Abstract
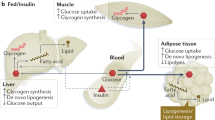
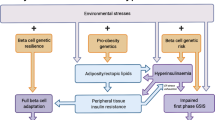
One of the essential biological actions of insulin in mammals is the maintenance of euglycaemia. This is a complex process and involves the uptake, storage and oxidation of glucose in skeletal muscle and adipose tissues, as well as the suppression of hepatic glucose production. A significant blunting of these actions in spite of the presence of normal or even high circulating levels of insulin indicates the presence of an “insulin resistant” phenotype. A variety of pathological states including type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, atherosclerosis and polycystic ovary disease are characterized by the presence of insulin resistance (1-6). In the case of type 2 diabetes it is generally accepted that insulin resistance must be accompanied by a β-cell defect for the full development of the disease. Although there is some debate as to which of these two defects is primary, longitudinal studies in several populations suggest that insulin resistance may be the first defect to be detected (2,7,8). The early insulin resistance observed in pre-diabetic individuals is initially compensated by an increase in insulin secretion by the islet β-cells that could represent either an enhanced secretory capacity or an increased islet/β-cell mass or a combination of both. Over a period of time, however, the β-cell compensation fails leading to uncontrolled hyperglycaemia and overt diabetes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reaven GM. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988; 37:1595–1607.
Kahn CR. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type 11 diabetes (Banting Lecture). Diabetes 1994; 43(8):1066–1084.
Goldberg RB. Cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. Med Clin North Am 2000; 84(1):81–93.
Hansen I, Tsalikian E, Beaufrere B, Gerich JE, Haymond MW, Rizza RA. Insulin resistance in acromegaly: Defects in both hepatic and extrahepatic insulin action. Am J Physiol 1986; 250(3 Pt 1):E269–E273.
Weinstein SP, Paquin T, Pritsker A, Haber RS. Glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance: dexamethasone inhibits the activation of glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle by both insulin-and non-insulin-related stimuli. Diabetes 1995; 44(4):441–445.
Franks S, Gilling-Smith C, Watson H, Willis D. Insulin action in the normal and polycystic ovary. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1999; 28(2):361–378.
Martin BC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Bergman RN, Soeldner JS, Kahn CR. Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of Type II diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet 1992; 340:925–929.
Lillioja S, Mott DM, Spraul M, Ferraro R, Foley JE, Ravussin E et al. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: prospective studies of Pima Indians. N Engl J Med 1993; 329(1988):1992.
Gapp DA, Leiter EH, Coleman DL, Schwizer RW. Temporal changes in pancreatic islet composition in C57BL/6J-db/db (diabetes) mice. Diabetologia 1983; 25(5):439–443.
Tomita T, Doull V, Pollock HG, Krizsan D. Pancreatic islets of obese hyperglycaemic mice (ob/ob). Pancreas 1992; 7(3):367–375.
Tokuyama Y, Sturis J, Depaoli AM, Takeda J, Stoffel M, Tang J et al. Evolution of 3-cell dysfunction in the male Zucker diabetic fatty rat. Diabetes 1995; 44(12):1447–1457.
Araki E, Lipes MA, Patti ME, Brüning JC, Haag BL, III, Johnson RS et al. Alternative pathway of insulin signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature 1994; 372:186–190.
Tamemoto H, Kadowaki T, Tobe K, Yagi T, Sakura H, Hayakawa T et al. Insulin resistance and growth retardation in mice lacking insulin receptor substrate-1. Nature 1994; 372(6502):182–186.
Bruning JC, Winnay J, Bonner-Weir S, Taylor SI, Accili D, Kahn CR. Development of a novel polygenic model of NIDDM in mice heterozygous for IR and IRS-1 null alleles. Cell 1997; 88(4):561–572.
Kulkami RN, Winnay JN, Daniels M, Bruning JC, Flier SN, Hanahan D et al. Altered function of insulin receptor substrate-l -deficient mouse islets and cultured 13-cell lines. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1999; 104(12):R69–R75.
Nielsen JH, Svensson C, Douglas E, Moldrup A, Billestrup N. Beta cell proliferation and growth factors. J Mol Med 1999; 77:62–66.
Bonner Weir S, Deery D, Leahy JL, Weir GC. Compensatory growth of pancreatic 1-cells in adult rats after short-term glucose infusion. Diabetes 1989; 38(1):49–53.
Parsons JA, Brelje TC, Sorenson RL. Adaptation of islets to pregnancy: Increased islet cell proliferation and insulin secretion correlates with the onset of placental lactogen secretion. Endocrinology 1992; 130(3):1459–1466.
Hill DJ, Hogg J. Growth factor control of pancreatic 3-cell hyperplasia. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991; 5(4):689–698.
Sorenson RL, Brelje TC. Adaptation of islets of Langerhans to pregnancy: 3-cell growth, enhanced insulin secretion and the role of lactogenic hormones. Horm Metab Res 1997; 29(6):301–307.
Nielsen JH, Linde S, Welinder BS, Billestrup N, Madsen OD. Growth hormone is a growth factor for the differentiated pancreatic 13-cell. Mol Endocrinol 1989; 3(1):165–173.
Swenne I, Heldin CH, Hill DJ, Hellerstrom C. Effects of platelet-derived growth factor and somatomedin- C/insulin-like growth factor I on the deoxyribonucleic acid replication of fetal rat islets of Langerhans in tissue culture. Endocrinology 1988; 122(1):214–218.
Otonkoski T, Beattie GM, Rubin JS, Lopez AD, Baird A, Hayek A. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor has insulinotropic activity in human fetal pancreatic cells. Diabetes 1994; 43(7):947–953.
Vasavada RC, Cavaliere C, D’Ercole Ai, Dann P, Burtis WJ, Madlener AL et al. Overexpression of parathyroid hormone-related protein in the pancreatic islets of transgenic mice causes islet hyperplasia, hyperinsulinemia, and hypoglycaemia. J Biol Chem 1996; 271(2):1200–1208.
Garcia-Ocana A, Takane KK, Syed MA, Philbrick WM, Vasavada RC, Stewart AF. Hepatocyte growth factor overexpression in the islet of transgenic mice increases beta cell proliferation, enhances islet mass, and induces mild hypoglycaemia. J Biol Chem 2000; 275(2):1226–1232.
Rane SG, Dubus P, Mettus RV, Galbreath EJ, Boden G, Reddy EP et al. Loss of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk4) expression causes insulin-deficient diabetes and cdk4 activation results in 13-islet cell hyperplasia. Nat Genet 1999; 22(1):44–52.
Petrik J, Pell JM, Arany E, McDonald TJ, Dean WL, Reik W et al. Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-II in transgenic mice is associated with pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia. Endocrinology 1999; 140(5):2353–2363.
Devedjian IC, George M, Casellas A, Pujol A, Visa J, Pelegrin M et al. Transgenic mice overexpressing insulin-like growth factor-II in ß-cells develop type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 2000; 105(6):731–740.
Hugl SR, White MF, Rhodes CJ. IGF-1 stimulated pancreatic ß-cell growth is glucose dependent: synergistic activation of IRS-mediated signal transduction pathways by glucose and IGF-1 in INS-1 cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273(28):17771–17779.
Kloppel G, Lohr M, Habich K, Oberholzer M, Heitz PU. Islet pathology and the pathogenesis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus revisited. Sury Synth Pathol Res 1985; 4(2):110–125.
Pinar H, Pinar T, Singer DB. Beta-cell hyperplasia in macrosomic infants and foetuses of nondiabetic mothers. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2000; 3(1):48–52.
Stefan Y, Orci L, Malaisse-Lagae F, Perrelet A, Patel Y, Unger RH. Quantitation of endocrine cell content in the pancreas of nondiabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes 1982; 31(8 Pt 1):694–700.
Gepts W, Lecompte PM. The pancreatic islets in diabetes. The American Journal of Medicine 1981; 70:105–115.
Westermark P, Wilander E. The influence of amyloid deposits on the islet volume in maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1978; 15:417–421.
Patti ME, Kahn CR. The insulin receptor--a critical link in glucose homeostasis and insulin action. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 1998; 9(2–4):89–109.
Lamothe B, Baudry A, Desbois P, Lamotte L, Bucchini D, De Meyts P et al. Genetic engineering in mice: impact on insulin signalling and action. Biochem J 1998; 335:193–204.
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins JA, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (lgf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (lgfir). Cell 1993; 75:59–72.
Accili D, Drago J, Lee EJ, Johnson MD, Cool MH, Salvatore P et al. Early neonatal death in mice homozygous for a null allele of the insulin receptor gene. Nat Genet 1996; 12(1):106–109.
Joshi RL, Lamothe B, Cordonnier N, Mesbah K, Monthioux E, Jami J et al. Targeted disruption of the insulin receptor gene in the mouse results in neonatal lethality. EMBO J 1996; 15(7):1542–1547.
Withers DJ, Gutierrez JS, Towery H, Burks DJ, Ren JM, Previs S et al. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 1998; 391(6670):900–904.
Kulkarni RN, Bruning JC, Winnay JN, Postic C, Magnuson MA, Kahn CR. Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic ß cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in Type 2 diabetes. Cell 1999; 96(3):329–339.
Cheatham B, Kahn CR. Insulin action and the insulin signalling network. Endocr Rev 1995; 16(2):117–142.
White MF, Kahn CR. The insulin signalling system. J Biol Chem 1994; 269(1):1–4.
White MF. The IRS-signalling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin and cytokine action. Recent Prog Horm Res 1998; 53:119–138.
Virkamaki A, Ueki K, Kahn CR. Protein-protein interaction in insulin signalling and the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 1999; 103(7):931–943.
Anal M, Ono H, Funaki M, Fukushima Y, Inukai K, Ogihara T et al. Different subcellular distribution and regulation of expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-3 from those of IRS-1 and IRS-2. J Biol Chem 1998; 273(45):29686–29692.
Fantin VR, Sparling ID, Slot JW, Keller SR, Lienhard GE, Lavan BE. Characterization of insulin receptor substrate 4 in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273(17):10726–10732.
Rothenberg PL, Willison LD, Simon J, Wolf BA. Glucose-induced insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in insulin-secreting ß-cells. Diabetes 1995; 44(7):802–809.
Leibiger IB, Leibiger B, Moede T, Berggren PO. Exocytosis of insulin promotes insulin gene transcription via the insulin receptor/PI-3 kinase/p70 s6 kinase and CaM kinase. Mol Cell 1998; 1(6):933–938.
Xu GG, Rothenberg PL. Insulin receptor signalling in the ß-cell influences insulin gene expression and insulin content. Diabetes 1998; 47:1243–1252.
Aspinwall CA, Lakey JR, Kennedy RT. Insulin-stimulated insulin secretion in single pancreatic ß-cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274(10):6360–6365.
Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic 13-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature 1985; 315(6015):115–122.
Efrat S, Linde S, Kofod H, Spector D, Delannoy M, Grant S et al. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1988; 85(23):9037–9041.
Efrat S, Leiser M, Surana M, Tal M, Fusco-DeMane D, Fleischer N. Murine insulinoma cell line with normal glucose-regulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 1993; 42(6):901–907.
Knaack DFDM, Surana M, Leiser M, Laurance M, Fusco-DeMane D, Hegre OD et al. Clonai insulinoma cell line that stably maintains correct glucose responsiveness. Diabetes 1994; 43(12):1413–1417.
D’Ambra R, Surana M, Efrat S, Starr RG, Fleischer N. Regulation of insulin secretion from beta-cell lines derived from trangenic mice insulinomas resembles that of normal beta-cells. Endocrinology 1990; 126(6):2815–2822.
Patti ME, Sun XJ, Bruning JC, Araki E, Lipes MA, White MF et al. 4PS/IRS-2 is the alternative substrate of the insulin receptor in IRS-1 deficient mice. J Biol Chem 1995; 270(42):24670–24673.
Bonner-Weir S, Withers DJ, Weir GC, Jonas JC. Impaired survival of differentiating beta cells but no insulin secretory defects result from ablation of IRS-2. Diabetes 48[Suppl.l], A3. 1999. Ref Type: Abstract
Kadowaki T, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Eto K, Yamauchi T, Kubota N. Molecular pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in knockout mice models. Keystone Symposia 2000, 119. 2000. Ref Type: Abstract
Van Schravendijk CF, Foriers A, Van den Brande JL, Pipeleers DG. Evidence for the presence of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors on rat pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology 1987; 121(5):1784–1788.
Sun XJ, Pons S, Wang LM, Zhang Y, Yenush L, Burks D et al. The IRS-2 gene on murine chromosome 8 encodes a unique signalling adapter for insulin and cytokine action. Mol Endocrinol 1997; 11(2)251–262.
Withers DJ, Burks DJ, Towery HH, Altamuro SL, Flint CL, White MF. IRS-2 coordinates IGF-1 receptor-mediated beta cell development and peripheral insulin signalling. Nat Genet 1999; 23(1):32–40.
Postel-Vinay MC, Kelly PA. Growth hormone receptor signalling. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996; 10(3):323–336.
Bole-Feysot C, Goffin V, Edery M, Binait N, Kelly PA. Prolactin (PRL) and its receptor: actions, signal transduction pathways and phenotypes observed in PRL receptor knockout mice. Endocr Rev 1998; 19(3):225–268.
Moldrup A, Billestrup N, Thorn NA, Lernmark A, Nielsen JH. Multiple growth hormone-binding proteins are expressed on insulin-producing cells. Mol Endocrinol 1989; 3(8):1173–1182.
Sorenson RL, Stout LE. Prolactin receptors and JAK2 in islets of Langerhans: An immunohistochemical analysis. Endocrinology 1995; 136(9):4092–4098.
Laakso M, Malkki M, Kekalainen P, Kuusisto J, Deeb SS. Insulin receptor substrate-1 variants in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest 1994; 94(3):1141–1146.
Almind K, Bjorbaek C, Vestergaard H, Hansen T, Echwald SM, Pedersen O. Amino acid polymorphisms of insulin receptor substrate-1 in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1993; 342(8875):828–832.
Imai Y, Fusco A, Suzuki Y, Lesniak MA, D’Alfonso R, Sesti G et al. Variant sequences of insulin receptor substrate-1 in patients with noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 79(6):1655–1658.
Zhang Y, Wat N, Stratton IM, Warren-Perry MG, Orho M, Groop L et al. UKPDS 19: Heterogeneity in NIDDM: Separate contributions of IRS-1 and 133-adrenergic-receptor mutations to insulin resistance and obesity respectively with no evidence for glycogen synthase gene mutations. UK Prospective Diabetes Study. Diabetologia 1996;39(12):1505–1511.
Bernal D, Almind K, Yenush L, Ayoub M, Zhang Y, Rosshani L et al. IRS-2 Amino acid polymorphisms are not associated with random type 2 diabetes amoung caucasians. Diabetes 1998; 47:976–979.
Porzio O, Federici M, Hribal ML, Lauro D, Accili D, Lauro R et al. The G1y972 to Arg amino acid polymorphism in IRS-1 impairs insulin secretion in pancreatic i cells. J Clin Invest 1999; 104:357364.
Liu SC, Wang Q, Lienhard GE, Keller SR. Insulin receptor substrate 3 is not essential for growth or glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem 1999; 274(25):18093–18099.
Fantin VR, Wang GE, Lienhard GE, Keller SR. Mice lacking insulin receptor substrate 4 exhibit mild defects in growth, reproduction, and homostasis. Am J Physiol 2000; 278:E127–133.
Patel YC, Amherdt M, Orci L. Quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography of insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin binding sites on islets. Science 1982; 217(4565):1155–1156.
Van Schravendijk CF, Foriers A, Hooghe-Peters EL, Rogiers V, De Meyts P, Sodoyez JC. Pancreatic hormone receptors on islet cells. Endocrinology 1985; 117(3):841–848.
Verspohl E, Ammon H. Evidence for the presence of insulin receptors in rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest 1980; 65:1230–1237.
Argoud GM, Schade DS, Eaton RP. Insulin suppresses its own secretion in vivo. Diabetes 1987; 36(8):959–962.
Elahi D, Nagulesparan M, Hershcopf RJ, Muller DC, Tobin JD, Blix PM et al. Feedback inhibition of insulin secretion by insulin: Relation to the hyperinsulinemia of obesity. N Engl J Med 1982; 306(20):1196–1202.
Iversen J, Miles DW. Evidence for a feedback inhibition of insulin on insulin secretion in the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes 1971; 20(1):1–9.
Ammon HP, Reiber C, Verspohl EJ. Indirect evidence for short-loop negative feedback of insulin secretion in the rat. J Endocrinol 1991; 128(1):27–34.
Stagner J, Samols E, Polonsky K, Pugh W. Lack of direct inhibition of insulin secretion by exogenous insulin in the canine pancreas. J Clin Invest 1986; 78(5):1193–1198.
Velloso LA, Cameiro EM, Crepaldi SC, Boschero AC, Saad MJ. Glucose-and insulin-induced phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and its primary substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2 in rat pancreatic islets. Growth Regul 1995; 377(3):353–357.
Harbeck MC, Louie DC, Howland J, Wolf BA, Rothenberg PL. Expression of insulin receptor mRNA and insulin receptor substrate 1 in pancreatic islet ß-cells. Diabetes 1996; 45(6):711–717.
Gu H, Marth JD, Orban PC, Mossmann H, Rajewsky K. Deletion of a DNA polymerase beta gene segment in T cells using cell type-specific gene targeting. Science 1994; 265(5168):103–106.
Metzger D, Clifford J, Chiba H, Chambon P. Conditional site-specific recombination in mammalian cells using a ligand-dependent chimeric Cre recombinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995; 92(15):6991–6995.
Pictet R, Rutter WJ. Development of the embryonic endocrine pancreas. In: Steiner DF, Freinkel M, editors. Handbook of Physiology. Washington, D.C.: American Physiological Society, 1972: 25–66.
Gannon M, Shiota C, Postic C, Wright CVE, Magnuson M. Analysis of the cre-mediated recombination driven by rat insulin promoter in embryonic and adult mouse pancreas. Genesis 2000; 26(2):139–141.
Flier JS, Kahn CR, Roth J, Bar RS. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science 1975; 190:63–65.
Taylor SI. Lilly Lecture: Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance - Lessons from patients with mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Diabetes 1992; 41:1473–1490.
Elders MJ, Schedewie HK, Olefsky J, Givens B, Char F, Bier DM et al. Endocrine-metabolic relationships in patients with leprechaunism. J Natl Med Assoc 1982; 74(12):1195–1210.
Kido Y, Burks DJ, Withers D, Bruning JC, Kahn CR, White MF et al. Tissue-specific insulin resistance in mice with mjutations in the insulin receptor, IRS-I, and IRS-2. J Clin Invest 2000; 105(2):199–205.
Pete G, Fuller CR, Oldham JM, Smith DR, D’Ercole AJ, Kahn CR et al. Postnatal growth responses to insulin-like growth factor I in insulin receptor substrate-I-deficient mice. Endocrinology 1999; 140(12):5478–5487.
Anello M, Gilon P, Henquin JC. Alterations of insulin secretion from mouse islets treated with sulphonylureas: perturbations of Ca2* regulation prevail over changes in insulin content. Br J Pharmacol 1999; 127(8):1883–1891.
Terauchi Y, Iwamoto K, Tamemoto H, Komeda K, Ishii C, Kanazawa Y et al. Development of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the double knockout mice with disruption of insulin receptor substrate-I and beta cell glucokinase genes. Genetic reconstitution of diabetes as a polygenic disease. J Clin Invest 1997; 99(5):861–866.
Leonard J, Peers B, Johnson T, Ferreri K, Lee S, Montminy MR. Characterization of somatostatin transactivating factor-1, a novel homeobox factor that stimulates somatostatin expression in pancreatic islet cells. Mol Endocrinol 1993; 7(10):1275–1283.
Miller CP, McGehee REJ, Habener JF. IDX-1: a new homeodomain transcription factor expressed in rat pancreatic islets and duodenum that transactivates the somatostatin gene. EMBO J 1994; 13(5):1145–1156.
Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund T, Edlund H. Insulin-promotor-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature 1994; 371(6498):606–609.
Stoffers DA, Zinkin NT, Stanojevic V, Clarke WL, Habener JF. Pancreatic agenesis attributable to a single nucleotide deletion in the human IPF1 gene coding sequence. Nat Genet 1997; 15(1):106–110.
Dutta S, Bonner-Weir S, Montminy M, Wright C. Regulatory factor linked to late-onset diabetes? Nature 1998; 392:560.
Stoffers DA, Ferrer J, Clarke WL, Habener JF. Early-onset type-II diabetes mellitus (MODY4) linked to IPF1. Nat Genet 1997; 17(2):138–139.
Kulkami RN, Winnay JN, Curtis S, Montminy MR. Creation of a polygenic model of type 2 diabetes: the triple heterozygous knockout. Diabetes 48[Suppl 1], A34. 1999. Ref Type: Abstract
Phillips LS, Pao CI, Villafuerte BC. Molecular regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I and its principal binding protein, IGFBP-3. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 1998; 60:195–265.
Lawrence JCJ, Fadden P, Haystead TA, Lin TA. PHAS proteins as mediators of the actions of insulin, growth factors and cAMP on protein synthesis and cell proliferation. Adv Enzyme Regul 1997; 37:239–267.
Villafuerte BC, Zhang WN, Phillips LS. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I regulate hepatic insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 by different mechanisms. Mol Endocrinology 1996; 10(6):622–630.
Mauvais-Jarvis F, Virkamaki A, Michael MD, Kulkami RN. Double tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta-cell and in skeletal muscle (BIRKO-MIRKO). Diabetes 48[Suppl. 1], A275. 1999. Ref Type: Abstract
Heron L, Virsolvy A, Peyrollier K, Gribble FM, Le Cam A, Ashcroft FM et al. Human alphaendosulfine, a possible regulator of sulfonylurea-sensitive KATP channel: molecular cloning, expression and biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1998; 95(14):8387–8391.
Heron L, Virsolvy A, Apiou F, Le Cam A, Bataille D. Isolation, characterization, and chromosomal localization of the human ENSA gene that encodes alpha-endosulfine, a regulator of beta-cell K(ATP) channels. Diabetes 1999; 48(9):1873–1876.
Kulkami RN, Wang ZL, Wang RM, Hurley JD, Smith DM, Ghatei MA et al. Leptin rapidly suppresses insulin release from insulinoma cells, rat and human islets and, in vivo, in mice. J Clin Invest 1997; 100(11):2729–2736.
Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The adipoinsular axis: effects of leptin on pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000; 278(1):El-E14.
Zarnegar R, Muga S, Rahija R, Michalopoulos G. Tissue distribution of hepatopoietin-A: a heparin-binding polypeptide growth factor for hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1990; 87(3):1252–1256.
Bonner-Weir S. Islet growth and development in the adult. J Endocrinology 2000; 24:297–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kulkarni, R.N., Kahn, C.R. (2001). Genetic models of Insulin Resistance:Alterations in β-cell biology. In: Habener, J.F., Hussain, M.A. (eds) Molecular Basis of Pancreas Development and Function. Endocrine Updates, vol 11. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1669-9_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1669-9_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5669-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1669-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive