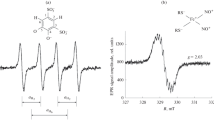
Abstract
A number of recent studies have implicated the involvement of ferritin iron in oxygen radical reactions. Hemosiderin has long been thought to be a degradation product of ferritin. A recent series of papers have indicated that oxygen radical damage to proteins result in an increase in susceptibility to a novel proteolytic system. We suggest a possible relationship between radical damage to ferritin and hemosiderin via this proteolytic system.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.E. Thomas, L.A. Morehouse, and S.D. Aust, Ferritin and Superoxide-dependent Lipid Peroxidation, J. Biol. Chem., 260(6):3275, (1985).
P. Biemond, A. Swaak, H. van Eijk, and J.F. Koster, Superoxide Dependent Iron Release From Ferritin in Inflammatory Diseases, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 4:185, (1988).
J.K. Grady, Y. Chen, N.D. Chasteen, and D.C. Harris, Hydroxyl Radical Production during Oxidative Deposition of Iron in Ferritin, J. Biol. Chem., 264, in press, (1989).
J-C. Sibille, K. Doi and P. Aisen, Hydroxyl Radical Formation and Iron-binding Proteins, J. Biol. Chem., 262(1):59, (1987).
B. Halliwell and J.M.C. Gutteridge, Oxygen Free Radicals and Iron in Relation to Biology and Medicine: Some Problems and Concepts, Arch. Biochem. Biophvs., 246(2):501, (1986).
W.A. Pryor, Cancer and Free Radicals, in “Antimutagenesis and Anticarcinogenesis Mechanisms”, D.M. Shankel, P.E. Hartman, T. Kada, and A. Hollaender (eds.), Plenum Press, New York, pgs. 45–59, 1986.
S.D. Aust, Sources of Iron for lipid Peroxidation in Biological Systems, in “Oxygen Radicals and Tissue Injury: Proceedings of the Upjohn Symposium”, 27–33, (1988).
B. Halliwell and J.M.C. Gutteridge, Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease, Biochem. J., 219:1, (1984).
T.G. Hoy and A. Jacobs, Ferritin Polymers and the Formation of Hemosiderin, Br. J. Haematol., 49:593, (1981).
C.E. Thomas and S.D. Aust, Reductive Release of Iron from Ferritin by Cation Free Radicals of Paraquat and Other Bipyridyls, J. Biol. Chem., 261(28):13064, (1986).
B.J. Bolann and R.J. Ulvik, Release of iron From ferritin by xanthine oxidase: Role of the superoxide radical, Biochem. J., 243:55, (1987).
P. Biemond, A.J.G. Swaak, C.M. Biendorff and J.F. Koster, Superoxide-dependent and -independent mechanism of iron mobilization from ferritin by xanthine oxidase: Implications for oxygen-free-radical-induced tissue destruction during ischemia and inflammation, Biochem. J., 239:169, (1986).
D.W. Reif, J. Schubert, and S.D. Aust, Iron Release from Ferritin and Lipid Peroxidation by Radiolytically Generated Reducing Radicals, Arch. Biochem. Biophvs., 264(1):238, (1988).
V.M. Samokyszyn, C.E. Thomas, D.W. Reif, M. Saito and S.D. Aust, Release of Iron From Ferritin and Its Role in Oxygen Toxicities, Drug. Metab. Rev., 193(3&4):283, (1988).
P. Biemond, A.J.G. Swaak, H.G. van Eijk and J.F. Koster, Intraarticular Ferritin-Bound Iron in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Arthritis Rheum., 29(10):1187, (1986).
R.F. Boyer, H.M. Clark and A.P. LaRoche, Reduction and Release of Ferritin Iron by Plant Phenolics J. Inorg. Biochem., 32:171, (1988).
C.E. Thomas and S.D. Aust, Release of Iron from Ferritin by Cardiotoxic Anthracycline Antibiotics, Arch. Biochem. Biophvs, 248(2):684, (1986).
G.J. Kontoghiorghes, Iron Mobilization from ferritin using α-oxohydroxy heteroaromatic chelators, Biochem. J., 233:299, (1986).
M.J. O’Connell and T.J. Peters, Ferritin and Haemosiderin in Free Radical Generation, Lipid Peroxidation and Protein Damage, Chem. Phvs. Lipids, 45:241, (1987).
S.C. Andrews, A. Treffry and P.M. Harrison, Siderosomal ferritin: The missing link between ferritin and hemosiderin?, Biochem. J., 245:439, (1987).
S.C. Andrews, A. Treffry and P.M. Harrison, A new form of ferritin heterogeneity explained: Isolation and identification of a nineteen-amino-acid-residue fragment from siderosomal ferritin of rat liver, Biochem. J., 245:447, (1987).
S.C. Andrews, M.C. Brady, A. Treffry, J.M. Williams, S. Mann, M.I. Cleton, W. de Bruijn and P.M. Harrison, Studies on haemosiderin and ferritin from iron-loaded rat liver, Biol. Metals, 1:33, (1988).
R.L. Wixom, L. Pritkin and H.N. Munro, Hemosiderin: Nature, Formation, and Significance, Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol., 22:193, (1980).
G. Richter, Studies of Iron Overload: Rat Liver Siderosome Ferritin, Lab. Invest., 50:26, (1984).
R.J. Ward, M.J. O’Connell, D.P.E. Dickson, N.M.K. Reid, V.J. Wade, S. Mann, A. Bomford and T.J. Peters, Biochemical studies of iron cores and polypeptide shells of haemosiderin isolated from patients with primary or secondary haemochromatosis, Biochim. Biophvs. Acta, 993(1):131, (1989).
M.P. Weir, J.F. Gibson and T.J. Peters, Biochemical studies on the isolation and characterization of human spleen haemosiderin, Biochem. J., 223:31, (1984).
M. Heusterspreute and R.R. Crichton, Amino Acid Sequence of Horse Spleen Apoferritin, FEBS. Lett., 129:322, (1981).
K.J.A Davies, Protein Damage and Degradation by Oxygen Radicals: I. General Aspects, J. Biol. Chem., 262(20):9895, (1987).
K.J.A Davies, M.E. Delsignore and S.W. Lin, Protein Damage and Degradation by Oxygen Radicals: II. Modification of Amino Acids, J. Biol. Chem., 262(20):9902, (1987).
K.J.A Davies and M.E. Delsignore, Protein Damage and Degradation by Oxygen Radicals: III. Modification of Secondary and Tertiary Structure, J. Biol. Chem., 262(20):9908, (1987).
K.J.A Davies, S.W. Lin and R.E. Pacifici, Protein Damage and Degradation by Oxygen Radicals: IV. Degradation of Denatured Protein, J. Biol. Chem., 262(20):9914, (1987).
P.M. Harrison, A. Treffry and T.H. Lilley, Ferritin as an Iron-Storage Protein: Mechanisms of Iron Uptake. J.Inorg. Biochem., 27:287, (1986).
E.C. Theil, Ferritin: Structure, Gene Regulation, and Cellular Function in Animals, Plants, and Microorganisms, Ann. Rev. Biochem., 56:289, (1987).
J.R. Mertz and E.C. Theil, Subunit Dimers in Sheep Spleen Apoferritin, J. Biol. Chem., 258:11719, (1983).
S. Mann, V.J. Wade, D.P.E. Dickson, N.M.K. Reid, R.J. Ward, M. O’Connell and T.J. Peters, Structural specificity of haemosiderin iron cores in iron-overload diseases, FEBS Lett., 234(1):69, (1988).
D.P.E. Dickson, N.M.K. Reid, S. Mann, V.J. Wade, R.J. Ward and T.J. Peters, Mossbauer Spectroscopy, Electron Microscopy and Electron Diffraction Studies of Small Particle Magnetic Systems: Identification of Disease Specific Haemosiderins, Hvperfine Interactions, 45:225, (1989).
K.R. Bridges, Ascorbic Acid Inhibits Lysosomal Autophagy of Ferritin, J. Biol. Chem., 262(30):14773, (1987).
S. Roberts and A. Bomford, Ferritin Iron Kinetics and Protein Turnover in K562 Cells, J. Biol. Chem., 263(35):19181, (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Grady, J.K., Chasteen, N.D. (1991). Some Speculations on the Role of Oxyradicals in the Conversion of Ferritin to Hemosiderin. In: Frankel, R.B., Blakemore, R.P. (eds) Iron Biominerals. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3810-3_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3810-3_22
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6699-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3810-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive