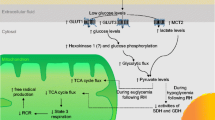
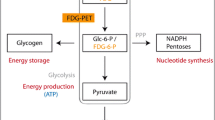
Abstract
Glucose is the predominant fuel used by the brain1–3. Dependency on glucose is demonstrated by the deleterious effect of hypoglycemia on brain functioning. It is therefore not surprising that many mechanisms have evolved to ensure an adequate supply of glucose to the brain. Among these the release of so called counterregulatory hormones during hypoglycemia plays an important role for upholding levels of blood glucose4.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. K. Siesjö, Utilization of substrates of brain tissues, in; Brain Energy Metabolism. New York: Wiley (1978).
L. Sokoloff, Cerebral circulation, energy metabolism and protein synthesis: general characteristics and principles of measurement, in: Positron emission tomography and autoradiography: Principles and applications for the brain and heart, New York, Raven Press pp. 1–71 (1986).
W. H. Pardridge, Brain metabolism from the blood-brain barrier, Physiol Rev 63:1481–1535 (1983).
P. E. Cryer and J. E. Gerich, Glucose counterregulation, hyperglycemia and intensive insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus, N Eng J Med 313:232–239 (1987).
C. Crone, Facilitated transfer of glucose from blood into brain tissue, J Physiol 181:103–113 (1965).
A. L. McCall, L. B. Fixman, N. Fleming, K. Tornheim, W. Chick and N. B. Ruderman, Chronic hypoglycemia increases brain glucose transport, Am J Physiol 251:E442–E447 (1986).
A. Gjedde and C. Crone, Blood-brain glucose transfer: repression in chronic hyperglycemia, Science 214:456–457 (1981).
A. L. McCall, W. R. Millington and R. J. Wurtman, Metabolic fuel and aminoacid transport into the brain in experimental diabetes mellitus, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 5406–5410 (1982).
S. I. Harik, S. A. Gravina and R. N. Kalaria, Glucose transporter of the blood-brain barrier and brain in chronic hyperglycemia, J Neurochem 51:1930–1934 (1988).
R. B. Duckrow, Glucose transfer into rat brain during acute and chronic hyperglycemia, Metabolic Brain Disease 3: 201–209 (1988).
R. B. Duckrow and R. M. Bryan, Regional cerebral glucose utilizatoin during hyperglycemia, J Neurochem 48: 989–993 (1987).
A. M Mans, M. R. De Joseph, D. W. Davis and R. A. Hawkins, Brain energy metabolism in streptozotocin-diabetes, Biochem J 249:57–62 (1988).
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT):Results of feasibility study, Diabetes Care 10:1–19 (1987).
M. Gutniak, G. Blomqvist, L. Widén, S, Stone-Elander, B. Hamberger and V. Grill, Brain uptake and metabolism of [U-ll-C]-D-glucose in insulindependent diabetic subjects, Am J Physiol. In press.
K. Mori, N. Cruz, G. Dienel, T. Nelson and L. Sokoloff, Direct chemical measurement of the lumped constant of the [14-C] deoxyglucose method in rat brain: effects of arterial plasma glucose level on the distribution spaces of [14-C] deoxy-glucose and glucose and on lambda, Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9:304–314 (1989).
E, Shapiro, M. Cooper, C.-T. Chen, B. D. Given and K. S. Polonsky, Change in hexose distribution volume and fractional utilization of [12F]-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glu-cose in brain during acute hypoglycemia in humans, Diabetes 39:175–181 (1990).
V. Grill, M. Gutniak, O. Björkman et al., Cerebral blood flow and substrate utilization in insulin-treated diabetic subjects, Am J Physiol. In press.
L. Sokoloff, M. Reivich, C. Kennedy et al., The 14C-deoxyglucose method for the measurements of local cerebral glucose utilization: Theory, procedure and normal values in the conscoius and anaesthetized albino rat, J Neurochem 28:897–916 (1977).
G. Blomqvist, S. Stone-Elander, S. Halldin et al., Measurement of cerebral glucose utilization with PET using [1-11-J D-glucose. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. In press.
P. E. Roland, L. Eriksson, S. Stone-Elander and L. Widen, Does mental activity change the oxidative metabolism of the brain? J Neurosci 7:2373–2389 (1987).
R. A. Koeppe, J. E. Holden and W. R. Ip, Performance comparison of parameter estimation techniques for the quantitation of local cerebral blood flow by dynamic positron computed tomography, J Cereb Blood Flow Metab5: 224–234 (1985).
D. J. Brooks, S. R. Gibbs, P. Sharp et al., Regional cerebral glucose transport in insulin-dependent diabetic patients studied using [ll-C]3-0-methyl-D-glucose and positron emission tomography, J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:240–244 (1986).
W. Sacks, Cerebral metabolism of isotopic glucose in normal human subjects, J Appl Physiol 10:37–44 (1957).
P. T. Fox, M. E. Raichle, M. A. Mintun and C. Dance, Non-oxidative glucose consumption during focal physiologic neural activity, Science 241:462–464 (1988).
K. A. Hossman and F. Linn, Regional energy metabolism during functional activation of the brain, J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7:S297 (1987).
B. K. Siesjö, Hypoglycemia: in: Brain Energy Metabolism. New York, Wiley (1978).
S. R. Nelson, D. W. Schultz, J. V. Passonneau and 0. H. Lowry, Control of glycogen levels in the brain, J Neuro Chem 15:1271–1279 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Grill, V. (1991). Metabolism of Glucose in the Brain of IDDM Subjects. In: Vranic, M., Efendic, S., Hollenberg, C.H. (eds) Fuel Homeostasis and the Nervous System. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 291. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5931-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5931-9_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5933-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5931-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive