Abstract
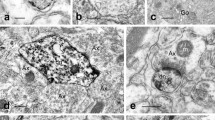
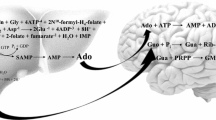
Brain is among the most active tissues in nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis (1) but the role of the blood brain barrier in regulating the transport of purine and pyrimidine has not, so far, well defined. The existence of a presynaptic purinergic modulation of trasmitter release in the central nervous system (1) emphasize a possibly important role of purine transport at the blood-brain barrier. Previous reports (2) have demonstrated the existence, on the luminal side of the blood-brain barrier, of two saturable purine transport systems, one is specific for adenine and hypoxanthine transport and the other one accounts for nucleoside transport. Recently Betz (3) has shown in isolated brain microvessels the existence of xanthine oxidase activity, as well as the capability of the isolated vessels to take up hypoxanthine which is subsequently degraded to xanthine and uric acid or incorporated in other compounds by energy dependent processes. The aim of this report was to establish whether, as in other tissues, in isolated brain microvessels, which are an in vitro model of the blood brain barrier, hypoxanthine transport and metabolism is regulated by the levels of inorganic phosphate and/or phosphate esters.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Paton, Presynaptic neuromodulation mediated by purinergic receptors, in: “Purinergic Receptors”, G. Burnstock, ed., Chapman and Hall, London (1981).
E.M. Cornford and W.H. Pardridge, Independent blood-brain barrier transport system for nuclei acid precursors, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 394: 211 (1975).
A.C. Betz, Identification of hypoxanthine transport and xanthine oxidase activity in brain capillaries, J. Neurochem. 44: 574 (1985).
C. Cangiano, P. Cardelli-Cangiano, J.H. James, F. Rossi Fanelli, M.A. Patrizi, K.A. Brackett, R. Strom, and J.E. Fischer, Brain microvessels take up neutral amino acids in exchange for glutamine, J. Biol. Chem. 258: 8949 (1983).
P. Cardelli-Cangiano, C. Cangiano, J.H. James, F. Ceci, J.E. Fischer, and R. Strom, Effect of ammonia on amino acid uptake by brain microvessels, J. Biol. Chem. 259: 5295 (1984).
A. Giacomello and C. Salerno, Human hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase: steady-state kinetics of the forward and reverse reactions, J. Biol. Chem. 253: 6038 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1986 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cardelli-Cangiano, P., Fiori, A., Giacomello, A., Strom, R., Salerno, C. (1986). Hypoxanthine Uptake by Isolated Brain Microvessels. In: Nyhan, W.L., Thompson, L.F., Watts, R.W.E. (eds) Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Man V. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 195B. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-1248-2_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-1248-2_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-1250-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-1248-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive