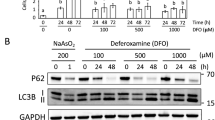
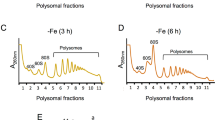
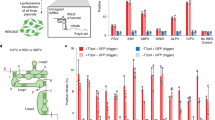
Abstract
An iron responsive element (IRE) located within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) of certain mRNAs (e.g., ferritin) serves as a binding site for a class of specific binding proteins [referred to as the iron regulatory proteins (IRPs)] which, when bound to an IRE, repress translation of those mRNAs [reviewed in Leibold and Guo (1992), Melefors and Hentze (1993), Klausner et al. (1993), Munro (1993), Theil (1993), Mascotti et al. (1995)]. Binding of an IRP to an IRE located proximally to the 5′ end of an mRNA is believed to prevent access of eIF-4F (the cap binding protein) to the 5′ cap structure, resulting in a blockage of initiation (Goossen et al. 1990; Bhasker et al. 1993; Gray and Hentze 1994). When chelatable iron levels are increased in the cell, an IRP is induced to dissociate from the IRE and allow initiation of translation of ferritin [reviewed in Leibold and Guo (1992), Melefors and Hentze (1993), Klausner et al. (1993), Munro (1993), Theil (1993)]. Messages that contain functional IREs in their 5′ UTRs code for ferritin (Leibold and Guo 1992; Melefors and Hentze 1993; Klausner et al. 1993; Munro 1993; Theil 1993), erythroid δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase (δ-ALAS) (Cox et al. 1991; Bhasker et al. 1993), mitochondrial aconitase (m-acon) (Dandekar et al. 1991), Drosophila melanogaster succinate dehydrogenase (Kohler et al. 1995; Gray et al. 1996), and possibly transferrin (Tf) (Cox and Adrian 1993; Cox et al. 1995).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balla G., H. S. Jacob, J. Balla, M. Rosenberg, K. Nath, F. Apple, J. W. Eaton, and G. M. Vercellotti. 1992. Ferritin: A cytoprotective antioxidant strategem of endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 18148–18153.
Balla J., H. Jacob, G. Balla, K. Nath, J. W. Eaton, and G. M. Vercellotti. 1993. Endothelialcell heme uptake from heme proteins: Induction of sensitization and desensitization to oxidant damage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 90: 9285–9289.
Basilion J. P., T. A. Rouault, C. M. Massinople, R. D. Klausner, and W. H. Burgess. 1994 a. The iron-responsive element-binding protein: Localization of the RNA-binding site to the aconitase active-site cleft. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 91: 574–578.
Basilion J. P., M. C. Kennedy, H. Beinert, C. M. Massinople, R. D. Klausner, and T. A. Rouault. 1994 b. Overexpression of iron-responsive element-binding protein and its analytical characterization as the RNA-binding form, devoid of an iron-sulfur cluster. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 311: 517–522.
Battistini A. B., E-M. Coccia, G. Marziali, D. Bulgarini, S. Scalzo, G. Fiorucci, G. Romeo, E. Affabris, U. Testa, G. B. Rossi, and C. Peschle. 1991. Intracellular heme coordinately modulates globin chain synthesis, transferrin receptor number, and ferritin content in differentiating friend erythroleukemia cells. Blood 78: 2098–2103.
Beinert H., and M. C. Kennedy. 1993. Aconitase, a two-faced protein: Enzyme and iron regulatory factor. FASEB J. 7: 1442–1449.
Bhasker C. R., G. Burgiel, B. Neupert, A. Emery-Goodman, L. C. Kuhn, and B. K. May. 1993. The putative iron-responsive element in the human erythroid 5-aminolevulinate synthase mRNA mediates translational control. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 12699–12705.
Cairo, G. and A. Pietrangelo. 1994. Transferrin receptor gene expression during rat liver regeneration: Evidence for post-translational regulation by iron regulatory factorB, a second iron-responsive element-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 6405–6409.
Cairo G., L. Tacchini, G. Pogliaghi, E. Anzon, A. Tomasi and A. Bernelli-Zazzera. 1995. Induction of ferritin synthesis by oxidative stress: Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation by expansion of the “free” iron pool. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 700–703.
Casey J. L., M. W. Hentze, D. M. Koeller, S. W. Caughman, T. A. Rouault, R. D. Klausner, and J. B. Harford. 1988. Iron responsive elements: Regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science 240: 924–928.
Casey J. L., D. M. Koeller, V. C. Ramin, R. D. Klausner, and J. B. Harford. 1989. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3’ untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 8: 3693–3699.
Constable A., S. Quick, N. K. Gray, and M. W. Hentze. 1992. Modulation of the RNA-binding activity of a regulatory protein by iron in vitro: Switching between enzymatic and genetic function? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89: 4554–4558.
Cox L. A., and G. S. Adrian. 1993. Posttranscriptional regulation of chimeric human transferrin genes by iron. Biochem. 32: 4738–4745.
Cox L. A., M. C. Kennedy, and G. S. Adrian. 1995. The 5’-untranslated region of human transferrin mRNA, which contains a putative iron-regulatory element, is bound by purified iron-regulatory protein in a sequence-specific manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 212: 925–932.
Cox T. C., M. J. Bawden, A. Martin, and B. K. May. 1991. Human erythroid 5-aminolevulinate synthase: Promoter analysis and identification of an iron-responsive element in the mRNA. EMBO J. 10: 1891–1902.
Dandekar T., R. Stripecke, N. K. Gray, B. Goossen, A. Constable, H. E. Johansson, and M. W. Hentze. 1991. Identification of a novel iron-responsive element in murine and human erythroid δ-aminolevulinic acid synthase mRNA. EMBO J. 10: 1903–1909.
Daniels-McQueen S., L. S. Goessling, and R. E. Thach. 1992. Inducible expression bovine papilloma virus shuttle vectors containing ferritin translational regulatory elements. Gene 122: 271–279.
Drapier, J-C, H. Hirling, J. Wietzerbin, P. Kaldy, and L. C. Kuhn. 1993. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide activates iron regulatory factor in macrophages. EMBO J. 12: 3643–3649.
Eisenstein R. S., D. Garcia-Mayol, W. Pettingell and H. N. Munro. 1991. Regulation of ferritin and heme oxygenase synthesis in rat fibroblasts by different forms of iron. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 88: 688–692.
Eisenstein R. S., and H. N. Munro. 1990/91. Translational regulation of ferritin synthesis by iron. Enzyme 44: 42–58.
Eisenstein R. S., P. T. Tuazon, K. L. Schalinske, S. A. Anderson, and J. A. Traugh. 1993. Iron-responsive element-binding protein: Phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J. Biol Chem. 268: 27363–27370.
Emery-Goodman A., H. Hirling, L. Scarpellino, B. Henderson, and L. C. Kuhn. 1993. Iron regulatory factor expressed from recombinant baculovirus: Conversion between the RNA-binding apoprotein and Fe-S cluster containing aconitase. Nucl Acid Res. 21: 1457–1461.
Goessling L. S., S. Daniels-McQueen, M. Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi, J.-J. Lin, and R. E. Thach. 1992. Enhanced degradation of the ferritin repressor protein during induction of ferritin messenger RNA translation. Science 256: 670–673.
Goessling L. S., D. P. Mascotti, M. Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi, H. Gang, and R. E. Thach. 1994. Irreversible steps in the ferritin synthesis induction pathway. J. Biol Chem. 269: 4343–4348.
Goossen B., S. W. Caughman, J. B. Harford, R. D. Klausner and M. W. Hentze. 1990. Translational repression by a complex between the iron-responsive element of ferritin mRNA and its specific cytoplasmic binding protein is position-dependents. in vivo. EMBO J. 9: 4127–4133.
Gray N. K., and M. W. Hentze. 1994. Iron regulatory protein prevents binding of the 43S translation pre-initiation complex to ferritin and eALAS mRNAs. EMBO J. 13: 3882–3891.
Gray N. K., K. Pantopoulos, T. Dandekar, B. A. Ackrell, and M. W. Hentze. 1996. Translational regulation of mammalian and Drosophila citric acid cycle enzymes via iron-responsive elements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93: 4925–4930.
Guo B., J. D. Phillips, Y. Yu, and E. A. Leibold. 1995. Iron regulates the intracellular degradation of iron regulatory protein 2 by the proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 21645–21651.
Guo B., Y. Yu, and E. A. Leibold. 1994. Iron regulates cytoplasmic levels of a novel iron-responsive element-binding protein without aconitase activity. J. Biol Chem. 269: 24252–24260.
Haile D. J., T. A. Rouault, J. B. Harford, and R. D. Klausner. 1990. The inhibition of the iron responsive element RNA-protein interaction by heme does not mimic in vivo iron regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 12786–12789.
Haile D. J., T. A. Rouault, J. B. Harford, M. C. Kennedy, G. A. Blondin, H. Beinert, and R. D. Klausner. 1992 a. Cellular regulation of the iron-responsive element binding protein: Disassembly of the cubane iron-sulfur cluster results in high-affinity RNA binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89: 11735–11739.
Haile D. J., T. A. Rouault, C. K. Tang, J. Chin, J. B. Harford, and R. D. Klausner. 1992 b. Reciprocal control of RNA binding and aconitase activity in the regulation of the iron responsive element binding protein: Role of the iron-sulfur cluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89: 7536–7540.
Henderson B. R., C. Seiser, and L. C. Kuhn. 1993. Characterization of a second RNA-binding protein in rodents with specificity for iron-responsive elements. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 27327–27334.
Henderson B. R., E. Menotti, C. Bonnard, and L. C. Kuhn. 1994. Optimal sequence and structure of iron-responsive elements: Selection of RNA stem loops with high affinity for iron regulatory factor. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 17481–17489.
Hirling H., B. R. Henderson, and L. C. Kuhn. 1994. Mutational analysis of the [4Fe-4S]-cluster converting iron regulatory factor from its RNA-binding form to cytoplasmic aconitase. EMBO J. 13: 453–461.
Hoffman R., N. Ibrahim, M. J. Murnane, A. Diamond, B. G. Forget, and R. D. Levere. 1980. Hemin control of heme biosynthesis and catabolism in a human leukemia cell line. Blood 56: 567–570.
Jungmann J., H. A. Reins, C. Schobert, and S. Jentsch. 1993. Resistance to cadmium mediated by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Nature 361: 369–371.
Kaptain S., W. E. Downey, C. Tang, C. Philpott, D. Haile, D. G. Orloff, J. B. Harford, T. A. Rouault, and R. D. Klausner. 1991. A regulated RNA binding protein also possesses aconitase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88: 10109–10113.
Kennedy M. C., L. Mende-Mueller, G. A. Blondin, and H. Beinert. 1992. Purification and characterization of cytosolic aconitase from beef liver and its relationship to the iron-responsive element binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89: 11730–11734.
Klausner R. D., and T. A. Rouault. 1993. A double life: Cytosolic aconitase as a regulatory RNA binding protein. Molec. Biol. 4: 1–5.
Klausner R. D., T. A. Rouault, and J. B. Harford. 1993. Regulating the fate of mRNA: The control of cellular iron metabolism.Cell 72: 19–2
Koeller D. M., J. L. Casey, M. W. Hentze, E. M. Gerhaardt, L-N.L. Chan, R. D. Klausner, and J. B. Harford. 1989. A cytosolic protein binds to structural elements within the iron regulatory region of the transferrin receptor mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 86: 3574–3578.
Koeppen A. H., A. C. Dickson, R. C. Chu, and R. E. Thach. 1993. The pathogenesis of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Ann. Neurol. 34: 646–653.
Koeppen A. H., C. G. Hurwitz, R. E. Dearborn, A. C. Dickson, R. C. Borke, and R. C. Chu. 1992. Experimental superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: Biochemical correlates. J. Neurol. Sci. 112: 38–45.
Kohler S. A., B. R. Henderson, and L. C. Kuhn. 1995. Succinate dehydrogenase b mRNA of Drosophila melanogaster has a functional iron-responsive element in its 5’-untranslated region. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 30781–30786.
Leibold E. A., and B. Guo. 1992. Iron-dependent regulation of ferritin and transferrin receptor expression by the iron-responsive element binding protein. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 12: 345–368.
Lin, J-J., S. Daniels-McQueen, L. Gaffield, M. M. Patino, W. E. Walden, and R. E. Thach. 1990 b. Specificity of the induction of ferritin synthesis by hemin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1050: 146–150.
Lin, J-J., S. Daniels-McQueen, M. M. Patino, L. Gaffield, W. E. Walden, and R. E. Thach. 1990a. Derepression of ferritin messenger RNA translation by hemin in vitro. Science 247: 74–77.
Lin, J-J., M. M. Patino, L. Gaffield, W. E. Walden, A. Smith, and R. E. Thach. 1991. Crosslinking of hemin to a specific site on the 90-kDa ferritin repressor protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 88: 6068–6071.
Lin, J-J., W. E. Walden, and R. E. Thach. 1990/91. Induction of ferritin synthesis in vitro: Problems of specificity inherent in the use of iron compounds. Enzyme 44: 59–67.
Mascotti D. P., D. Rup, and R. E. Thach. 1995. Regulation of iron metabolism: Translational effects mediated by iron, heme and cytokines. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 15: 239–261.
Melefors O., and M. W. Hentze. 1993. Translational regulation by mRNA/protein interactions in eukaryotic cells: Ferritin and beyond. Bioessays 15: 85–90.
Mullner E. W., and L. C. Kuhn. 1988. A stem-loop in the 3’ untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell 53: 815–825.
Mullner E. W., B. Neupert, and L. C. Kuhn. 1989. A specific mRNA binding factor regulates the iron-dependent stability of cytoplasmic transferrin receptor mRNA. Cell 58: 373–382.
Mullner E. W., S. Rothenberger, A. M. Muller, and L. C. Kuhn. 1992. In vivo and in vitro modulation of the mRNA-binding activity of iron-regulatory factor: Tissue distribution and effects of cell proliferation, iron levels and redox state. Eur. J. Biochem. 208: 597–605.
Munro, H. 1993. The ferritin genes: Their response to iron status. Nutr. Rev. 51: 65–73.
Murakami Y., S. Matsufuji, T. Kameji, S.-I. Hayashi, K. Igarashi, T. Tamura, K. Tanaka, and A. Ichihara. 1992. Ornithine decarboxylase is degraded by the 26S proteasome without ubiquitation. Nature 360: 597–599.
Philpott C. C., D. Haile, T. A. Rouault, and R. D. Klausner. 1993. Modification of a free Fe-S cluster cysteine residue in the active iron-responsive element-binding protein prevents RNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 17655–17658.
Rice-Evans C. A., and R. H. Burdon. 1994. In Free Radical Damage and its Control. Elsevier, New York.
Rogers J. T., and H. N. Munro. 1987. Translation of ferritin light and heavy subunit mRNAs is regulated by intracellular chelatable iron levels in rat hepatoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 84: 2277–2281.
Samaniego F., J. Chin, K. Iwai, T. A. Rouault, and R. D. Klausner. 1994. Molecular characterization of a second iron-responsive element binding protein, iron regulatory protein vn2: Structure, function, and post-translational regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 30904–30910.
Tang C. K., J. Chin, J. B. Harford, R. D. Klausner, and T. A. Rouault. 1992. Iron regulates the activity of the iron-responsive element binding protein without changing its rate of synthesis or degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 24466–24470.
Theil, E. C. 1993. The IRE (iron regulatory element) family: Structures which regulate mRNA translation or stability. Biofactors 4: 87–93.
Weiss G., B. Goossen, W. Doppler, D. Fuchs, K. Pantopoulos, G. Werner-Felmayer, H. Wachter, and M. W. Hentze. 1993. Translational regulation via iron-responsive elements by the nitric oxide/NO-synthase pathway. EMBO J. 12: 3651–3657.
Yu Y., E. Radisky, and E. A. Leibold. 1992. The iron-responsive element binding protein. J. Biol Chem. 267: 19005–19010.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mascotti, D.P., Goessling, L.S., Rup, D., Thach, R.E. (1998). Mechanisms for Induction and Rerepression of Ferritin Synthesis. In: Silver, S., Walden, W. (eds) Metal Ions in Gene Regulation. Chapman & Hall Microbiology Series. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5993-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5993-1_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7745-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-5993-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive