Abstract
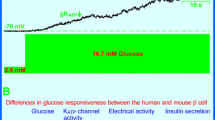
It is well established that glucose-stimulated insulin release from the pancreatic β-cell is associated with the initiation of electrical activity (see recent review by Henquin & Meissner10). Microelectrode recordings have shown that in the absence of glucose the β-cell is electrically silent. Increasing plasma glucose depolarises the membrane by an amount that is dependent on the glucose concentration and electrical activity is initiated when this depolarisation exceeds a threshold level. There is considerable evidence that the initial slow depolarisation induced by glucose results from a decrease in the resting potassium permeability of the membrane5,8,14 as a consequence of glucose metabolism9).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J.H. Ashcroft, Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis, Diabetologia 18:5 (1980).
F.M. Ashcroft, D.E. Harrison, and S.J.H. Ashcroft, Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells, Nature 312:446 (1984).
F.M. Ashcroft, D.E. Harrison, and S.J.H. Ashcroft, The glucose-sensitive potassium channel in rat pancreatic beta-cells is inhibited by intracellular ATP, J . Physiol. 369:101P(1985).
S.J.H. Ashcroft, L.C.C. Weerasinghe, and P.J. Randle, Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release, Biochem J. 132:223 (1973).
I. Atwater, B. Ribalet, and E. Rojas, Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the β-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse, J. Physiol. 278:117 (1978).
D. Cook and N. Hales, Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic β-celis, Nature 311:271 (1984).
O.P. Hamil, A. Marty, E. Neher, B. Sakmann, and F. Sigworth, Improved patch clamp techniques for high resolution current recordings from cells and cell-free membrane patches, Pflügers Arch. 391:85 (1981).
J.C. Henquin, D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells, Nature 271:271 (1978).
J.C. Henquin, Metabolic control of the potassium permeability in pancreatic islet cells, Biochem. J. 186:541 (1980).
J.C. Henquin and H.P. Meissner, Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic beta-cells, Experientia 40:1024 (1984).
M. Kakei, A. Noma, and T. Shibasaki, Properties of adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells, J. Physiol. 363:441 (1985).
A. Lernmark, The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets, Diabetologia 10:445 (1974).
O.H. Petersen, this book.
J. Sehlin and I.-B. Täljedal, Transport of rubidium and sodium in pancreatic islets, Nature 253:635 (1975).
A.E. Spruce, N.B. Standen, and P.R. Stanfield, Voltage-dependent ATP-sensitive potassium channels of skeletal muscle membrane, Nature 316:736 (1985).
G. Trube and J. Hescheler, Inward-rectifying channels in isolated patches of the heart cell-membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches, Pflügers Arch. 410:178 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1986 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ashcroft, F.M., Harrison, D.E., Ashcroft, S.J.H. (1986). A Potassium Channel Modulated by Glucose Metabolism in Rat Pancreatic β-Cells. In: Atwater, I., Rojas, E., Soria, B. (eds) Biophysics of the Pancreatic β-Cell. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 211. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5314-0_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5314-0_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5316-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5314-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive