret, M., Moreno, D.A., APARICIO, M.L., and Ranninger, C. (1988). Stainless steel corrosion analysis in semicontinous culture of sulphate-reducing bacteria. In: Microbial Corrosion 1, pp. 335–360 ( C.A.C. Sequeira and A.K. Tiller, eds.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Mansfeld, F., Tsai, R., Shih, H., Little, B., Ray, R., and Wagner, P. (1990). Results of exposure of stainless steels and titanium to natural seawater. Corrosion/90, paper no. 109, Houston, NACE.
Mansfeld, F., and Little, B. (1991). A technical review of electrochemical techniques applied to microbiologically influenced corrosion. Cor.Sci., 32 (3), 247–272.
Marmo, S.A., Nurmiaho-Lassila, E.L., Varjonen, O., and Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S. (1991). Biofouling and microbially induced corrosion on paper machines. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 4/ pp. 33–38 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Maxwell, S., and Hamilton, W.A. (1986). Modified radiorespirometric assay for determining the sulfate reduction activity of biofilms on metal surfaces. J. Microbiol. Met., 5 (2), 83–91.
Mele, M.F.L. de, Moreno, D.A., (bars, J.R., and Videla, H.A. (1991). Effect of inorganic and biogenic sulfide on localized corrosion of heat-treated type 304 stainless steel. Corrosion, 47 (1), 24–30.
Mollica, A., Trevis, A., Traverso, E., Ventura, G., Scotto, V., Alabiso, G., Marcenaro, G., Montini, V., de Carolis, G. and Dellepiane, R. (1984). Interaction between biofouling and oxygen reduction rate on stainless steel in seawater. In: Proc. 6th Intl. Congr. on Marine Corrosion andFoulinq, p 269–281. Athens, Greece.
Mollica, A., Trevis, A., Traverso, E., Ventura, G., Carolis, G. de, and Dellepiane, R. (1989). Cathodic performance of stainless steels in natural seawater as a function of microorganism settlement and temperature. Corrosion, 45 (1), 48–56.
Mollica, A., (1992). Biofilm and corrosion on active-passive alloys in seawater. In: International Biodeterioration, in press.
Moreno, D.A. (1990). Anälisis de la susceptibilidad a la corrosión microbiana de los aceros inoxidables en diferentes estados microestructurales. Ph.D. Dissertation. Universidad de Alcalà de Henares, Madrid, Spain.
Moreno, D.A., Mele, M.F.L. de, (bars, J.R., and Videla, H.A. (1991). Influence of microstructure on the electrochemical behavior of type 410 stainless steel in cloride media with inorganic and biogenic sulfide. Corrosion, 47 (1), 2–9.
Moreno, D.A., (bars, J.R., Ranninger, C., and Videla, H.A. (1992). Technical note: Use of potentiodynamic polarization to assess pitting of stainless steels by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Corrosion, in press.
Nekoksa, G., and Gutherman, B. (1991). Test results from electrochemical exposure racks at the Crystal river nuclear power plant. Corrosion/91, paper no. 275, Houston, NACE.
Nivens, D.E., Nichols, P.D., Henson, J.M., Geesey, G.G., and White, D.C. (1986). Reversible acceleration of the corrosion of AISI 304 stainless steel exposed to seawater induced by growth and secretions of the marine bacterium Vibrio natriegens. Corrosion, 42 (4), 204–210. OCIDE. (1988). Corrosión bacteriana de aceros inoxidables. Final Report, Proj. no. 120. 11. Madrid, Spain.
Ortiz, C., Guiamet, P.S., and Videla, H.A. (1990). Relationship between biofilms and corrosion of steel by microbial contaminants of cutting oil emulsions. International Biodeterioration, 26 (5), 315–326.
Pope, D.H. (1986). A study of microbiologically influenced corrosion in nuclear power plants and a practical guide for countermeasures. Electric Power Research Institute. Final Report EPRI NP-4582s. Palo Alto, CA.
Pope, D.H. (1990). Development of methods to detect sulfate-reducing bacteria - Agents of microbiologically influenced corrosion; Publication no. 37, Materials Technology Institute of the Chemical Process Industries, Inc., St. Louis, MO.
Pope, D.H., Soracco, R.J., and Wilde, E.W. (1982). Studies on biologically induced corrosion in heat exchanger systems at the Savannah River Plant, Aiken, SC. Mat. Perf., 21 (7), 43–50.
Pope, D.H., Duquette, D., Wayner, P.C. and Johannes, A.H. (1989). The case for microbiologically influenced corrosion of stainless steels. In: Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion: A State-of-the-Art Review, second edition, Publication 13, Materials Technology Institute of t h e Chemical Process Industries, Inc. Columbus. Ohio.
Prasad, R. (1988). Pros and cons of ATP measurement in oil field waters, Corrosion/88, paper no. 87, Houston, NACE.
Ringas, C., and Robinson, F.P.A. (1988a). Corrosion of stainless steel by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Electrochemical Techniques. Corrosion, 44 (6), 386–396.
Ringas, C., and Robinson, F.P.A. (1988b). Corrosion of stainless steel by sulfate-reducing bacteria–Total immersion test results. Corrosion, 44 (9), 671–678.
Salvago, G., Taccani, G., and Fumagalli, G. (1991a). Electrochemical approach to biofilms monitoring. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 5/ pp. 1–7 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Salvago, G., Taccani, G., Fumagalli, G., and Galelli, L. (1991b). Acidification effects on the electrochemical behaviour of stainless steel in seawater. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 8/ pp.5–11 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Scott, P.J.B., and Davies, M. (1989). Microbiologically influenced corrosion of high molybdenum austenitic stainless steel. Corrosion/89, paper no. 186, Houston, NACE.
Scott, P.J.B., Goldie, J., and Davies, M. (1991). Ranking alloys for susceptibility to MIC - A preliminary report on high-Mo alloys. Mat. Perf., 30 (1), 5557.
Scotto, V., di Cintio, R., and Marcenaro, G. (1985). The influence of marine aerobic microbial film on stainless steel corrosion behaviour. Cor. Sci., 25 (3), 185–194.
Scotto, V., Alabiso, G., and Marcenaro, G. (1986). The behaviour of stainless steels in natural seawater. In: Bioelectrochemistry and Bioenergetics, 16, 347–355.
Silva, A.J.N., Tanis, J.N., Silva, J.O., and Silva, R.A. (1986). Alcohol industry biofilms and their effect on corrosion of 304 stainless steel. In: Biologically Induced Corrosion, pp. 76–82 (S.C. Dexter, ed.), NACE-8, International Corrosion Conference Series, Houston, NACE.
Silva, R.A., and Videla, H.A. (1989). A corrosao microbiológica e sua relacao corn a presenca de biofilmes en metais e ligas de use industrial. Proc. 3rd Iberoamerican Congress of Corrosion and Protection–Brazilian Corrosion Congress/89, pp. 1580–1592. Río de Janeiro, Brazil.
Sinha, U.P., Wolfram, J.H., and Rogers, R.D. (1991). Microbially influenced corrosion of stainless steels in nuclear power plants. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 4/ pp.51–60 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Stein, A.A. (1991). Metallurgical factors affecting the resistance of 300 series stainless steels to microbiologically influenced corrosion. Corrosion/91, paper no. 107, Houston, NACE.
Stoecker, J.G., and Pope, D.H. (1986). Study of biological corrosion in high temperature demineralized water. Mat. Perf., 25 (6), 51–56.
Tatnall, R.E. (1981). Fundamentals of Bacteria Induced Corrosion. Materials Performance, 20 (9), 32–38.
Tatnall, R.E. (1991). New perspectives on testing for sulfate reducing bacteria. In: Microbially Influenced Corrosion and Biodeterioration, 5/ pp.17–32 ( N.J. Dowling, M.W. Mittleman and J.C. Danko, eds.), The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN.
Varjonen, O., Hakkarainen, T., Nurmiaho-Lassila, E., and Salkinoja-Salonen, M. (1988). The brackish water biofilm on stainless steels: an electrochemical and morphological study. In: Microbial Cor. 1, pp. 164–178 ( C.A.C. Sequeira and A.K. Tiller, eds.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Varjonen, O.A., Hakkarainen, T.J., and Marmo, S.A. (1991). Observations on biofilms and corrosion resistance of stainless steels in paper machine environments. Corrosion/91, paper no. 190, Houston, NACE.
Videla, H.A. (1989a). Metal dissolution/redox in biofilms. In: Structure and Function of Biofilms, pp. 301–320 ( W.G.Characklis and P.A.Wilderer, eds.), John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK.
Videla, H.A. (1989b). Biological corrosion and biofilm effects on metal biodeterioration. In: Biodeterioration Research 2, pp.39–50 ( C.E. O’Rear and G.C. Llewellyn, eds.), Plenum Press, New York.
Videla, H.A. (1991). Microbially induced corrosion: an updated overview. In: Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 8, pp. 63–88 ( H.W.Rossmoore, ed.), Elsevier Applied Science, London.
Videla, H.A., Mele, M.F.L. de, and Brankevich, G. (1987). Microfouling of several metal surfaces in polluted sea water and its relation with corrosion. Corrosion/87, paper no. 365, Houston, NACE.
Videla, H.A., Mele, M.F.L. de, and Brankevich, G. (1989). Biofouling and corrosion of stainless steel and 70/30 copper - nickel samples after several weeks of immersion in seawater. Corrosion/89, paper no. 291, Houston, NACE.
Videla, H.A., Mele, M.F.L., Silva, R.A., Bianchi, F., and Gonzales Canales, C. (1990). A practical approach to the study of the interaction between biofouling and passive layers on mild steel and stainless steel in cooling water. Corrosion/90, paper no. 124, Houston, NACE.
Videla, H.A., Guiamet, P.S., Pardini, O.R., Echarte, E., Trujillo, D., and Freitas, M.M.S. (1991). Monitoring biofilms and MIC in an oilfield water injection system. Corrosion/91, paper no. 103, Houston, NACE.
Ward, G.L., and Anderson, S. (1991). MIC and corrosion of service water system materials. Corrosion/91, paper no. 278, Houston, NACE.
Wagner, P. (1992). Investigations of MIC using environmental scanning electron microscopy. Corrosion/92, paper no. 185, Houston, TX.
Webster, B.J., Newman, R.C., and Kelly, R.G. (1991). SRB-Induced localized corrosion of stainless steels. Corrosion/91, paper no. 106, Houston, NACE.
Weimer, P.J., and Ng, T.K. (1988). Use of two-stage continuous culture to assess biocorrosion by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Corrosion/88, paper no. 90, Houston, NACE.
Zamanzadeh, M., O’Connor, K., and Bavarian, B. (1989). Case histories of corrosion problems in waste-water facilities. Mat. Perf., 28 (9), 43–48.
Zhang, X., Buchanan, R.A., Stansbury, E.E., and Dowling, N.J.E. (1989). Electrochemical responses of structural materials to microbially influenced corrosion. Corrosion/89, paper no. 512, Houston, NACE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Moreno, D.A., Ibars, J.R., Ranninger, C., De Mele, M.F.L., Videla, H.A. (1994). Evaluation of Stainless Steel Susceptibility to Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion: An Updated Review. In: Llewellyn, G.C., Dashek, W.V., O’Rear, C.E. (eds) Mycotoxins, Wood Decay, Plant Stress, Biocorrosion, and General Biodeterioration. Biodeterioration Research, vol 4. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9450-2_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9450-2_42
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4757-9452-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4757-9450-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive