Abstract
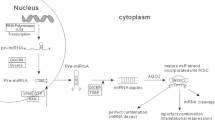
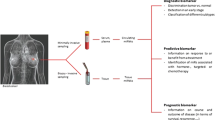
Over the years, remarkable progress has been made in regards to our understanding of breast cancer biology and consequently the development of novel treatments. One idea that has proven to be immensely valuable is the use of microRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and even for treatment. The miRNAs are short RNA molecules that are able to post-transcriptionally regulate the expression of genes at multiple levels. Past and current research has continued to classify miRNAs as either highly or rarely expressed in cancer cells in relation to their normal non-cancerous counterparts. This classification is also used to organize the various miRNAs as either tumor suppressing or oncogenic. For example, aberrant expression of certain miRNAs is widely accepted to signify different stages of cancer. This chapter summarizes our current understanding of the role of miRNAs in cancer, while enlightening the readers with the role of specific miRNAs in breast cancer development and progression, and their exploitation for designing innovative therapeutic strategies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lynam-Lennon N, Maher SG, Reynolds JV (2009) The roles of microRNA in cancer and apoptosis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 84:55–71
Iorio MV, Casalini P, Piovan C et al (2011) Breast cancer and microRNAs: therapeutic impact. Breast 20(3):S63–S70
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L et al (2009) MicroRNAs: key players in carcinogenesis and novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol 35:339–347
Kim VN, Nam JW (2006) Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet 22:165–173
Ali AS, Ali S, Ahmad A, Philip A, Sarkar FH (2011) MicroRNAs in cancer invasion and metastasis. Springer Science, New York
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z et al (2010) Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat 13:57–66
Andorfer CA, Necela BM, Thompson EA et al (2011) MicroRNA signatures: clinical biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Trends Mol Med 17:313–319
Jensen EV, Cheng G, Palmieri C et al (2001) Estrogen receptors and proliferation markers in primary and recurrent breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:15197–15202
Sugiura H, Toyama T, Hara Y et al (2007) Expression of estrogen receptor beta wild-type and its variant ERbetacx/beta2 is correlated with better prognosis in breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:820–828
Paris O, Ferraro L, Grober OM et al (2012) Direct regulation of microRNA biogenesis and expression by estrogen receptor beta in hormone-responsive breast cancer. Oncogene 4196–4206
Lazennec G, Bresson D, Lucas A et al (2001) ER beta inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 142:4120–4130
Paruthiyil S, Parmar H, Kerekatte V et al (2004) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation by causing a G2 cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res 64:423–428
Shaaban AM, Green AR, Karthik S et al (2008) Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of ERbeta1, ERbeta2, and ERbeta5 identifies distinct prognostic outcome for breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 14:5228–5235
Guttilla IK, Adams BD, White BA (2012) ERalpha, microRNAs, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23:73–82
Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Richer JK (2012) The role of miRNAs in progesterone action. Mol Cell Endocrinol 357:50–59
Radojicic J, Zaravinos A, Vrekoussis T et al (2011) MicroRNA expression analysis in triple-negative (ER, PR and Her2/neu) breast cancer. Cell Cycle 10:17–507
Ahmad A, Ali AS, Ali S, Wang Z, Kong D, Sarkar FH (2011) MicroRNAs: targets of interest in breast cancer research. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Le QJ, Caldas C (2010) Micro-RNAs and breast cancer. Mol Oncol 4:230–241
Sempere LF, Christensen M, Silahtaroglu A et al (2007) Altered MicroRNA expression confined to specific epithelial cell subpopulations in breast cancer. Cancer Res 67:11612–11620
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P et al (2007) Let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131:23–1109
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A et al (2010) The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:F19–F36
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E et al (2008) The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 22:894–907
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL et al (2008) The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10:593–601
Dykxhoorn DM, Wu Y, Xie H et al (2009) miR-200 enhances mouse breast cancer cell colonization to form distant metastases. PLoS ONE 4:e7181
Iorio MV, Casalini P, Piovan C et al (2009) microRNA-205 regulates HER3 in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 69:2195–2200
Edmonds MD, Hurst DR, Vaidya KS et al (2009) Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 coordinately regulates metastasis-associated microRNA expression. Int J Cancer 125:1778–1785
Li W, Duan R, Kooy F et al (2009) Germline mutation of microRNA-125a is associated with breast cancer. J Med Genet 46:358–360
Saetrom P, Biesinger J, Li SM et al (2009) A risk variant in an miR-125b binding site in BMPR1B is associated with breast cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Res 69:7459–7465
Le QJ, Jones J, Warren J et al (2012) Biological and prognostic associations of miR-205 and let-7b in breast cancer revealed by in situ hybridisation analysis of micro-RNA expression in arrays of archival tumour tissue. J Pathol 1–28. doi:10.1002/path.3983
Augoff K, McCue B, Plow EF et al (2012) miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer 11:5
Sossey-Alaoui K, Downs-Kelly E, Das M et al (2011) WAVE3, an actin remodeling protein, is regulated by the metastasis suppressor microRNA, miR-31, during the invasion-metastasis cascade. Int J Cancer 129:1331–1343
Yu Z, Wang C, Wang M et al (2008) A cyclin D1/microRNA 17/20 regulatory feedback loop in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biol 182:509–517
Yu Z, Willmarth NE, Zhou J et al (2010) microRNA 17/20 inhibits cellular invasion and tumor metastasis in breast cancer by heterotypic signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:8231–8236
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C et al (2010) Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Src-mediated twist signaling, microRNA-10b expression, and RhoA/RhoC up-regulation, leading to Rho-kinase-associated cytoskeleton activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem 285:36721–36735
Haque I, Banerjee S, Mehta S et al (2011) Cysteine-rich 61-connective tissue growth factor-nephroblastoma-overexpressed 5 (CCN5)/Wnt-1-induced signaling protein-2 (WISP-2) regulates microRNA-10b via hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-TWIST signaling networks in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 286:43475–43485
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449:682–688
Gee HE, Camps C, Buffa FM et al (2008) MicroRNA-10b and breast cancer metastasis. Nature 455:8–9
Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH et al (2010) MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res 70:3119–3127
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H et al (2010) miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 12:247–256
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA et al (2008) Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res 68:3645–3654
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M et al (2008) The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 10:202–210
Ma L, Weinberg RA (2008) Micromanagers of malignancy: role of microRNAs in regulating metastasis. Trends Genet 24:448–456
Valastyan S (2012) Roles of microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in breast cancer metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 17:23–32
Neelakandan K, Babu P, Nair S (2012) Emerging roles for modulation of microRNA signatures in cancer chemoprevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 716–740
Lee YS, Dutta A (2007) The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev 21:1025–1030
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J et al (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP (2007) Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 315:1576–1579
Park SM, Shell S, Radjabi AR et al (2007) Let-7 prevents early cancer progression by suppressing expression of the embryonic gene HMGA2. Cell Cycle 6:2585–2590
Kong W, He L, Coppola M et al (2010) MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival, growth, and chemosensitivity by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 285:17869–17879
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M et al (2008) Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13021–13026
Camps C, Buffa FM, Colella S et al (2008) hsa-miR-210 Is induced by hypoxia and is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:1340–1348
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ahmed, A., Ali, A.S., Ali, S., Ahmad, A., Philip, P.A., Sarkar, F.H. (2013). MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer Research: Progress and Promise. In: Ahmad, A. (eds) Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5647-6_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5647-6_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-5646-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-5647-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)